Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- CBCT study of mandibular first molars with a distolingual root in Koreans
- Hee-Ho Kim, Hyoung-Hoon Jo, Jeong-Bum Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e33. Published online July 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
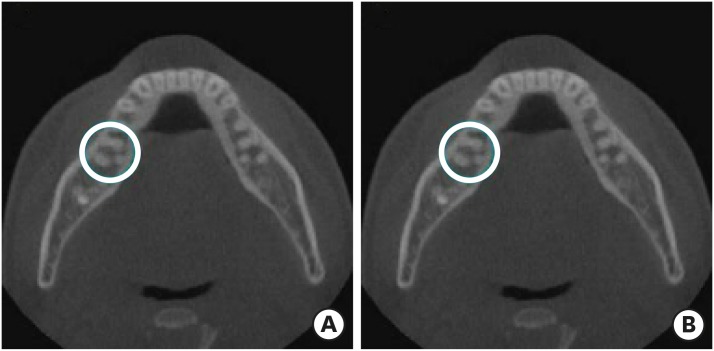
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of a separate distolingual root and to measure the thickness of the buccal cortical bone in mandibular first molars in Koreans using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images.
Materials and Methods High-quality CBCT data from 432 patients were analyzed in this study. The prevalence of a separate distolingual root of the mandibular first molar was investigated. The distance from the distobuccal and distolingual root apices to the outer surface of the buccal cortical bone was measured. We also evaluated the thickness of the buccal cortical bone.
Results The prevalence of a separate distolingual root (2 separate distal roots with 1 canal in each root; 2R2C) was 23.26%. In mandibular first molars with 2R2C, the distance from the distobuccal root apex to the outer surface of the buccal cortical bone was 5.51 mm. Furthermore, the distance from the distolingual root apex to the outer surface of the buccal cortical bone was 12.09 mm. In mandibular first molars with 2R2C morphology, the thickness of the buccal cortical bone at the distobuccal root apex of the mandibular first molar was 3.30 mm. The buccal cortical bone at the distobuccal root apex was significantly thicker in the right side (3.38 mm) than the left side (3.09 mm) (
p < 0.05).Conclusions A separate distolingual root is not rare in mandibular first molars in the Korean population. Anatomic and morphologic knowledge of the mandibular first molar can be useful in treatment planning, including surgical endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The association between complex root canal morphology of mandibular anteriors and distolingual roots in mandibular first molars in a Turkish population
Özge Kurt, Elif Solakoğlu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radix molaris is a hidden truth of mandibular first permanent molars: A descriptive- analytic study using cone beam computed tomography
Mohammed A. Alobaid, Saurabh Chaturvedi, Ebtihal Mobarak S. Alshahrani, Ebtsam M. Alshehri, Amal S. Shaiban, Mohamed Khaled Addas, Giuseppe Minervini
Technology and Health Care.2023; 31(5): 1957. CrossRef - Prevalence of radix entomolaris in India and its comparison with the rest of the world
Sumit MOHAN, Jyoti THAKUR
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A critical analysis of laboratory and clinical research methods to study root and canal anatomy
Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 229. CrossRef - Three‐Rooted Permanent Mandibular First Molars: A Meta‐Analysis of Prevalence
Nyan M. Aung, Kyaw K. Myint, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Reproducibilidad en el diagnóstico imagenológico de periodontitis apical a partir de CBCT
Sandra Milena Buitrago Rojas, Yeny Zulay Castellanos Dominguez, Jhonny Alexander Contreras Vargas, Yosdi Tomás Solano Diaz, Eder Fabián Gutierrez Argote
Acta Odontológica Colombiana.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Root and Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Molars using CBCT
Yoomin Choi, Seonmi Kim, Namki Choi
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2020; 47(1): 25. CrossRef - The prevalence of radix molaris in the mandibular first molars of a Saudi subpopulation based on cone-beam computed tomography
Hassan AL-Alawi, Saad Al-Nazhan, Nassr Al-Maflehi, Mazen A. Aldosimani, Mohammed Nabil Zahid, Ghadeer N. Shihabi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Preferred Reporting Items for Epidemiologic Cross-sectional Studies on Root and Root Canal Anatomy Using Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Technology: A Systematized Assessment
Jorge N.R. Martins, Anil Kishen, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(7): 915. CrossRef - Evaluation of roots and canal systems of mandibular first molars in a vietnamese subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography
KhoaVan Pham, AnhHoang Lan Le
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2019; 9(4): 356. CrossRef
- The association between complex root canal morphology of mandibular anteriors and distolingual roots in mandibular first molars in a Turkish population
- 1,891 View
- 10 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using cone-beam computed tomography
- Hyoung-Hoon Jo, Jeong-Bum Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):55-62. Published online January 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the incidence of root fusion and C-shaped root canals in maxillary molars, and to classify the types of C-shaped canal by analyzing cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) in a Korean population.
Materials and Methods Digitized CBCT images from 911 subjects were obtained in Chosun University Dental Hospital between February 2010 and July 2012 for orthodontic treatment. Among them, a total of selected 3,553 data of maxillary molars were analyzed retrospectively. Tomography sections in the axial, coronal, and sagittal planes were displayed by PiViewstar and Rapidia MPR software (Infinitt Co.). The incidence and types of root fusion and C-shaped root canals were evaluated and the incidence between the first and the second molar was compared using Chi-square test.
Results Root fusion was present in 3.2% of the first molars and 19.5% of the second molars, and fusion of mesiobuccal and palatal root was dominant. C-shaped root canals were present in 0.8% of the first molars and 2.7% of the second molars. The frequency of root fusion and C-shaped canal was significantly higher in the second molar than the first molar (
p < 0.001).Conclusions In a Korean population, maxillary molars showed total 11.3% of root fusion and 1.8% of C-shaped root canals. Furthermore, root fusion and C-shaped root canals were seen more frequently in the maxillary second molars.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of C‐Shaped Canals in Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population: A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Analysis
Amin Salem Milani, Shahin Namvar Asl Amirkhizi, Tahmineh Razi, Ahmad Nouroloyouni, Pouya Sabanik, Nikhat Kaura
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of c-shaped canal morphology in premolar and molar teeth assessed by cone-beam computed tomography: systematic review and meta-analysis
Faezeh Yousefi, Younes Mohammadi, Elham Shokri
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of C‐Shaped Canal Configuration in Maxillary Molars Among an Iranian Population
Nafiseh Nikkerdar, Mohammad Moslehi, Amin Golshah, Mario Dioguardi
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of a C‐shaped mandibular second molar with narrow dentinal thickness: A case report
Mina Mehrjouei, Hamid Jafarzadeh, Pourya Esmaeelpour, Maryam Khorasanchi
Clinical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of 2- and 3-dimensional anatomic parameters of C-shaped root canals with cone beam computed tomography, microcomputed tomography, and nanocomputed tomography
Miguel Angel Ventura Molina, Giovane Oliveira Silva, Amanda Pelegrin Candemil, Rafael Verardino de Camargo, Ruben Pauwels, Reinhilde Jacobs, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2023; 136(6): 759. CrossRef - Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Analysis of an Unusual Configuration of the Upper First Molar With a C-shaped Canal With Apically Fused Roots: A Case Report
Kapil D Wahane, Anand V Bansod, Sudha mattigatti, Rushikesh Mahaparale, Yuvraj B Rote, Mayur B Wanjari
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of C-Shaped Canal Morphology in Mandibular and Maxillary Second Molars in an Iraqi Subpopulation Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Kazhan Abdalrahman, Ranjdar Talabani, Sara Kazzaz, Dlsoz Babarasul, Berndt Koslowski
Scanning.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Root and canal-specific features of maxillary first molars with fused roots
Katarina Beljic-Ivanovic, Branislav Karadzic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2022; 79(11): 1092. CrossRef - Diagnosis and treatment of maxillary molar with abnormality
Kkot-Byeol Bae, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Oral Biology Research.2022; 46(4): 195. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of the maxillary first molar with palatal canal variations: A case report and review of literature
Kai Chen, Xing Ran, Yan Wang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(32): 12036. CrossRef - Evaluation of C-shaped canals in maxillary molars in a Chinese population using CBCT
Yuyan Qian, Yamei Li, Jukun Song, Ping Zhang, Zhu Chen
BMC Medical Imaging.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive evaluation of root and root canal morphology of mandibular second molars in a Saudi subpopulation evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography
Moazzy I. Almansour, Saad M. Al‑Zubaidi, Abdulmjeed S. Enizy, Ahmed A. Madfa
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of C-shaped canal configuration in maxillary molars: A retrospective cone-beam computed tomography study
Emre KÖSE, Rüya AK
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2021; 11(3): 444. CrossRef - Maxillary First Molars with Two Palatal Root Canals
Kun-Hwa Sung, Ho-Keel Hwang, Hyoung-Hoon Jo, Konstantinos Michalakis
Case Reports in Dentistry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Preferred Reporting Items for Epidemiologic Cross-sectional Studies on Root and Root Canal Anatomy Using Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Technology: A Systematized Assessment
Jorge N.R. Martins, Anil Kishen, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(7): 915. CrossRef - Evaluation of root and root canal morphology of elderly Korean patients maxillary molars using cone-beam computed tomography
Tae-Yong Lee, Mi-Yeon Kim, Sun-Ho Kim, Jeong-Hee Kim
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2020; 58(2): 95. CrossRef - Second mesiobuccal root canal in maxillary molars—A systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence studies using cone beam computed tomography
Jorge N.R. Martins, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Archives of Oral Biology.2020; 113: 104589. CrossRef - Prevalência estimada de canais “C- Shaped”: Uma revisão sistemática e meta-análise
Natália Pereira da Silva Falcão, Sandro Junio de Oliveira Tavares, Ludmila Silva Guimarães, Katherine Azevedo Batistela Rodrigues Thuller, Leonardo dos Santos Antunes, Estefano Borgo Sarmento, Fellipe Navarro Azevedo de Azevedo, Cinthya Cristina Gomes, Ca
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2020; : 91. CrossRef - Evaluation of the internal anatomy of paramolar tubercles using cone-beam computed tomography
G. Colakoglu, I. Kaya Buyukbayram, M. A. Elcin, M. Kazak, H. Sezer
Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy.2020; 42(1): 15. CrossRef - Analysis of Prevalence of Pyramidal Molars in Adolescent
Woojin Kwon, Hyung-Jun Choi, Jaeho Lee, Je Seon Song
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2020; 47(4): 389. CrossRef - Prevalence Studies on Root Canal Anatomy Using Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Imaging: A Systematic Review
Jorge N.R. Martins, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(4): 372. CrossRef - Fused roots of maxillary molars: characterization and prevalence in a Latin American sub-population: a cone beam computed tomography study
Maytté Marcano-Caldera, Jose Luis Mejia-Cardona, María del Pilar Blanco-Uribe, Elena Carolina Chaverra-Mesa, Didier Rodríguez-Lezama, Jose Hernán Parra-Sánchez
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - An original micro‐CT study and meta‐analysis of the internal and external anatomy of maxillary molars—implications for endodontic treatment
Iwona M. Tomaszewska, Anna Jarzębska, Bendik Skinningsrud, Przemysław A. Pękala, Sebastian Wroński, Joe Iwanaga
Clinical Anatomy.2018; 31(6): 838. CrossRef - A Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Study of Root and Canal Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Permanent Molars in a Thai Population
Roserin Ratanajirasut, Anchana Panichuttra, Soontra Panmekiate
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(1): 56. CrossRef - Retrospective Assessment of Healing Outcome of Endodontic Treatment for Mandibular Molars with C-shaped Root Canal
Kishore Kumar Majety, Basanta Kumar Choudhury, Anika Bansal, Achla Sethi, Jaina Panjabi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2017; 18(7): 591. CrossRef - The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography in a polish population
Katarzyna Olczak, Halina Pawlicka
BMC Medical Imaging.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prevalence of C‐Shaped Canals in Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population: A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Analysis
- 1,976 View
- 14 Download
- 26 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


