-
Cleaning protocols to enhance bond strength of fiberglass posts on root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: an in vitro comparative study
-
Thiago Bessa Marconato Antunes, Juliana Delatorre Bronzato, Joice Graciani, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Francisco Haiter Neto, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano da Silva
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e20. Published online May 21, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e20
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
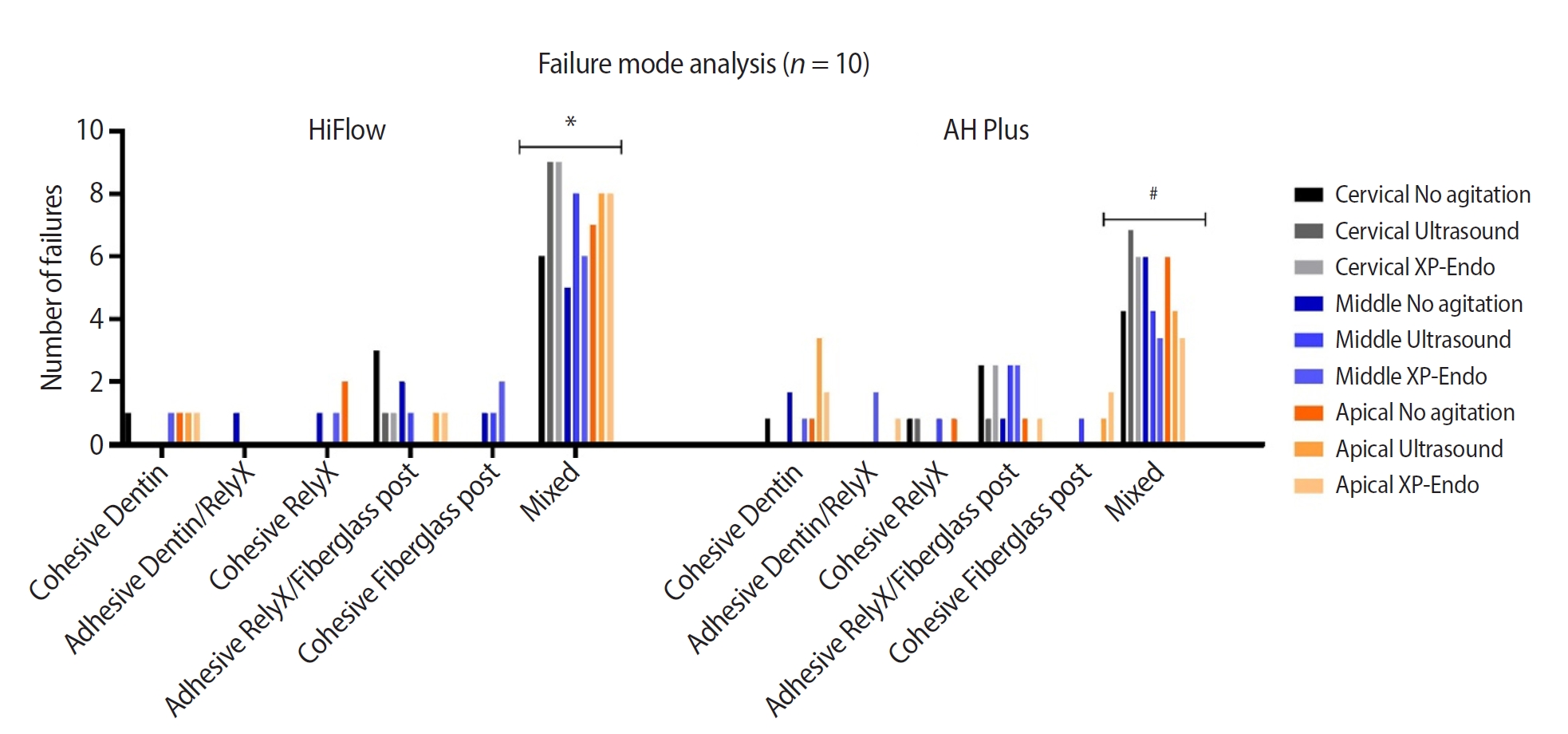
This study aimed to evaluate whether the agitation protocols using ultrasonic inserts or the XP-endo Finisher R file improved the removal of two different endodontic sealer remnants and the bond strength of fiberglass posts to dentin.
Methods
Seventy-two human teeth were selected. The canals were prepared with Reciproc 50 and Easy ProDesign 30/.10 and root filled according to the endodontic sealer groups: AH Plus or EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow. The samples were kept at 37ºC and 95% humidity for 28 days. During the post space preparation, the obturation was removed with Largo burs, and the groups were divided according to the irrigant agitation protocols (n = 12): no agitation, agitation with R1-Clearsonic associated with E1-Irrisonic ultrasonic inserts, or agitation with XP-endo Finisher R file. The fiberglass posts were cemented with RelyX ARC. The roots were sectioned into slices and submitted to the push-out test. Micro-computed tomography analysis was used to check the effectiveness of irrigating solution agitation in the elimination of remnants.
Results
The cleaning protocols with agitation were more effective in increasing the bond strength of posts to dentin for both sealer groups compared to non-agitation (p < 0.05). There was no difference between the same cleaning protocols for the different sealers. Among the different thirds, there was no statistical difference for the same sealer in the different cleaning protocols (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
Both agitation protocols effectively clean root-filled canals sealed with resin-based and calcium silicate-based sealers during fiberglass post space preparation. These protocols result in improved bond strength compared to non-agitation methods.
-
Which factors related to apical radiolucency may influence its radiographic detection? A study using CBCT as reference standard
-
Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Eduarda Helena Leandro Nascimento, Hugo Gaêta-Araujo, Laís Oliveira de Araujo Cardelli, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e43. Published online July 21, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e43
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the detection rate of apical radiolucencies in 2-dimensional images using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) as the reference standard, and to determine which factors related to the apical radiolucencies and the teeth could influence its detection. Materials and MethodsThe sample consisted of exams of patients who had panoramic (PAN) and/or periapical (PERI) radiography and CBCT. The exams were assessed by 2 oral radiologists and divided into PAN+CBCT (227 teeth–285 roots) and PERI+CBCT (94 teeth–115 roots). Radiographic images were evaluated for the presence of apical radiolucency, while CBCT images were assessed for presence, size, location, and involvement of the cortical bone (thinning, expansion, and destruction). Diagnostic values were obtained for PERI and PAN. ResultsPERI and PAN presented high accuracy (0.83 and 0.77, respectively) and specificity (0.89 and 0.91, respectively), but low sensitivity, especially for PAN (0.40 vs. 0.65 of PERI). The size of the apical radiolucency was positively correlated with its detection in PERI and PAN (p < 0.001). For PAN, apical radiolucencies were 3.93 times more frequently detected when related to single-rooted teeth (p = 0.038). The other factors did not influence apical radiolucency detection (p > 0.05). ConclusionsPERI presents slightly better accuracy than PAN for the detection of apical radiolucency. The size is the only factor related to radiolucency that influences its detection, for both radiographic exams. For PAN, apical radiolucency is most often detected in single-rooted teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Three-dimensional clinical assessment for MRONJ risk in oncologic patients following tooth extractions
Catalina Moreno Rabie, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Nicolly Oliveira Santos, Fernanda Nogueira Reis, Tim Van den Wyngaert, Reinhilde Jacobs
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of techniques used to assess clinical outcomes of regenerative endodontic treatment in necrotic mature teeth
Roy George
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2022; 23(3): 98. CrossRef
-
448
View
-
10
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
|