-
Isolating design variables by assessing the impact of cross-section geometry on the mechanical performance of nickel-titanium rotary instruments: a comparative in vitro study
-
Anne Rafaella Tenório Vieira, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Murilo Priori Alcalde
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e28. Published online July 24, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e28
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
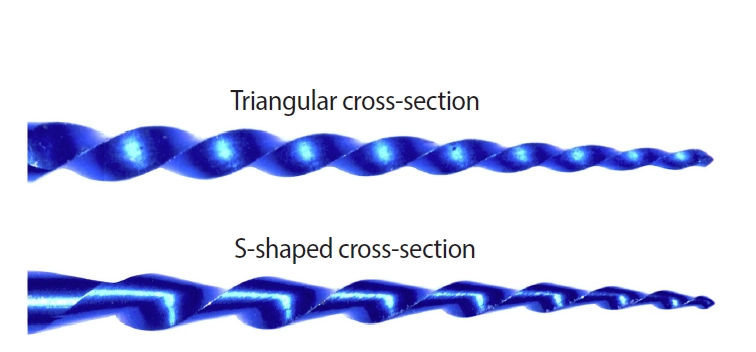
This study aimed to assess the effect of cross-section geometry on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments by comparing two instruments with identical tip size, taper, and thermal treatment but differing in cross-section design.
Methods
One hundred four NiTi rotary instruments, being S-shaped and triangular cross-section, manufactured with Blueish thermal treatment, were tested (n = 52 per group). Differential scanning calorimetry was employed, and the metal mass volume and cross-section area were assessed. The cyclic fatigue, torsional, and bending resistance tests were assessed. Data were analyzed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Student t tests, and the level of significance was set at 5%.
Results
The instruments exhibited similar start and finish temperatures of phase transformation. The S-shaped instruments had significantly lower metal mass volume and cross-sectional area (p < 0.05). S-shaped instruments demonstrated superior cyclic fatigue resistance, greater angular deflection, and lower bending stiffness (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Cross-section geometry significantly influences the mechanical properties of NiTi rotary instruments.
-
Bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system: trends, collaborations, and research gaps
-
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Thais de Moraes Souza, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e17. Published online May 12, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e17
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The study aimed to conduct a bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system (Sonendo, Inc.).
Methods
An electronic search was conducted in June 2024 using the Web of Science Collection database. Two reviewers independently screened publications, extracting data on authorship, publication details, study design, and citation metrics. Statistical analyses were performed in R to assess variable correlations, while the VOSviewer (Visualization of Similarities Viewer) software was used to map author and keyword networks.
Results
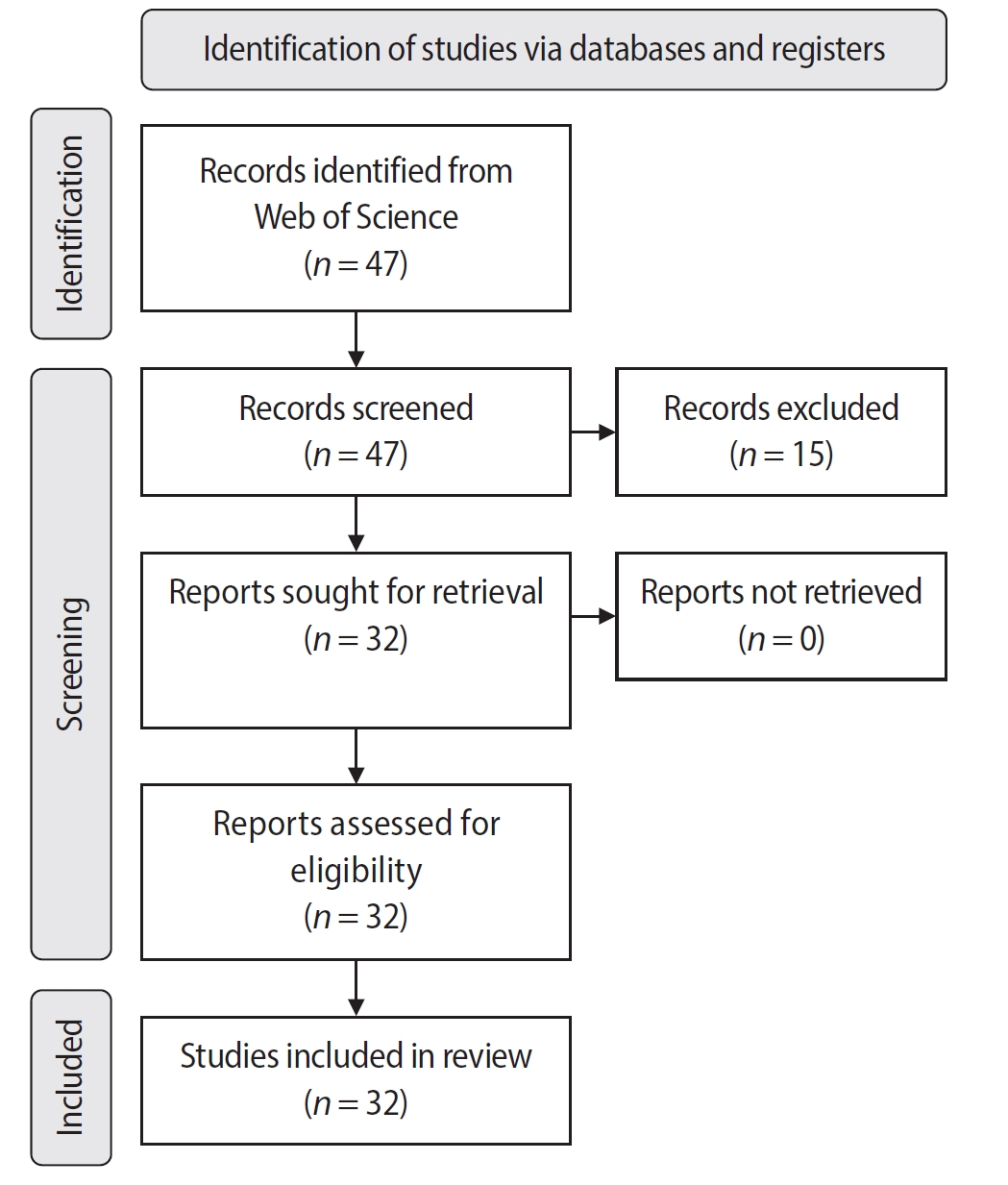
The search yielded 47 records, with 32 studies included. Publications spanned 2014 to 2024. The Journal of Endodontics published the highest number of studies (n = 15), and the International Endodontic Journal had the highest impact factor (5.4). The University of British Columbia and Sonendo, Inc. were the most frequent affiliations. Among the 32 articles, 28 were in vitro studies, primarily focusing on microbiology (n = 9). A total of 95 authors were identified, with Haapasalo and Shen being the most cited (n = 229). The articles accumulated 495 citations, demonstrating a strong positive correlation between the number of studies and citation counts (r = 0.98).
Conclusions
The analysis highlights a predominance of in vitro studies. Geographic concentration in the United States and Canada limits diversity, while the strong correlation between study numbers and citations suggests that increased publication volume enhances visibility.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Three-year Outcomes of Conventional Versus Minimally Invasive Endodontic Treatment Protocols: A Retrospective Study
Kiavash Hossini, He Liu, Ya Shen, Jolanta Aleksejuniene, Fahda Algahtani, Ahmed Hieawy
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
3,546
View
-
88
Download
-
1
Crossref
|