Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
- Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e56. Published online October 27, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e56
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
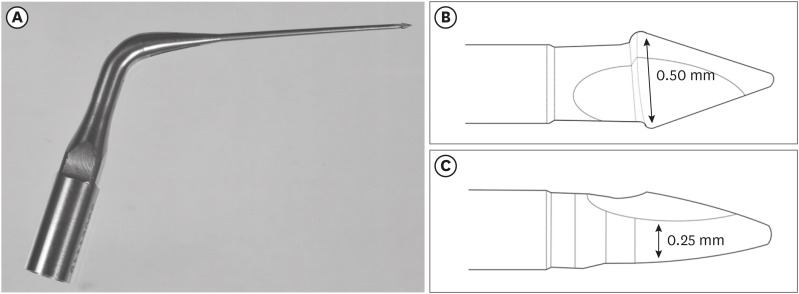
ePub Objectives This study evaluated 2 nickel-titanium rotary systems and a complementary protocol with an ultrasonic tip and a small-diameter instrument in flattened root canals.
Materials and Methods Thirty-two human maxillary second premolars with flattened canals (buccolingual diameter ≥4 times larger than the mesiodistal diameter) at 9 mm from the radiographic apex were selected. The root canals were prepared by ProDesign Logic (PDL) 30/0.01 and 30/0.05 or Hyflex EDM (HEDM) 10/0.05 and 25/0.08 (
n = 16), followed by application of the Flatsonic ultrasonic tip in the cervical and middle thirds and a PDL 25/0.03 file in the apical third (FPDL). The teeth were scanned using micro-computed tomography before and after the procedures. The percentage of volume increase, debris, and uninstrumented surface area were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn, Wilcoxon, analysis of variance/Tukey, and paired and unpairedt -tests (α = 0.05).Results No significant difference was found in the volume increase and uninstrumented surface area between PDL and HEDM (
p > 0.05). PDL had a higher percentage of debris than HEDM in the middle and apical thirds (p < 0.05). The FPDL protocol resulted in less debris and uninstrumented surface area for PDL and HEDM (p < 0.05). This protocol, with HEDM, reduced debris in the middle and apical thirds and uninstrumented surface area in the apical third (p < 0.05).Conclusions High percentages of debris and uninstrumented surface area were observed after preparation of flattened root canals. The HEDM, Flatsonic tip, and 25/0.03 instrument protocol enhanced cleaning in flattened root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Kök Kanal Tedavisi Yenilemelerinde Ultrasonik Uç Kullanımı
Ayşenur Kızıltaş Gül, Turan Mert Hisar, Seniha Miçooğulları
Selcuk Dental Journal.2025; 12(1): 157. CrossRef - Flatsonic Ultrasonic Tip Optimizes the Removal of Remaining Filling Material in Flattened Root Canals: A Micro–computed Tomographic Analysis
Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 612. CrossRef - The Effect of Combined Ultrasonic Tip and Mechanized Instrumentation on the Reduction of the Percentage of Non-Instrumented Surfaces in Oval/Flat Root Canals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Marcella Dewes Cassal, Pedro Cardoso Soares, Marcelo dos Santos
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Heat-treated NiTi instruments and final irrigation protocols for biomechanical preparation of flattened canals
Kleber Kildare Teodoro CARVALHO, Igor Bassi Ferreira PETEAN, Alice Corrêa SILVA-SOUSA, Rafael Verardino CAMARGO, Jardel Francisco MAZZI-CHAVES, Yara Terezinha Corrêa SILVA-SOUSA, Manoel Damião SOUSA-NETO
Brazilian Oral Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Kök Kanal Tedavisi Yenilemelerinde Ultrasonik Uç Kullanımı
- 1,830 View
- 26 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
- Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e34. Published online June 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
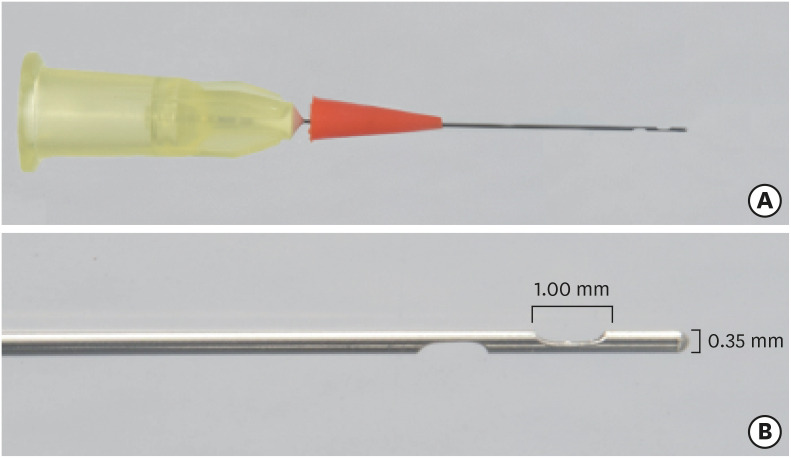
ePub Objectives This study evaluated by using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) the filling ability and sealer apical extrusion promoted by a new Sealer Injection System (SIS; Angelus) with side openings needle, in comparison with the conventional injection system, associated with a new ready-to-use calcium silicate-based sealer (Bio-C Sealer).
Materials and Methods Acrylic resin models containing a main curved artificial canal and 3 simulated lateral canals in apical, middle and cervical thirds were used. The main root canals were prepared using a rotary system up to size 35.05. The canals were filled with Bio-C sealer by using a single cone technique and the conventional delivery system or SIS. Samples were scanned in micro-CT. The percentage of voids throughout the entire extension of the main root canal and in each third of the lateral canals, besides the apical extrusion of the sealer was calculated. Data were submitted to
t -test (p < 0.05).Results There was no difference between both systems in the main root canals filling. Although the volume percentage of voids was similar in the apical and middle thirds of lateral canals, SIS had the greatest filling ability of the cervical third lateral canal. Moreover, the conventional system showed the highest apical extrusion of the sealer.
Conclusions The conventional and SIS obturation systems had an appropriate filling ability of the main root canal. SIS had the best filling of the cervical third of the lateral canals, besides lower sealer apical extrusion, suggesting its clinical indication.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
Amira Galal Ismail, Manar M. Galal, Tamer M. Hamdy
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2026; 16(2): 101400. CrossRef - Remineralizing capacity of zinc oxide eugenol sealer following the addition of nanohydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid: An in vivo animal study
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2025; 67(1): 100567. CrossRef - Advanced analytical tests and acellular bioactivity of zinc oxide eugenol sealer following the addition of nanohydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid: An in vitro study
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 149. CrossRef - Tissues response and bone-forming capacity of zinc oxide–eugenol sealer following the addition of nanohydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid: An in vivo animal study
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(3): 322. CrossRef - Filling ability of ready-to-use or powder-liquid calcium silicate-based sealers after ultrasonic agitation
Mário Tanomaru-Filho, Maíra Bonassi Lucchesi, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment the bioactivity of zinc oxid eugenol sealer after the addition of different concentrations of nano hydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243733. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of dentinal tubule penetration and push-out bond strength of new injectable hydraulic calcium disilicate based root canal sealer: A single blinded in vitro study
Aman Verma, Anshul Arora, Sonali Taneja
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2024; 14(2): 143. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography in preventive and restorative dental research: A review
Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Reza Tayefeh Davalloo, Gelareh Tajziehchi, Paria Shams
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2021; 51(4): 341. CrossRef - Contribution of XP‐Endo files to the root canal filling removal: A systematic review and meta‐analysis ofin vitrostudies
Emel Uzunoglu‐Özyürek, Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Sevilay Karahan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 703. CrossRef - Micro‐CT evaluation of filling of flattened root canals using a new premixed ready‐to‐use calcium silicate sealer by single‐cone technique
Karina I. M. C. Tavares, Jáder C. Pinto, Airton O. Santos‐Junior, Fernanda F. E. Torres, Juliane M. Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(5): 976. CrossRef - Development of A Nano-Apatite Based Composite Sealer for Endodontic Root Canal Filling
Angelica Bertacci, Daniele Moro, Gianfranco Ulian, Giovanni Valdrè
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(1): 30. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
- 1,933 View
- 16 Download
- 12 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


