Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium instruments: a systematic review
- Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Mayara Zanon, Fernanda Hecksher, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Rafaela Andrade de Vasconcelos, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e25. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
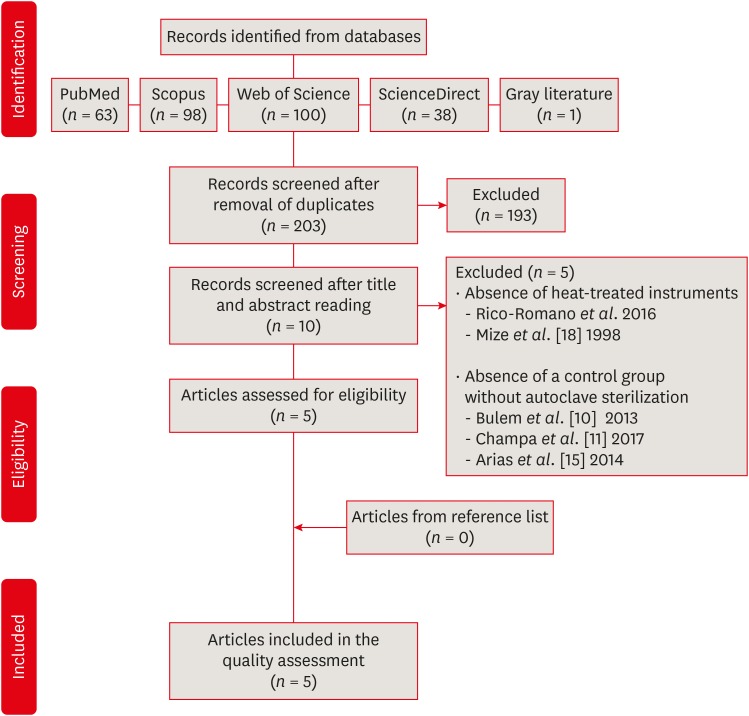
ePub Objectives This systematic review evaluated the influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments.
Materials and Methods A systematic search without restrictions was conducted in the following electronic databases: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, ScienceDirect, Cochrane, and Open Grey. The hand search was also performed in the main endodontic journals. The eligible studies were submitted to the methodological assessment and data extraction.
Results From 203 abstracts, a total of 10 articles matched the eligible criteria. After reading the full articles, 2 were excluded because of the absence of the heat-treated instruments in the experimental design and 3 due to the lack of a control group using heat-treated instruments without autoclave sterilization. From the 5 included studies, 1 presented a low risk of bias, 3 presented moderate and 1 high risk. It was observed heterogeneous findings in the included studies, with autoclave sterilization cycles increasing, decreasing or not affecting the cyclic fatigue life of heat-treated NiTi instruments. However, the retrieved studies evaluating the cyclic fatigue resistance of endodontic instruments presented different protocols and assessing outcomes, this variability makes the findings less comparable within and also between groups and preclude the establishment of an unbiased scientific evidence base.
Conclusions Considering the little scientific evidence and considerable risk of bias, it is still possible to conclude that autoclave sterilization procedures appear to influence the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated NiTi instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Autoclaving on the Mechanical Performance and Metallurgical Behavior of ProTaper Ultimate, BlueShaper, and ZenFlex Nickel–Titanium Systems
Fatima Bardan, Mohamed El-Kishawi, Ensanya Ali Abou Neel, Saaid Al Shehadat, Rashid El Abed, Ahmed Jamleh
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 292. CrossRef - Impact of Repeated Use on Cyclic and Torsional Fatigue of 3 Rotary Files: Implications for Clinical Safety
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Rafael da Rocha Tavares Duarte, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Leonardo Rigoldi Bonjardim
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 954. CrossRef - EndoMagic Gold M06 Eğelerinde Boyut ve Konikliğin Döngüsel Yorgunluğa Etkisi: Bir İn Vitro Çalışma
Bircan Kuloğlu, Ayşe Çoban, Hatice Büyüközer Özkan
Akdeniz Diş Hekimliği Dergisi.2025; 4(3): 212. CrossRef - Effect of simulated clinical use and sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel titanium files
Mohammad Alajemi, Ammar AbuMostafa
PeerJ.2024; 12: e17418. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue of Different Ni-Ti Endodontic Rotary File Alloys: A Comprehensive Review
Dina Abdellatif, Alfredo Iandolo, Michela Scorziello, Giuseppe Sangiovanni, Massimo Pisano
Bioengineering.2024; 11(5): 499. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Rotary versus Reciprocating Endodontic Files: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ana De Pedro-Muñoz, Cristina Rico-Romano, Patricia Sánchez-Llobet, José María Montiel-Company, Jesús Mena-Álvarez
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(3): 882. CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite on cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel–titanium instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Lucas Guimarães Abreu, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Kiani dos Santos de Paula, Sabrina de Castro Oliveira, Juliana Goto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Francine Benetti
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6291. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of EdgeTaper Platinum, Protaper Gold, and TruNatomy Prime rotary files before and after autoclave sterilization
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem M. Barakat, Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal F. Alkadi
PeerJ.2023; 11: e14656. CrossRef - Effect of calcium hydroxide on fracture resistance and microhardness of dentin in human teeth
Simar Sethi, Alpa Gupta, Ansy Hanna Kurian, Dax Abraham, Parul Chauhan, Kritika Aneja, Sucheta Jala, Arundeep Singh
Endodontology.2022; 34(4): 223. CrossRef - Effect of body temperature on the cyclic fatigue resistance of the nickel”titanium endodontic instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Selventhra Savitha, Sidhartha Sharma, Vijay Kumar, Amrita Chawla, Perumal Vanamail, Ajay Logani
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 338. CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files After Usage and Autoclave Sterilization: An In Vitro Study
Rashid El Abed, Aisha Alshehhi, Yoo Jung Kang, Dana Al Raeesi, Amar H. Khamis, Mohamed Jamal, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(11): 1428. CrossRef - Effect of Autoclaving Cycles on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Race and Race Evo Nickel-Titanium Endodontic Rotary Files: An In Vitro Study
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem Barakat, Aroob Albakri, Manal Altamimi
Metals.2021; 11(12): 1947. CrossRef - Effect of number of uses and sterilization on the instrumented area and resistance of reciprocating instruments
Victor de Ornelas Peraça, Samantha Rodrigues Xavier, Fabio de Almeida Gomes, Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Erick Miranda Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of sterilization procedures on the physical and mechanical properties of rotating endodontic instruments: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Claudia Arena, Diego Sovereto, Riccardo Aiuto, Luigi Laino, Gaetano Illuzzi, Enrica Laneve, Bruna Raddato, Vito Carlo Alberto Caponio, Antonio Dioguardi, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Giuseppe Troiano, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Impact of Autoclaving on the Mechanical Performance and Metallurgical Behavior of ProTaper Ultimate, BlueShaper, and ZenFlex Nickel–Titanium Systems
- 2,707 View
- 47 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Infection control of light curing units
- Hoon-Sang Chang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):235-237. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.235
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub When curing the composite restorations with light curing units, the light guides are often in direct contact with oral tissues, therefore contamination of light guides is inevitable. Curing light guides fall into the "semicritical" instrument category according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and must be heat or vapor-sterilized or at a minimum, these semicritical instruments must be sterilized in a liquid chemical agent. Currently, most common methods of maintaining sterility of the light guides are wiping the guide with a disinfectant, such as glutaraldehyde, after each patient use; using autoclavable guides; using presterilized, single-use plastic guides; and using translucent disposable barriers to cover the guide.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of a multi-layer infection control barrier on the micro-hardness of a composite resin
In-Nam Hwang, Sung-Ok Hong, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2012; 20(5): 576. CrossRef - Power density of various light curing units through resin inlays with modified layer thickness
Sung-Ok Hong, Yonghui Oh, Jeong-Bum Min, Jin-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(3): 130. CrossRef
- Effect of a multi-layer infection control barrier on the micro-hardness of a composite resin
- 1,060 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- CYCLIC FATIGUE OF THE SODIUM HYPOCHLORITE TREATED AND /OR STEAM AUTOCLAVED NICKEL-TITANIUM ENDODONTIC FILES
- Hye-Young Cho, Il-Young Jung, Chan-Young Lee, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):54-65. Published online January 14, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.054
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of sodium hypochlorite and steam autoclaving on the cyclic fatigue of nickel-titanium endodontic files.
Two types of files with a .06 taper and #30 were used, K3® (SybronEndo, Glendora, California, USA) and Hero642®(Micro-Mega, Besançon, France).
The files were divided into 6 experimental groups containing 10 files each group depending the soaking time in 6% sodium hypochlorite solution and number of cycles of steam autoclave. After sterilization, a cyclic fatigue test was performed on each file, and the fracture time was recorded in seconds. The control group underwent the cyclic fatigue test only. After the test, the surface characteristics of the files were observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
All groups containing the Hero 642® files showed a similar cyclic fatigue fracture time. However, the cyclic fatigue fracture time with the K3® files was significantly shorter in groups which were treated with sodium hypochlorite than in the control group (P < 0.05). SEM revealed both Hero642® and K3® files to have significant corrosion on the file surface in groups treated with sodium hypochlorite, compared with the sharp and regular blades of the control group. K3® files showed more corrosion than the Hero642® files. Bluntness of the blades of the K3® file was observed in groups treated with steam autoclave. Although there was no obvious destruction on the surface of steam autoclaved Hero642® files, slight bluntness was observed.
Sterilizing with a steam autoclave is much less destructive to K3® files than sodium hypochlorite. The longer time exposed to sodium hypochlorite, the more destructive pattern was shown on the blades of the files. Therefore, when using sodium hypochlorite solution, the exposure time should be as short as possible in order to prevent corrosion and increase the cyclic fatigue fracture time.
- 877 View
- 1 Download

- The effect of NaOCl treatment and sterilization procedures on the corrosion of endodontic files
- Won-Kyung Yang, Yoon-Sik Ra, Young-Kyoo Lee, Ho-Hyun Son, Mi-Ri Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(2):121-127. Published online March 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.2.121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub A variety files made of stainless steel (S-S) or nickel-titanium (Ni-Ti) are used during endodontic treatment. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the corrosion susceptibility of S-S and Ni-Ti endodontic files. Three brands of files were used for this study: K-flex® S-S files (Maillefer, USA), Profile® Ni-Ti files (Maillefer, USA), K-3® Ni-Ti files (SybronEndo, USA). 120 files of each brands (21mm, ISO size #20) were divided into 12 groups according to 1) sterilization methods using Autoclave or Ethylene Oxide (E-O) gas, 2) Irrigation solutions using 5.25 % NaOCl or Saline, 3) the number of sterilization (1, 5, 10 times). After above procedures, each of the files was inspected by three examiners with a light microscope and camera at X25. Each file was judged and ranked according to the following criteria: 0; no corrosion, 1; mild corrosion, 2; moderate corrosion, and 3; severe corrosion. The files of high score were examined under the Scanning Electron Microscope.
Data were statistically analyzed with the Kruskal-Wallis test (p < 0.05). Most of the ten time-autoclaved files had showed mild to moderate corrosion. But, one or five time-autoclaved files did not show corrosive surface. NaOCl treatment and E-O gas sterilization did not influence on corrosion. There was a significant difference in corrosion susceptibility between sterilization methods and the number of autoclaving. However, there was no significant difference between brands and file materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Various Cold Sterilization Techniques on Routinely used Carbide Burs and Diamond Points
Suganthi Ranganathan, Supriya Manvi, Srivatsa Gopalakrishna, Chaitra Koppal Renukanath
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2017; 7(3): 97. CrossRef
- Comparison of Various Cold Sterilization Techniques on Routinely used Carbide Burs and Diamond Points
- 1,135 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


