-
Impact of post adhesion on stress distribution: an in silico study
-
Kkot-Byeol Bae, Jae-Yoon Choi, Young-Tae Cho, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e19. Published online May 21, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e19
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the stress distribution in teeth restored with different post materials and bonding conditions using finite element analysis (FEA).
Methods
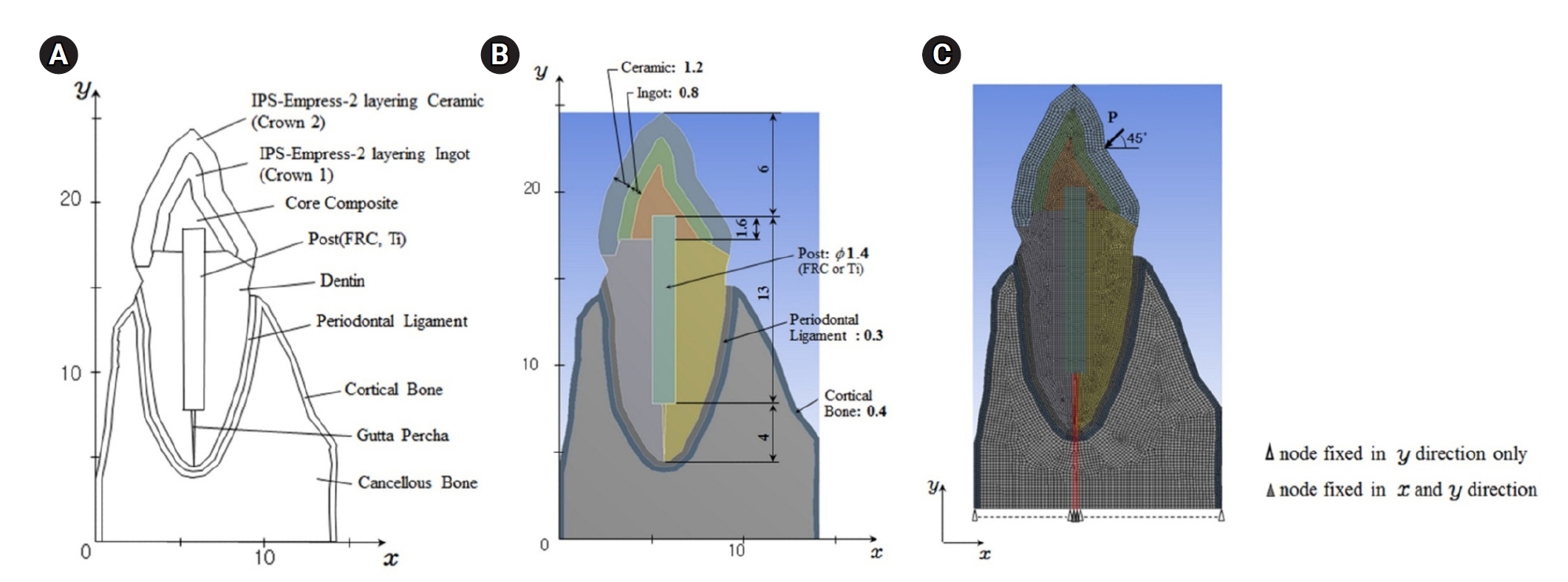
A two-dimensional FEA model of a maxillary central incisor restored with IPS-Empress-2 crown (Ivoclar Vivadent), composite resin core, and posts were created. The model simulated bonded and non-bonded conditions for both fiber-reinforced composite (FRC) and titanium (Ti) posts. Stress distribution was analyzed using ANSYS 14.0 software under a 100-N load applied at a 45° angle to the long axis of the tooth.
Results
The results revealed that stress concentration was significantly higher in non-bonded posts compared to bonded ones. FRC posts exhibited stress values closer to those of dentin, whereas Ti posts demonstrated higher stress concentration, particularly in non-bonded states, increasing the potential risk of damage to surrounding tissues.
Conclusions
FRC posts, with elastic properties similar to dentin and proper adhesion, minimize stress concentration and potential damage to surrounding tissues. Conversely, materials with higher elastic modulus like Ti, can cause unfavorable stress concentrations if not properly bonded, emphasizing the importance of post adhesion in tooth restoration.
|