-
How protocol, posts, and experience affect fracture detection in multi-rooted teeth using cone-beam computed tomography: an ex vivo experimental study
-
Gleica Dal’ Ongaro Savegnago, Gabriela Marzullo de Abreu, Carolina Baumgratz Spiger, Lucas Machado Maracci, Wislem Miranda de Mello, Gabriela Salatino Liedke
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e23. Published online July 24, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e23
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
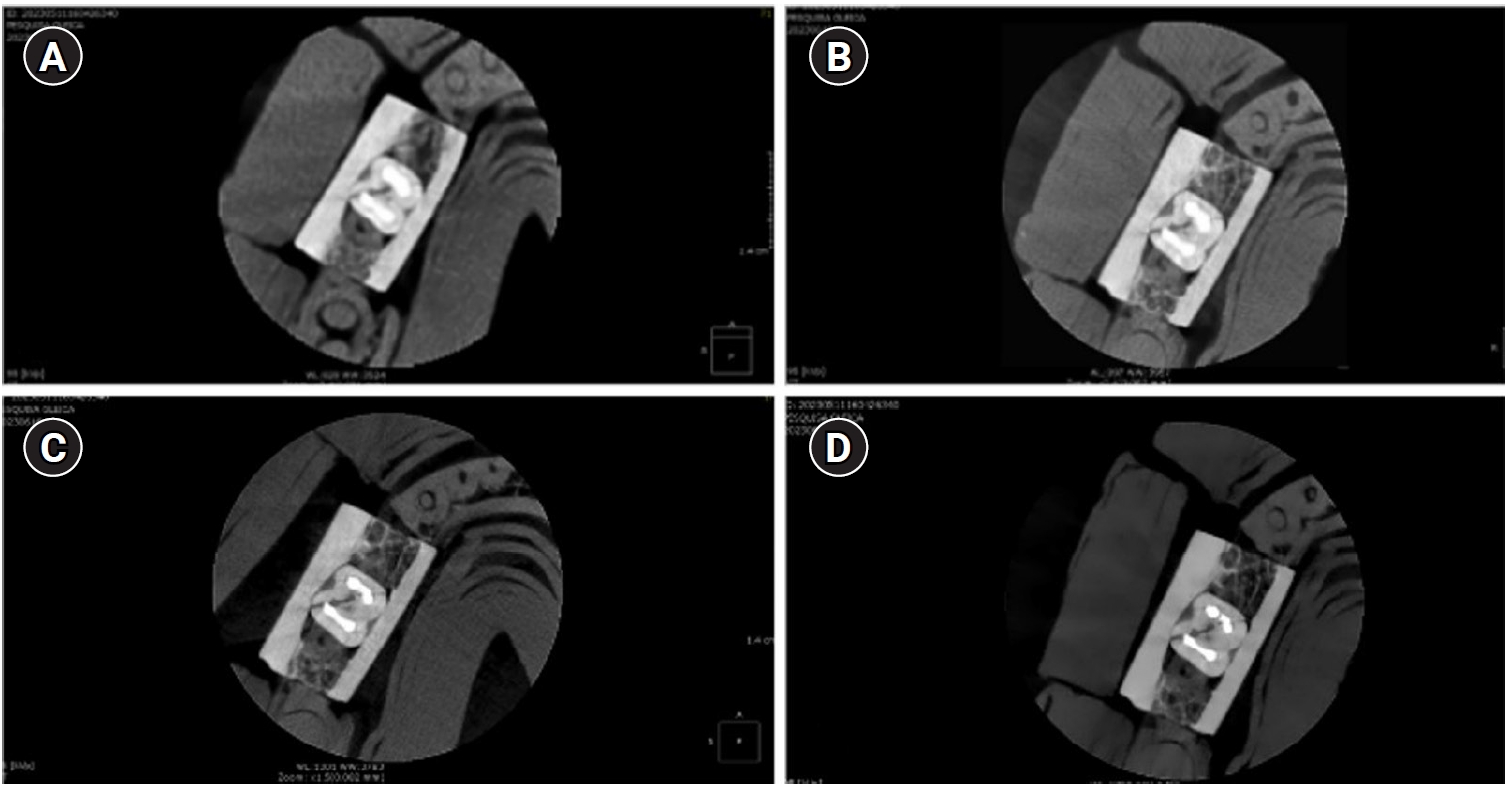
This study aimed to evaluate the influence of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) acquisition protocol, the presence of intraradicular metal post, and examiner experience on the detection of complete root fractures in multi-rooted teeth.
Methods
Twenty human molar teeth filled with gutta-percha were placed into artificial alveoli created in bovine ribs. The sample was divided into two groups based on the presence or absence of intraradicular posts in the distal roots. CBCT scans were obtained using four acquisition protocols with varying voxel sizes (0.28, 0.2, 0.125, and 0.80 mm). Following the creation of controlled fractures using a chisel and hammer, CBCT imaging was repeated, resulting in 160 images. Five examiners assessed the images using OnDemand software (KaVo Dental GmbH). Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were calculated for each examiner, CBCT protocol, and post-condition. Statistical comparisons were performed using Cochran’s Q test and McNemar test, and a significance level of 5%.
Results
In teeth without metallic posts, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy values exceeded 0.70, 0.70, and 0.80, respectively. However, the presence of metallic posts significantly reduced diagnostic performance, particularly in low-resolution protocols evaluated by less-experienced examiners.
Conclusions
CBCT acquisition protocols should be selected based on the presence of metallic posts to optimize root fracture detection in multi-rooted teeth. Examiner experience also plays a critical role in diagnostic accuracy.
-
Outcome of endodontic treatments performed by Brazilian undergraduate students: 3- to 8-year follow up
-
Jéssica Gabriele da Rocha, Isabella Marian Lena, Jéssica Lopes Trindade, Gabriela Salatino Liedke, Renata Dornelles Morgental, Carlos Alexandre Souza Bier
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e34. Published online August 18, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e34
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the success rate of endodontic treatments performed by undergraduate students and the factors associated with the outcome. Materials and MethodsA follow-up of 3 to 8 years after root canal filling was carried out in 91 patients. At the follow-up visits, medical and dental history questionnaires were applied along with clinical and radiographic examinations. Data collected in the clinical exam included: the presence of pain, swelling, sinus tract, mobility, tenderness to palpation and percussion, periodontal probing profile, and type/quality of coronal restoration. Postoperative and follow-up radiographs were digitalized and analyzed by 2 trained and calibrated examiners to assess periapical healing. The treatment outcome was based on strict clinical and radiographic criteria and classified as success (absence of any clinical and radiographic sign of apical periodontitis) or failure (other combination). Logistic regression was used to investigate the impact of clinical and radiographic variables on endodontic treatment outcomes at a 5% significance level. ResultsThe success rate of endodontic treatments was 60.7%. The only risk factor significantly associated with failure was the presence of a periapical lesion on the postoperative radiograph (odds ratio, 3.35; 95% confidence interval, 1.17–9.54). ConclusionsThe success rate of endodontic treatments performed by undergraduate students was low and was jeopardized by the presence of a periapical lesion on the postoperative radiograph.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of quality of radiographs taken during root canal treatment on technical quality of root canal fillings and endodontic outcome
Jia Min Ng, Yan Yee Lee, Prashanti Chippagiri, Elaheh Ahanin, Abhishek Parolia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(1): e3. CrossRef - Outcomes of root canal treatment performed by undergraduate students: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Philip Y.‐H. Chien, Sepanta Hosseinpour, Ove A. Peters, Christine I. Peters
International Endodontic Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Long-Term Survival and Success of Endodontically Treated and Retreated Teeth: An Ambispective Study at an Educational Hospital
Reem Barakat, Rahaf Almohareb, Ghaliah Alsawah, Hadeel Busuhail, Shahad A. Alshihri, Ghadah T. Alrashid, Ghadeer Y. Alotaibi, Mamata Hebbal
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(21): 7826. CrossRef - A bibliometric comparison of undergraduate and postgraduate endodontic education publications: The topics, trends, and challenges
Jinglan Zhang, Xiaowei Liu, Lei Yang, Yiran Wang, Dingming Huang, Xuelian Tan
Journal of Dental Education.2023; 87(12): 1661. CrossRef
-
4,963
View
-
44
Download
-
5
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
|