Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
-
In vitro evaluation of octenidine as an antimicrobial agent againstStaphylococcus epidermidis in disinfecting the root canal system - Jia Da Chum, Darryl Jun Zhi Lim, Sultan Omer Sheriff, Shaju Jacob Pulikkotil, Anand Suresh, Fabian Davamani
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e8. Published online February 8, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
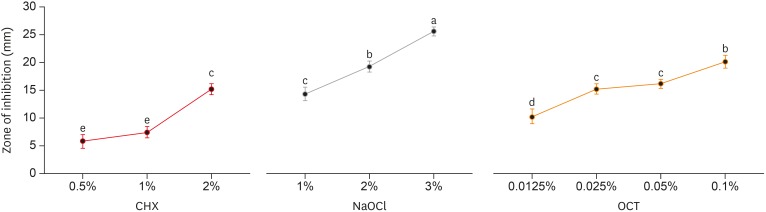
ePub Objectives Irrigants are imperative in endodontic therapy for the elimination of pathogens from the infected root canal. The present study compared the antimicrobial efficacy of octenidine dihydrochloride (OCT) with chlorhexidine (CHX) and sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) against
Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis ) for root canal disinfection.Materials and Methods The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was obtained using serial dilution method. The agar diffusion method was then used to determine the zones of inhibition for each irrigant. Lastly, forty 6-mm dentin blocks were prepared from human mandibular premolars and inoculated with
S. epidermidis . Samples were randomly divided into 4 groups of 10 blocks and irrigated for 3 minutes with saline (control), 2% CHX, 3% NaOCl, or 0.1% OCT. Dentin samples were then collected immediately for microbial analysis, including an analysis of colony-forming units (CFUs).Results The MICs of each tested irrigant were 0.05% for CHX, 0.25% for NaOCl, and 0.0125% for OCT. All tested irrigants showed concentration-dependent increase in zones of inhibition, and 3% NaOCl showed the largest zone of inhibition amongst all tested irrigants (
p < 0.05). There were no significant differences among the CFU measurements of 2% CHX, 3% NaOCl, and 0.1% OCT showing complete elimination ofS. epidermidis in all samples.Conclusions This study showed that OCT was comparable to or even more effective than CHX and NaOCl, demonstrating antimicrobial activity at low concentrations against
S. epidermidis .-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of final irrigation protocols on the bond strength and dentinal tubule penetration of root canal sealers: an ex vivo laboratory study
Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Gülgün Atay Yılmaz, Nihan Şengül, Ahmet Keleş, Selen Küçükkaya Eren
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - WITHDRAWN: Substantivity of different antiseptic oral gels. An In vitro study
Nirit Tagger Green, Roni Kolerman, Carlos Nemcovsky, Shlomo Matalon, Dan Gaukhman, Liat Chaushu
Heliyon.2025; : e42654. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activity of crustacean-derived chitosan against Salmonella Typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes
Sivainesh Devi Remesh, Pratheep Sandrasaigaran, Santhaniswarman Remesh, Veeradasan Perumal, Joshua Yap Lip Vun, Sivasangkary Gandhi, Hanan Hasan
Food Bioscience.2025; : 106697. CrossRef - Glycerol-Enhanced Gum Karaya Hydrogel Films with a Sandwich-like Structure Enriched with Octenidine for Antibacterial Action against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria
Eva Černá, Vilém Neděla, Eva Tihlařiková, Jana Brtníková, Zdenka Fohlerová, Břetislav Lipový, Lukáš Vacek, Filip Růžička, Jana Matulová, Lucy Vojtová
ACS Omega.2025; 10(27): 29530. CrossRef - Effect of Mouth Rinsing and Antiseptic Solutions on Periodontitis Bacteria in an In Vitro Oral Human Biofilm Model
Jan Tinson Strenge, Ralf Smeets, Maria Geffken, Thomas Beikler, Ewa Klara Stuermer
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(7): 324. CrossRef - In Vitro Investigation of the Effects of Octenidine Dihydrochloride on Nasal Septum Squamous Carcinoma Cells
Ihsan Hakki Ciftci, Asuman Deveci Ozkan, Gulay Erman, Elmas Pinar Kahraman Kilbas, Mehmet Koroglu
Biomedicines.2025; 13(11): 2668. CrossRef - Peptidoglycan Recognition Protein-S as a Dual-Action Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Agent Against Staphylococcus aureus
Priya Verma, Priyanka Swaroop, Surabhi Pandit, Ved Prakash, Surender Kumar Sharawat, T. P. Singh, Sujata Sharma, Pradeep Sharma
Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Effects of Endodontic Irrigants Containing Disodium Edetate and Chlorhexidine Gluconate, Octenidine Dihydrochloride, and Benzalkonium Bromide Against Intracanal Enterococcus faecalis
Anna Siemińska, Katarzyna Kot, Ewa Marek, Agnieszka Chamarczuk, Magdalena Kaczała, Joanna Rasławska-Socha, Laurentia Schuster, Till Dammaschke, Liliana Szyszka-Sommerfeld, Mariusz Lipski
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(19): 7100. CrossRef - Evaluation of postoperative pain in endodontic retreatment with apical periodontitis using ozonated 2% chlorhexidine and 0.1% octenidine application: A randomized clinical trial
Nidhi Sinha, Geeta Asthana, Girish Parmar, Akshayraj Langaliya, Jinali Shah, Bijay Singh
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(6): 654. CrossRef - Research on NiTi instruments combined with ultrasonic irrigation and multiantibiotic paste in root canal therapy of periapical inflammation in deciduous teeth
Zongxia Zhu, Guangli Fu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of 0.1% octenidine dihydrochloride, superoxidized solution, ozonated water, 0.1% silver nanoparticle solution, and Q mix™ 2 in 1 in root canals infected with Enterococcus faecalis
Mahenaz Salam Inamdar, Dayanand G. Chole, Shrinivas S. Bakle, Preeti B. Vaprani, Neha P. Gandhi, Nikhil R. Hatte
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(10): 1059. CrossRef - Causal relationship, shared genes between rheumatoid arthritis and pulp and periapical disease: evidence from GWAS and transcriptome data
Huili Wu, Lijuan Wang, Chenjie Qiu
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of octenidine dihydrochloride on the antibacterial activity of a formulated resin composite: an in vitro study
Mahitab Mansour, Tarek Salah, Haidy N. Salem
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between pulp and periapical disease with type 2 diabetes: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization
Yuqiang Wang, Jiakang Zhu, Ying Tang, Cui Huang
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(5): 566. CrossRef - New Insights Regarding the Use of Relevant Synthetic Compounds in Dentistry
Stefania-Irina Dumitrel, Anamaria Matichescu, Stefania Dinu, Roxana Buzatu, Ramona Popovici, Dorin Dinu, Dana Bratu
Molecules.2024; 29(16): 3802. CrossRef - Formulation and Characterization of a Novel Palm-Oil-Based α-Mangostin Nano-Emulsion (PO-AMNE) as an Antimicrobial Endodontic Irrigant: An In Vitro Study
Omer Sheriff Sultan, Haresh Kumar A/L Kantilal, Khoo Suan Phaik, Hira Choudhury, Fabian Davamani
Processes.2023; 11(3): 798. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Herbal Formulations of Septilin and Triphala with Conventional 2% Chlorhexidine on Root Canal and Oral Commensal Bacteria using Kirby Bauer Method
Shadab Ahmed, Kamil Shahnawaz, Tapan Kumar Mandal, Mamnoon Ghafir, Shiva Shankar Gummaluri, Gaurav Vishal
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(4): 383. CrossRef - A comparative assessment of pomegranate extract, sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidine, Myrrh (Commiphora molmol), tulsi extract against Enterococcus faecalis, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Staphylococci epidermidis
Mallwika Sisodiya, Shadab Ahmed, Ranjan Sengupta, Priyanka, Ankit Kumar Saha, Gourav Verma
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2021; 25(2): 369. CrossRef - Effects of Octenidine on the Formation and Disruption of Dental Biofilms: An Exploratory In Situ Study in Healthy Subjects
B. Reda, J. Dudek, M. Martínez-Hernández, M. Hannig
Journal of Dental Research.2021; 100(9): 950. CrossRef - Does Cavity Disinfectant Affect Sealing Ability of Universal Self-etch Adhesive?
S Lata, Prasanti Kumari Pradhan, Gaurav Patri, Subhasmita Bhol, Kanhu C Sahoo, Khushboo Ghosh
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(3): 273. CrossRef - Effect of duration and dilution on antimicrobial efficacy of octenidine hydrochloride as an intracanal medicament with chitosan carrier against Enterococcus faecalis – A modified direct contact test
VinayaSusan Varghese, Nirmal Kurian
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2020; 23(5): 463. CrossRef
- Effect of final irrigation protocols on the bond strength and dentinal tubule penetration of root canal sealers: an ex vivo laboratory study
- 2,572 View
- 20 Download
- 21 Crossref

- White mineral trioxide aggregate mixed with calcium chloride dihydrate: chemical analysis and biological properties
- Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Norhayati Luddin, Thirumulu Ponnuraj Kannan, Khairani Idah Mokhtar, Azlina Ahmad
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):176-187. Published online April 17, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.176
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the chemical and biological properties of fast-set white mineral trioxide aggregate (FS WMTA), which was WMTA combined with calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O), compared to that of WMTA.
Materials and Methods Surface morphology, elemental, and phase analysis were examined using scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis (EDX), and X-ray diffraction (XRD), respectively. The cytotoxicity and cell attachment properties were evaluated on human periodontal ligament fibroblasts (HPLFs) using methyl-thiazol-diphenyltetrazolium (MTT) assay and under SEM after 24 and 72 hours, respectively.
Results Results showed that the addition of CaCl2·2H2O to WMTA affected the surface morphology and chemical composition. Although FS WMTA exhibited a non-cytotoxic profile, the cell viability values of this combination were lesser than WMTA, and the difference was significant in 7 out of 10 concentrations at the 2 time intervals (
p < 0.05). HPLFs adhered over the surface of WMTA and at the interface, after 24 hours of incubation. After 72 hours, there were increased numbers of HPLFs with prominent cytoplasmic processes. Similar findings were observed with FS WMTA, but the cells were not as confluent as with WMTA.Conclusions The addition of CaCl2·2H2O to WMTA affected its chemical properties. The favorable biological profile of FS WMTA towards HPLFs may have a potential impact on its clinical application for repair of perforation defects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of three additives on properties of mineral trioxide aggregate cements: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Behnam Bolhari, Faranak Noori, Hadi Assadian, Amir Raee, Sholeh Ghabraei, Ahmad-Reza Shamshiri, Artak Heboyan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of sorption and solubility of materials based on calcium aluminate
Renata Josipovic, Violeta Petrovic, Marijana Popovic-Bajic, Irena Kuzmanovic-Radman, Mirjana Umicevic-Davidovic, Aleksandra Djeri, Slavoljub Zivkovic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2023; 70(1): 26. CrossRef - Chitosan-Based Accelerated Portland Cement Promotes Dentinogenic/Osteogenic Differentiation and Mineralization Activity of SHED
Hasan Subhi, Adam Husein, Dasmawati Mohamad, Nik Rozainah Nik Abdul Ghani, Asma-Abdullah Nurul
Polymers.2021; 13(19): 3358. CrossRef - Chemical modification of MTA and CEM cement to decrease setting time and improve bioactivity properties by adding alkaline salts
Faeze Jamali Zavare, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Maryam Moezizadeh, Mehdi Daneshpooya
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2020; 14(1): 1. CrossRef - Biological effects of acid-eroded MTA Repair HP and ProRoot MTA on human periodontal ligament stem cells
Mar Collado-González, Sergio López-García, David García-Bernal, Ricardo E. Oñate-Sánchez, Christopher J. Tomás-Catalá, Jose M. Moraleda, Adrián Lozano, Leopoldo Forner, Francisco J. Rodríguez-Lozano
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(10): 3915. CrossRef - Comparative Cytocompatibility and Mineralization Potential of Bio-C Sealer and TotalFill BC Sealer
Sergio López-García, Miguel R. Pecci-Lloret, Julia Guerrero-Gironés, María P. Pecci-Lloret, Adrián Lozano, Carmen Llena, Francisco Javier Rodríguez-Lozano, Leopoldo Forner
Materials.2019; 12(19): 3087. CrossRef - Evaluation of changes in ion release and biological properties of NeoMTA‐Plus and Endocem‐MTA exposed to an acidic environment
F. J. Rodríguez‐Lozano, M. Collado‐González, S. López‐García, D. García‐Bernal, J. M. Moraleda, A. Lozano, L. Forner, L. Murcia, R. E. Oñate‐Sánchez
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1196. CrossRef
- The effect of three additives on properties of mineral trioxide aggregate cements: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
- 1,688 View
- 9 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Evaluation of the effect of blood contamination on the compressive strength of MTA modified with hydration accelerators
- Kaveh Oloomi, Eshaghali Saberi, Hadi Mokhtari, Hamid Reza Mokhtari Zonouzi, Ali Nosrat, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):128-133. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.128
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was performed to evaluate the effect of blood contamination on the compressive strength (CS) of Root MTA (RMTA) modified with Calcium chloride (CaCl2) and Disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4) as setting accelerators over time.
Materials and Methods A total of 110 cylindrical specimens of RMTA were divided into 6 experimental groups as follows: Group1, RMTA; Group 2, RMTA modified with CaCl2 (RMTA-C); Group 3, RMTA modified with Na2HPO4 (RMTA-N); Group 4, RMTA contaminated with blood; Group 5, RMTA-C contaminated with blood; Group 6, RMTA-N contaminated with blood. The CS of specimens in all groups was evaluated after 3 hr, 24 hr, and 1 wk. In the modified groups (groups 2, 3, 5, and 6) the CS of five specimens per group was also evaluated after 1 hr.
Results Blood contamination significantly reduced the CS of all materials at all time intervals (
p < 0.05). After 3 hr, the CS of specimens in the RMTA groups (with and without blood contamination) was significantly lower than those in the RMTA-C and RMTA-N groups (p < 0.05). The CS values were not significantly different at the other time intervals. In all groups, the CS of specimens significantly increased over time (p < 0.05).Conclusions Blood contamination decreased the CS of both original and accelerated RMTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comparative evaluation of setting time in the presence of blood contamination of four root end filling biomaterials (MTA angelus, biodentine, endosequence root repair material, bio-C repair) An in-vitro study
Damini Kesarwani, Sunandan Mittal, Tarun Kumar, Vanita Keshav, Vidushi Gilhotra, Arisha Jain
Endodontology.2026; 38(1): 50. CrossRef - The effect of three additives on properties of mineral trioxide aggregate cements: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Behnam Bolhari, Faranak Noori, Hadi Assadian, Amir Raee, Sholeh Ghabraei, Ahmad-Reza Shamshiri, Artak Heboyan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Push‐out bond strength of the calcium silicate‐based endodontic cements in the presence of blood: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of in vitro studies
Mahdieh Alipour, Leili Faraji Gavgani, Negin Ghasemi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2022; 8(2): 571. CrossRef - Effect of bioactive glass addition on the physical properties of mineral trioxide aggregate
Jei Kim, Hyun-Jung Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh, Sun-Young Kim, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Biomaterials Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the addition of nanoparticles of CaCO3 and different water‐to‐powder ratios on the physicochemical properties of white Portland cement
Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Jessica Coelho Wasielewsky, Giovanna Slongo dos Santos, Anarela Bernardi, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(4): 592. CrossRef - Assessment of the interaction of Portland cement-based materials with blood and tissue fluids using an animal model
P. Schembri Wismayer, C. Y. K. Lung, F. Rappa, F. Cappello, J. Camilleri
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the plant-based hemostatic agent Ankaferd Blood Stopper® on the biocompatibility of mineral trioxide aggregate
Muzaffer Emir Dinçol, Hakan Ozbas, Bulent Yılmaz, Handan Ersev, Selcuk Gokyay, Vakur Olgac
BMC Oral Health.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Surface microhardness of three thicknesses of mineral trioxide aggregate in different setting conditions
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Leila Jafargholizadeh, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Maryam Raoof
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 253. CrossRef - Surgical management of a failed internal root resorption treatment: a histological and clinical report
Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Leili Mehrdad, Sanam Kheirieh, Ali Nosrat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 137. CrossRef
- A comparative evaluation of setting time in the presence of blood contamination of four root end filling biomaterials (MTA angelus, biodentine, endosequence root repair material, bio-C repair) An in-vitro study
- 1,894 View
- 4 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Comparative analysis of various corrosive environmental conditions for NiTi rotary files
- Ji-Wan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):377-388. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.377
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of the present study is to compare the corrosion tendency using two kinds of NiTi files in the various environmental conditions through the visual examination and electrochemical analysis. ProTaper Universal S2, 21 mm (Dentsply Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) and Hero 642, 0.06 tapers, size 25, 21 mm (Micromega, Besancon, France) rotary instruments were tested. The instruments were randomly divided into eighteen groups (n = 5) by the immersion temperature, the type of solution, the brand of NiTi rotary instrument and the presence of mechanical loading. Each file was examined at various magnifications using Scanning Electron Microscope (JEOL, Akishima, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis (EDX). EDX was used to determine the components of the endodontic file alloy in corroded and noncorroded areas. The corrosion resistance of unused and used NiTi files after repeated uses in the human teeth was evaluated electrochemically by potentiodynamic polarization test using a potentiostat (Applied Corrosion Monitoring, Cark-in-Cartmel, UK).
Solution temperature and chloride ion concentration may affect on passivity of NiTi files. Under the conditions of this in vitro study, the corrosion resistance is slightly increased after clinical use.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A novel approach to assess surface roughness and EDX profiling of blue rotary NiTi files following dynamic immersion in various hypochlorite concentrations
Hebatullah Ahmad Safwat, Nesreen Y. Mohammed, Asmaa Abd El-Hady
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Free Recovery Transformation Temperature of NiTi Endodontic Single-File Systems Using a Novel Testing Setup
Emad Youssef, Holger Jungbluth, Søren Jepsen, Manfred Gruener, Christoph Bourauel
Materials.2024; 17(3): 566. CrossRef - The Determination of the Corrosion Rates of Rotary Ni-Ti Instruments in Various Irrigation Solutions
Tolga Özcan, Bade Sonat, Meltem Dartar Öztan, Fatma Basmaci, Umut Aksoy
Cyprus Journal of Medical Sciences.2023; 8(2): 136. CrossRef - A Nonlinear Probabilistic Pitting Corrosion Model of Ni–Ti Alloy Immersed in Shallow Seawater
Špiro Ivošević, Gyöngyi Vastag, Nataša Kovač, Peter Majerič, Rebeka Rudolf
Micromachines.2022; 13(7): 1031. CrossRef - Corrosion resistance assessment of nickel-titanium endodontic files with and without heat treatment
Tatiana Dias Costa, Elison da Fonseca e Silva, Paula Liparini Caetano, Marcio José da Silva Campos, Leandro Marques Resende, André Guimarães Machado, Antônio Márcio Resende do Carmo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite, EDTA, and Chitosan Solution on Corrosion and Quantity of Extruded Nickel Ions Using Two Rotary Instruments (In Vitro)
Eltica Oktavia, Trimurni Abidin
World Journal of Dentistry.2019; 10(3): 207. CrossRef
- A novel approach to assess surface roughness and EDX profiling of blue rotary NiTi files following dynamic immersion in various hypochlorite concentrations
- 1,694 View
- 6 Download
- 6 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


