Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Biological mechanisms underlying the inflammatory radicular cyst formation-focus on epithelial proliferation: a systematic review of experimental cell and tissue models
- Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Sandra Briñez-Rodríguez, David Betancur-Calle, Marggie Grajales, Óscar Mauricio Jiménez-Peña, Mario Guerrero-Torres, Rafael Fernández-Grisales
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent ;Published online February 12, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e7 [Epub ahead of print]
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to assess the molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in the epithelial proliferation that leads to the transformation of periapical granulomas (PGs) into inflammatory radicular cysts (IRCs).
Methods
A comprehensive search was conducted in three databases. Experimental, observational, or descriptive studies using human or animal tissue samples, or epithelial cell cultures that assessed the molecular and/or cellular mechanisms driving the proliferation of epithelial rests of Malassez and their role in the transformation of PGs into IRCs were included. The risk of bias and applicability of the included studies were assessed using the QUADAS-2.
Results
Fourteen studies (including 399 samples) met the inclusion criteria for qualitative synthesis. The studies highlight the role of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6), growth factors (EGF, KGF, TGF-β, and IGF), and signaling pathways (NF-κB, MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT, and Smad) in the progression of PG to IRC. Biomarkers of epithelial proliferation, such as Ki-67, PCNA, and CD34, are consistently associated with this process, while MMP-13 emerges as a key regulator of epithelial behavior and matrix remodeling.
Conclusions
IRC development arises from a transition from homeostatic to pathological signaling, in which pro-inflammatory mediator levels inside the periapical chronic inflammation override regulatory checkpoints.
- 58 View
- 8 Download

- Persistent pain after successful endodontic treatment in a patient with Wegener’s granulomatosis: a case report
- Ricardo Machado, Jorge Aleixo Pereira, Filipe Colombo Vitali, Michele Bolan, Elena Riet Correa Rivero
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e26. Published online June 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
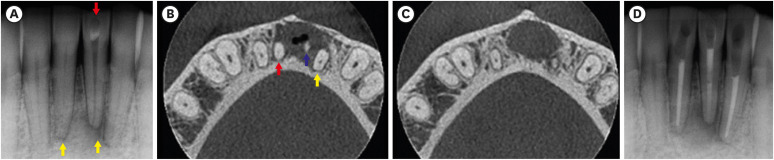
ePub Wegener’s granulomatosis (WG) is a condition with immune-mediated pathogenesis that can present oral manifestations. This report describes the case of a patient diagnosed with WG 14 years previously, who was affected by persistent pain of non-odontogenic origin after successful endodontic treatment. A 39-year-old woman with WG was diagnosed with pulp necrosis and apical periodontitis of teeth #31, #32, and #41, after evaluation through a clinical examination and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). At the first appointment, these teeth were subjected to conventional endodontic treatment. At 6- and 12-month follow-up visits, the patient complained of persistent pain associated with the endodontically treated teeth (mainly in tooth #31), despite complete remission of the periapical lesions shown by radiographic and CBCT exams proving the effectiveness of the endodontic treatments, thus indicating a probable diagnostic of persistent pain of non-odontogenic nature. After the surgical procedure was performed to curette the lesion and section 3 mm of the apical third of tooth #31, the histopathological analysis suggested that the painful condition was likely associated with the patient's systemic condition. Based on clinical, radiographic, and histopathological findings, this unusual case report suggests that WG may be related to non-odontogenic persistent pain after successful endodontic treatments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Toothaches of Non-odontogenic Origin
Davis C. Thomas, Tanvee Somaiya, Ahana Ajayakumar, Vaishnavi Prabhakar
Dental Clinics of North America.2026; 70(1): 209. CrossRef
- Toothaches of Non-odontogenic Origin
- 4,958 View
- 57 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Interplay of collagen and mast cells in periapical granulomas and periapical cysts: a comparative polarizing microscopic and immunohistochemical study
- Deepty Bansal, Mala Kamboj, Anjali Narwal, Anju Devi, Nisha Marwah
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e12. Published online February 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
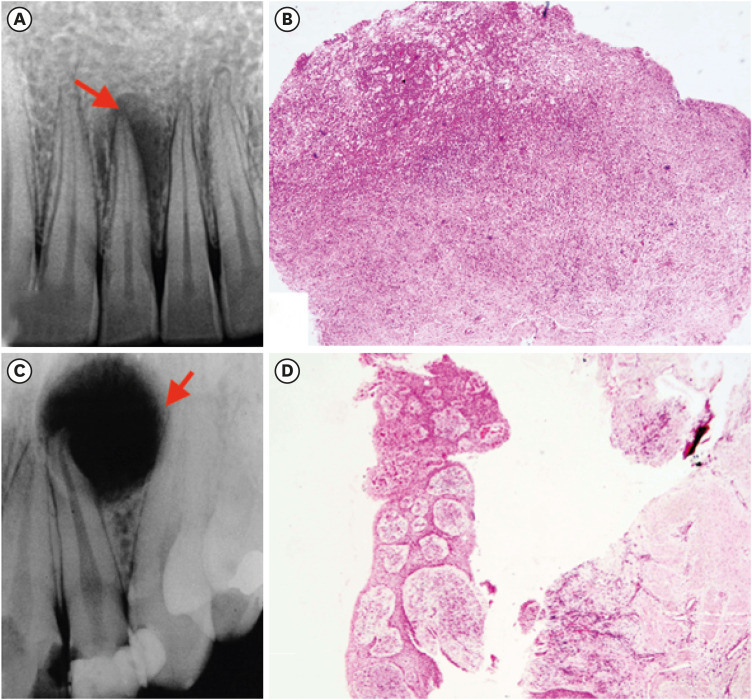
ePub Objectives This pilot study aimed to establish the interrelationship between collagen and mast cells in periapical granulomas and periapical cysts.
Materials and Methods An observational cross-sectional study was conducted on the paraffin-embedded tissue sections of 68 specimens (34 periapical granulomas and 34 periapical cysts). The specimens were stained with picrosirius to observe collagen fiber birefringence and anti-tryptase antibody to evaluate the mast cell count immunohistochemically. The mean number and birefringence of collagen fibers, as well as the mean number of mast cells (total, granulated, and degranulated), and the mean inflammatory cell density were calculated. The data obtained were analyzed using the Kruskal Wallis test, Mann Whitney
U test, and Spearman correlation test (p < 0.05).Results The mean number of thick collagen fibers was higher in periapical cysts, while that of thin fibers was higher in granulomas (
p = 0.00). Cysts emitted orange-yellow to red birefringence, whereas periapical granulomas had predominantly green fibers (p = 0.00). The mean inflammatory cell density was comparable in all groups (p = 0.129). The number of total, degranulated, and granulated mast cells exhibited significant results (p = 0.00) in both groups. Thick cyst fibers showed significant inverse correlations with inflammation and degranulated mast cells (p = 0.041, 0.04 respectively).Conclusions Mast cells and inflammatory cells influenced the nature of collagen fiber formation and its birefringence. This finding may assist in the prediction of the nature, pathogenesis, and biological behavior of periapical lesions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Mystifying Role of Mast Cells in the Pathogenesis of Periapical Pathologies - A Systematic Review
Mala Kamboj, Shashibala Malik, R. Keerthika, Anjali Narwal, Anju Devi, Gopikrishnan Vijayakumar, Adarsh Kumar
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 845. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Analysis of CD117 in the Mast Cells of Odontogenic Keratocysts
Sujatha Varma, Shameena PM, Plakkil Viswanathan Deepthi, Indu G
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical evaluation of cyclooxygenase‐2 and mast cell density in periapical lesions
Shashibala Malik, Mala Kamboj, Anjali Narwal, Anju Devi
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(8): 980. CrossRef
- The Mystifying Role of Mast Cells in the Pathogenesis of Periapical Pathologies - A Systematic Review
- 2,190 View
- 21 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Chronic maxillary sinusitis caused by root canal overfilling of Calcipex II
- Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Soh-Ra Park, Sang-Shin Lee, Suk-Keun Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):63-67. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.63
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This is a case report of chronic maxillary sinusitis caused by root canal overfilling of Calcipex II (Techno-Dent). A 60 year-old male complained of dull pain in the right maxillary molar area after complicated endodontic treatment using Calcipex II paste and was finally diagnosed with a chronic maxillary sinusitis through a clinical and radiological observation. In the biopsy examination, the periapical granuloma contained a lot of dark and translucent Calcipex II granules which were not stained with hematoxylin and eosin. They were usually engulfed by macrophages but rarely resorbed, resulting in scattering and migrating into antral mucosa. Most of the Calcipex II granules were also accumulated in the cytoplasms of secretory columnar epithelial cells, and small amount of Calcipex II granules were gradually secreted into sinus lumen by exocytosis. However, chronic granulomatous inflammation occurred without the additional recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) and lymphocytes, and many macrophages which engulfed the Calcipex II granules were finally destroyed in the processes of cellular apoptosis. It is presumed that Calcipex II granules are likely to have a causative role to induce the granulomatous foreign body inflammation in the periapical region, and subsequently to exacerbate the chronic maxillary sinusitis in this study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal of Calcium Hydroxide Paste Leaked Into the Maxillary Sinus
Dohee Kim, Young Kim, Jeong Joon Han
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Synergistic effects of reduced graphene oxide on the antibacterial activity of calcium hydroxide-based intracanal medicaments containing different vehicles
Mi-Ah Kim, Min-Kyeong Kim, Eun-Sook Kang, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2025; 67(1): 35. CrossRef - The effect of extrusion of the filling material on the periapical status
M. Yu. Pokrovsky, T. P. Goryacheva, A. М. Pokrovskiy, O. А. Aleshina
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(1): 31. CrossRef - Rheological properties and handling characteristics of four injectable calcium hydroxide pastes
Min-Jung KIM, In-Bog LEE
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(6): 796. CrossRef - Assessing the efficacy of jet dispenser versus direct syringe injection for calcium hydroxide paste placement in artificial root canals
Youngwook Song, Hwichan Ham, WooCheol Lee, Ryan Jin Young Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A white cloud in the antrum: Maxillary sinusitis following an endodontic treatment
Kamis Gaballah, Mawada Hassan
Asian Journal of Surgery.2023; 46(4): 1690. CrossRef - Electronic Apex Locators and their Implications in Contemporary Clinical Practice: A Review
Zainab Shirazi, Anas Al-Jadaa, Abdul Rahman Saleh
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The significance of diagnosis and treatment planning in periapical lesion overfilled with calcium hydroxide paste
Kyoung-Hwa Jung, Eun-Young Kwon, Youn-Kyung Choi, So-Yeun Kim, Hye-Mi Jeon, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2021; 37(2): 95. CrossRef - Maxillary antroliths detected by cone-beam computed tomography in an adult dental population
Bong-Hae Cho, Yun-Hoa Jung, Jae-Joon Hwang
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2019; 49(1): 59. CrossRef - Influence of the Maxillary Sinus on the Accuracy of the Root ZX Apex Locator: An Ex Vivo Study
Roula El Hachem, Elie Wassef, Nadim Mokbel, Richard Abboud, Carla Zogheib, Nada El Osta, Alfred Naaman
Dentistry Journal.2019; 7(1): 3. CrossRef - Removal efficacy and cytotoxicity of a calcium hydroxide paste using N-2-methyl-pyrrolidone as a vehicle
Myung-Jin Lim, Hyun-Jin Jang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 290. CrossRef - A case of high density abnormality in x-ray findings of mandible caused by leakage of root canal filling paste
Haruko Kashiwamura, Kyoko Oka, Yoko Tuchihashi, Hanako Yoshioka, Mayumi Kato, Atsuko Baba, Toyohiro Kagawa, Kazuhiko Okamura, Masao Ozaki
Pediatric Dental Journal.2017; 27(3): 162. CrossRef - Maxillary Sinus Impaction of a Core Carrier Causing Sustained Apical Periodontitis, Sinusitis, and Nasal Stenosis: A 3-year Follow-up
Lars Bjørndal, Catharina Amaloo, Merete Markvart, Vibe Rud, Klaus Qvortrup, Camilla Stavnsbjerg, Thomas Bjarnsholt
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(12): 1851. CrossRef - Proximity of Posterior Teeth to the Maxillary Sinus and Buccal Bone Thickness: A Biometric Assessment Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography
Sung Hyun Kang, Bom Sahn Kim, Yemi Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(11): 1839. CrossRef
- Removal of Calcium Hydroxide Paste Leaked Into the Maxillary Sinus
- 2,170 View
- 8 Download
- 14 Crossref

- The relationship of radiographic lesion size and characteristics to diagnosis of periapical cysts and granulomas
- Ho-Sik Choi, Woo-Cheol Lee, Won-Jun Shon, Kee-Yeon Kum, Kwang-Shik Bae, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(1):24-29. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.1.024
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to find out the relationship of radiographic lesion size, gender, age of patients and radiographic character to the diagnosis of periapical cyst and granuloma.
The data was collected from 187 periapical lesions of 167 patients who undergone apical surgery at Department of Conservative Dentistry, Seoul National University Dental Hospital from 2003 to 2005. The lesion were surgically removed and send for biopsy to the Oral Pathology Laboratory. From the initial radiograph, lesion size was calculated using PiViewSTAR® (INFINITT, Korea) program. The obtained data were statistically evaluated using SPSS (p < 0.05).
The result were as followings:
From 187 biopsy samples, the incidence of periapical cyst was 28.34% and granuloma was 65.24%.
There was a significant correlation between periapical cyst and the size of radiographic lesion (p < 0.01).
There were no significant correlations between age, gender, location of lesion and the final diagnosis (p > 0.05).
There was a significant correlation between the non-demarcation of the lesion and the incidence of periapical granuloma (p < 0.01).
- 2,061 View
- 20 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


