-
Stress distribution of restorations in external cervical root resorption under occlusal and traumatic loads: a finite element analysis
-
Padmapriya Ramanujam, Paul Kevin Abishek Karthikeyan, Vignesh Srinivasan, Selvakarthikeyan Ulaganathan, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Nandini Suresh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e21. Published online May 21, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e21
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
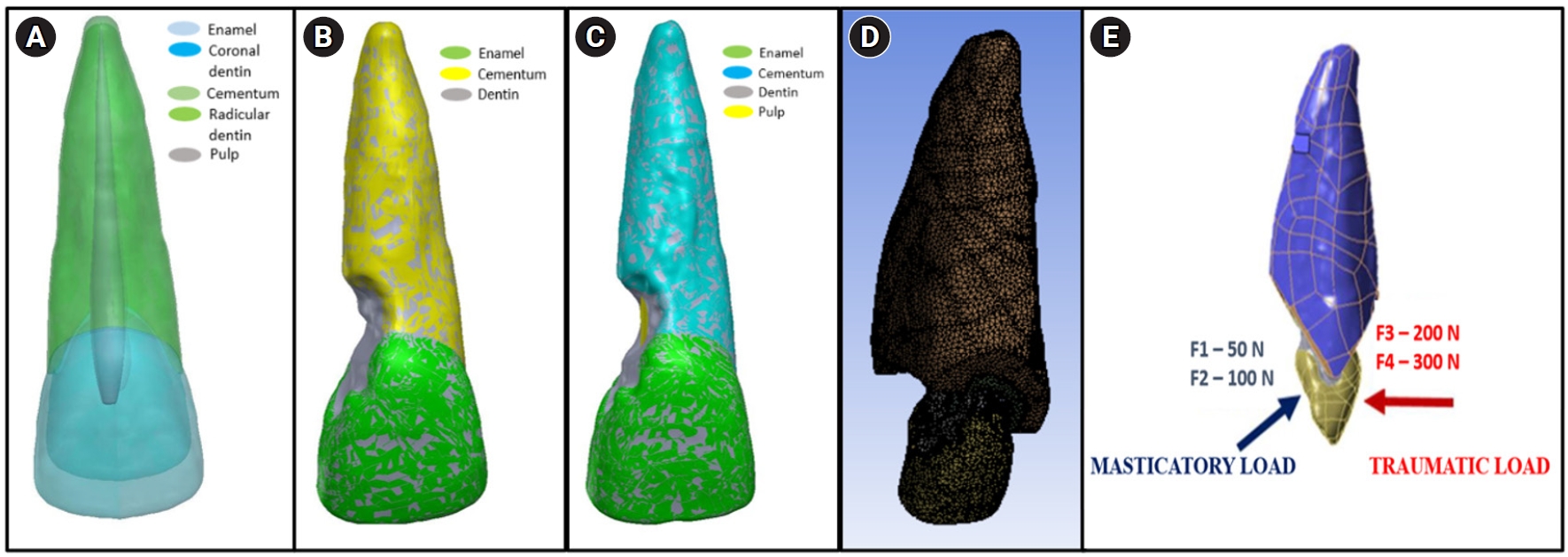
This study analyzed the stress distribution in a maxillary central incisor with external cervical resorptive defect restored with different restorative materials under normal masticatory and traumatic loading conditions using finite element analysis.
Methods
Cone-beam computed tomography of an extracted intact incisor and created resorptive models (Patel’s 3D classification-2Bd and 2Bp) in the maxillary central incisor was performed for finite element models. The 2Bd models were restored either with glass ionomer cement (GIC)/Biodentine (Septodont) or a combination of both with composite resin. 2Bp models were restored externally with a combination technique and internally with root canal treatment. The other model was external restoration with GIC and internal with fiber post. Two masticatory loads were applied at 45˚ to the palatal aspect, and two traumatic loads were applied at 90˚ to the buccal aspect. Maximum von Mises stresses were calculated, and stress distribution patterns were studied.
Results
In 2Bd models, all restorative strategies decreased stress considerably, similar to the control model under all loads. In 2Bp models, the dentin component showed maximum stress at the deepest portion of the resorptive defect, which transfers into the adjacent pulp space. In 2Bp defects, a multilayered restoration externally and root canal treatment internally provides better stress distribution compared to the placement of a fiber post.
Conclusions
Increase in load, proportionally increased von Mises stress, despite the direction or angulation of the load. Multilayered restoration is preferred for 2Bd defects, and using an internal approach of root canal treatment is suggested to restore 2Bp defects.
|