Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Analysis of the reciprocating kinematics of the VDW Silver Reciproc, E-Connect Pro, Ecom, and Endopen endodontic motors: an in vitro experimental study
- Cristielly França, Juliana D. Bronzato, Dieimes Braambati, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Carla C. R. B. Félix, Michelle A. N. S. Ferreira, Marcos Frozoni
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e5. Published online January 20, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e5

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
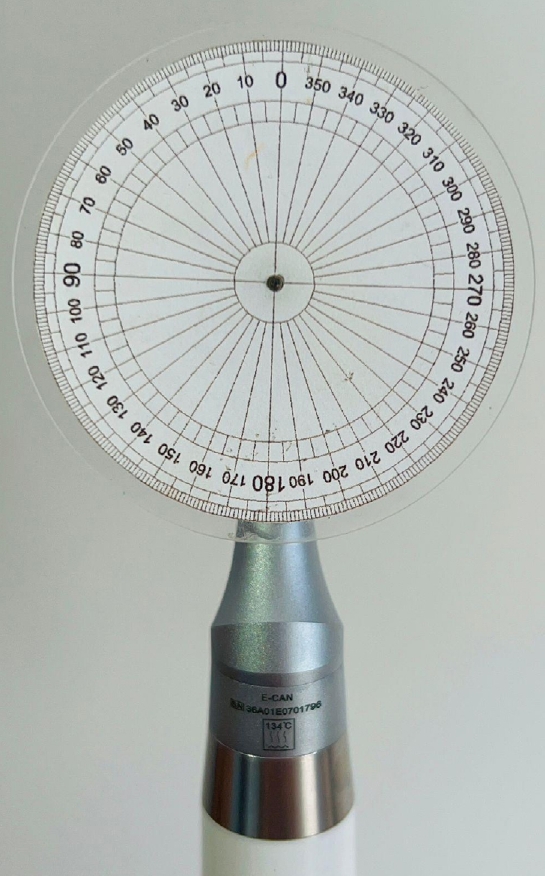
This study aimed to evaluate the actual parameters of four endodontic motors, each adjusted for reciprocating motion, and compare them to the manufacturers’ declared values.
Methods
The motors used were the VDW Silver Reciproc (VDW GmbH), E-Connect Pro (MK Life), Ecom (Woodpecker), and Endopen (Schuster Woodpecker). A custom optical target was attached to the motor contra-angle, the movements were recorded with a high-resolution camera, and the images were analyzed. Engagement, disengagement, net angles, and speed for each operation cycle, duration of clockwise (CW) and counter-clockwise (CCW) movement, duration of standstill after CW and CCW movement, and the number of cycles to complete a full rotation were analyzed. The data were statistically analyzed at a significance level of 5%. The replicability of all reciprocal parameters analyzed was statistically different from that reported by the manufacturers.
Results
There was no statistically significant difference between the VDW Silver Reciproc, Ecom, and Endopen for the engagement angle. The E-Connect Pro was the least reliable at the 150°/30° settings for both angle parameters. There was no significant difference between the set and actual cycle net angles for the VDW Silver Reciproc (p = 0.493). While the actual values for the Ecom and E-Connect Pro were significantly higher than the set (p < 0.001), the actual values for the Endopen were significantly lower than the set (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Experiments on four commercially available reciprocating endodontic motors revealed that the actual motor values differed significantly from the set values.
- 586 View
- 27 Download

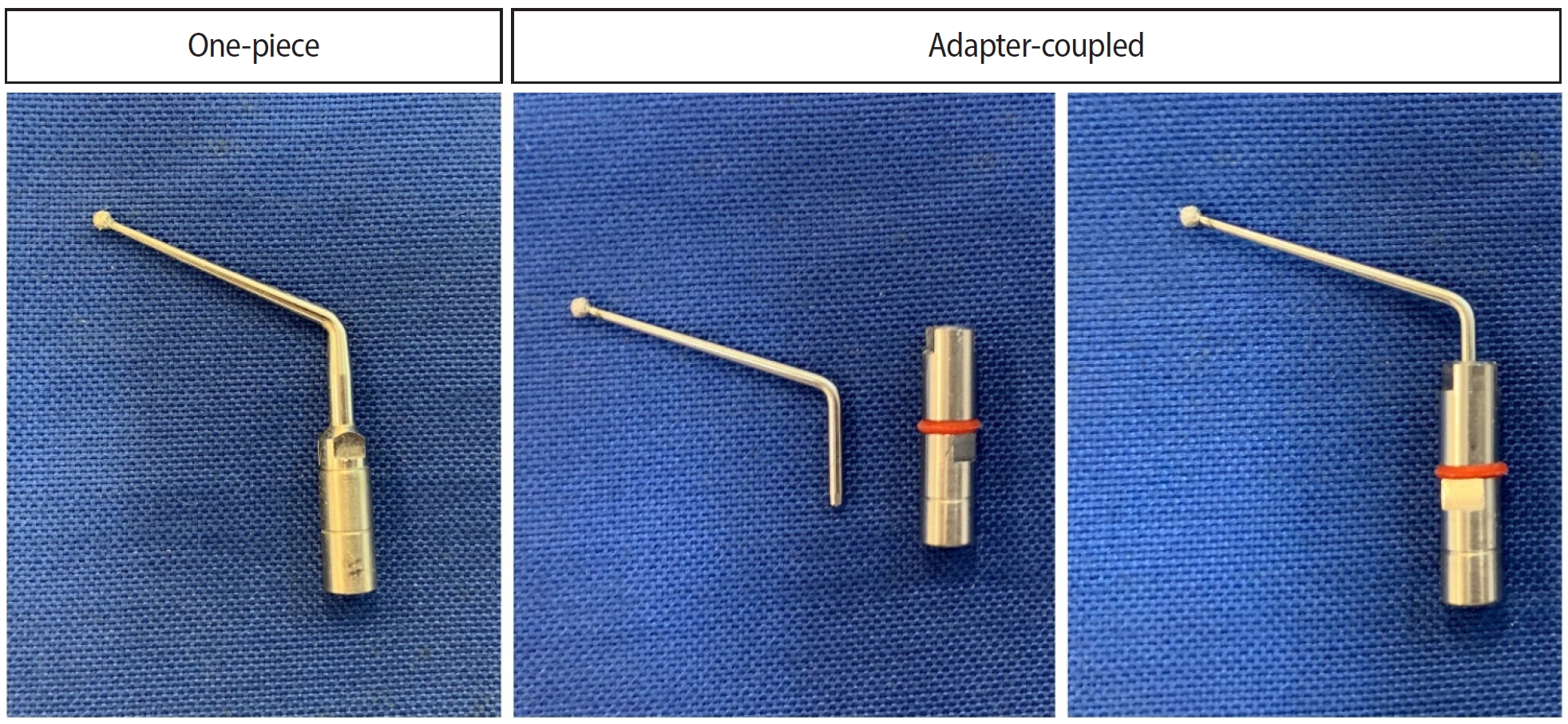
- Analysis of thermal profiles on tooth structure and insert during one-piece or adapter-coupled ultrasonic insert use: an in vitro experimental study
- Gabriela Loewen Brotto, Bruno Monguilhott Crozeta, Bruno Marques-da-Silva, Alysson Nunes Diógenes, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Flávia Sens Fagundes Tomazinho
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e24. Published online July 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This in vitro study aimed to evaluate temperature variation on the external surface of mandibular molars and within ultrasonic inserts when using adapter-coupled versus one-piece inserts.
Methods
Twenty-four extracted human mandibular molars were divided into two groups based on the type of ultrasonic insert used: adapter-coupled and one-piece inserts. Temperature on the external surface of each tooth was measured with a thermocouple probe positioned in the furcation area, capturing data continuously. The temperature of the ultrasonic inserts was monitored in real-time using a thermal imaging camera. Measurements were taken in a controlled environment without cooling for over 120 seconds. Statistical analysis was conducted using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and two-way ANOVA with repeated measures to evaluate temperature variations between groups and over time, with significance set at 5%.
Results
In the external tooth surface temperature measurements, no significant differences were observed between the groups during the initial 15 seconds (p = 0.185) and 30 seconds (p = 0.067). However, significant differences emerged at 60 seconds (p = 0.025), 90 seconds (p = 0.024), and 120 seconds (p = 0.020), with the one-piece insert group demonstrating higher temperatures in the furcation region. Thermal imaging of the inserts revealed a significant difference at all time points (p < 0.001), with adapter-coupled inserts showing greater heating.
Conclusions
The use of ultrasonic inserts leads to a gradual rise in temperature on the external tooth surface. One-piece inserts generated higher temperatures on the tooth, while adapter-coupled inserts exhibited greater heating within the insert.
- 1,811 View
- 95 Download

- Comparative analysis of torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProGlider, WaveOne Gold Glider, and TruNatomy Glider in simulated curved canal
- Pedro de Souza Dias, Augusto Shoji Kato, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Rina Andréa Pelegrine
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e4. Published online December 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare the torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProGlider (PG), WaveOne Gold Glider (WGG), and TruNatomy Glider (TNG).
Materials and Methods A total of 15 instruments of each glide path system (
n = 15) were used for each test. A custom-made device simulating an angle of 90° and a radius of 5 millimeters was used to assess cyclic fatigue resistance, with calculation of number of cycles to failure. Torsional fatigue resistance was assessed by maximum torque and angle of rotation. Fractured instruments were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Data were analyzed with Shapiro-Wilk and Kruskal-Wallis tests, and the significance level was set at 5%.Results The WGG group showed greater cyclic fatigue resistance than the PG and TNG groups (
p < 0.05). In the torsional fatigue test, the TNG group showed a higher angle of rotation, followed by the PG and WGG groups (p < 0.05). The TNG group was superior to the PG group in torsional resistance (p < 0.05). SEM analysis revealed ductile morphology, typical of the 2 fracture modes: cyclic fatigue and torsional fatigue.Conclusions Reciprocating WGG instruments showed greater cyclic fatigue resistance, while TNG instruments were better in torsional fatigue resistance. The significance of these findings lies in the identification of the instruments’ clinical applicability to guide the choice of the most appropriate instrument and enable the clinician to provide a more predictable glide path preparation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
Ujjwal Das, Rajesh Kumar Das, Kallol Kumar Saha, Lugu Buru Murmu, Srimanta Banerjee, Rishila Nag
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 384. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the remaining dentin volume following instrumentation with rotary, reciprocating, and hand files during root canal treatment in primary molars: An ex vivo study
İrem Eren, Berkant Sezer
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2126. CrossRef - Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Evaluation of shaping ability of different glide path instruments: a micro-computed tomography study
Merve Yeniçeri Özata, Seda Falakaloğlu, Ali Keleş, Özkan Adıgüzel, Mustafa Gündoğar
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
- 2,907 View
- 68 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

-
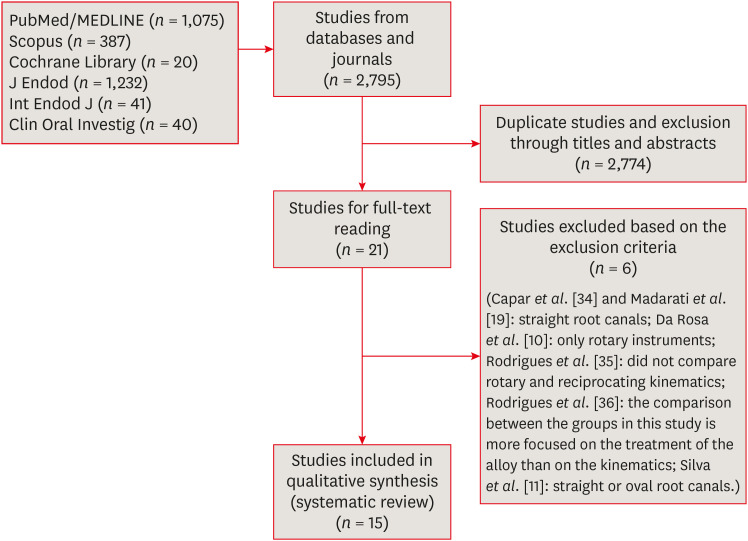
Effectiveness and safety of rotary and reciprocating kinematics for retreatment of curved root canals: a systematic review of
in vitro studies - Lucas Pinho Simões, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Carlos Roberto Emerenciano Bueno, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Cleidiel Aparecido Araújo Lemos, Francine Benetti
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e22. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This systematic review (register-osf.io/wg7ba) compared the efficacy and safety of rotary and reciprocating kinematics in the removal of filling material from curved root canals.
Materials and Methods Only
in vitro studies evaluating both kinematics during retreatment were included. A systematic search (PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, and other databases, until January 2021), data extraction, and risk of bias analysis (Joanna Briggs Institute checklist) were performed. Efficacy in filling removal was the primary outcome.Results The search resulted in 2,795 studies, of which 15 were included. Efficacy was measured in terms of the remaining filling material and the time required for this. Nine studies evaluated filling material removal, of which 7 found no significant differences between rotary and reciprocating kinematics. Regarding the time for filling removal, 5 studies showed no difference between both kinematics, 2 studies showed faster results with rotary systems, and other 2 showed the opposite. No significant differences were found in apical transportation, centering ability, instrument failure, dentin removed and extruded debris. A low risk of bias was observed.
Conclusions This review suggests that the choice of rotary or reciprocating kinematics does not influence the efficacy of filling removal from curved root canals. Further studies are needed to compare the kinematics safety in curved root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apical Third Cleaning Efficiency of Hand, Rotary, and Reciprocating Root Canal Instrumentation: A Quantitative In Vitro Scanning Electron Microscopic Study
B. Sai Krishna, Sita Mahalakshmi Koppu, Dilip Katakam, Sahithi Nammaniwar, Ambika Belam, Akshita Balivada, Divakar K. P.
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Selective Nonsurgical Endodontic Retreatment: Relevant Aspects for Clinical Application—A Scoping Review
Tomás Manuel Braz Marinho, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Anne Caroline Brito Cabral dos Santos, Djessyca Miranda‐e‐Paulo, Rui Barbosa de Brito Júnior, João Marcos da Costa Ribeiro, Felipe de Souza Matos
Australian Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE AFTER ENDODONTIC FILLING IN TEETH WITH APICAL WIDENING: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Isabella da Costa Ferreira, Gabriela da Costa Ferreira, Isabella Figueiredo de Assis Macedo, Gustavo Oliveira Campos, Isabella Faria da Cunha Peixoto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Warley Luciano Fonseca Tavares
ARACÊ .2025; 7(10): e8792. CrossRef - Fifteen years of engine‐driven nickel–titanium reciprocating instruments, what do we know so far? An umbrella review
Felipe Immich, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 409. CrossRef - Efficacy of Various Heat-treated Retreatment File Systems on the Apical Deformity and Canal Centering Ability in a Single-rooted Teeth using Nano CT
Swathi S, Pradeep Solete, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Delphine Priscilla Antony S, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Dona Sanju
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
Gülsen Kiraz, Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Mert Ocak, Muhammet Bora Uzuner, Hakan Hamdi Çelik
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite on cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel–titanium instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Lucas Guimarães Abreu, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Kiani dos Santos de Paula, Sabrina de Castro Oliveira, Juliana Goto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Francine Benetti
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6291. CrossRef - Retreatment of XP-endo Shaper and R-Endo files in curved root canals
Hayam Y. Hassan, Fahd M. Hadhoud, Ayman Mandorah
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing Endodontics through Kinematics
Shilpa Bhandi, Dario Di Nardo, Francesco Pagnoni, Rosemary Abbagnale
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 479. CrossRef
- Apical Third Cleaning Efficiency of Hand, Rotary, and Reciprocating Root Canal Instrumentation: A Quantitative In Vitro Scanning Electron Microscopic Study
- 3,423 View
- 65 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Impact of root canal curvature and instrument type on the amount of extruded debris during retreatment
- Burcu Serefoglu, Gözde Kandemir Demirci, Seniha Miçooğulları Kurt, İlknur Kaşıkçı Bilgi, Mehmet Kemal Çalışkan
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e5. Published online December 17, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of the current study was to assess whether the amount of extruded debris differs for straight and severely curved root canals during retreatment using H-files, R-Endo, Reciproc and ProTaper Universal Retreatment (PTU-R) files. Additionally, the area of residual filling material was evaluated.
Materials and Methods Severely curved (
n = 104) and straight (n = 104) root canals of maxillary molar teeth were prepared with WaveOne Primary file and obturated with gutta-percha and AH Plus sealer. Root canal filling materials were removed with one of the preparation techniques: group 1: H-file; group 2: R-Endo; group 3: Reciproc; group 4: PTU-R (n = 26). The amount of extruded material and the area of the residual filling material was measured. The data were analyzed with 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and 1-way ANOVA at the 0.05 significance level.Results Except for Reciproc group (
p > 0.05), PTU-R, R-Endo, and H-file systems extruded significantly more debris in severely curved canals (p < 0.05). Each file system caused more residual filling material in severely curved canals than in straight ones (p < 0.05).Conclusions All instruments used in this study caused apical debris extrusion. Root canal curvature had an effect on extruded debris, except for Reciproc system. Clinicians should be aware that the difficult morphology of the severely curved root canals is a factor increasing the amount of extruded debris during the retreatment procedure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Effectiveness of MicroMega Remover, ProTaper Universal Retreatment, Reciproc, and Hedstrom Files in the Retreatment of Curved Root Canals Obturated with Different Techniques: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study
Pınar Hava Dursun, Fatma Semra Sevimay, Arda Buyuksungur, Berkan Celikten
Medicina.2026; 62(1): 188. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Root Canal Curvature Measurement Methods for Permanent Mandibular Molars Distal Root: An Observational Study
Tanu Singh, Saurav Bathla, Anuraag Gurtu, Shubhi Gupta, Sana Saifi, Madhusudan Astekar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(10): 945. CrossRef - Do Continuous Rotating Endodontic Instruments Extrude Fewer Apical Debris Than Reciprocating Instruments in Non-Surgical Endodontic Retreatments? A Systematic Review
Francesco Puleio, Francesco Giordano, Ugo Bellezza, David Rizzo, Valentina Coppini, Roberto Lo Giudice
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(4): 1621. CrossRef - Intracanal removal and apical extrusion of filling material after retreatment using rotary or reciprocating instruments: A new approach using human cadavers
Thamyres M. Monteiro, Victor O. Cortes‐Cid, Marilia F. V. Marceliano‐Alves, Andrea F. Campello, Luan F. Bastos, Ricardo T. Lopes, José F. Siqueira, Flávio R. F. Alves
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(1): 100. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of methods for measuring root canal curvature based on periapical radiography: A laboratory study
Rafael Chies Hartmann, Eduardo Silva Ferraz, Theodoro Weissheimer, Jose Antônio Poli de Figueiredo, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele, Maximiliano Schünke Gomes
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(12): 1848. CrossRef - Evaluation of apically extruded debris during root canal filling material removal in teeth with external apical root resorption: a comparison of different obturation techniques
Büşra Melike Çağlar, İsmail Uzun
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of apically extruded debris using protaper universal, protaper next, one curve, Xp shaper, and edge file: An in vitro study
Murtada Qadir Muhaibes, Shatha Abdulkareem Alwakeel
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 31. CrossRef - A quantitative comparison of apically extruded debris during root canal preparation using NiTi full-sequence rotary and single-file rotary systems: An in vitro study
Pallavi Goel, R. Vikram, R. Anithakumari, M. S. Adarsha, M. E. Sudhanva
Endodontology.2024; 36(3): 235. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of filling material removal and apical debris extrusion after retreatment using Reciproc blue, Hyflex EDM and ProTaper retreatment files
Passent Abdelnaby, Mohamed Ibrahim, Rania ElBackly
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Shaping Ability and Cleaning Efficiency of Two Different Single-File Systems, Reciprocating Wave One Versus Continuous Rotation F360, Evaluated by Scanning Electron Microscope: An In Vitro Study
Arunkumar Samudrala, Chandrakanth Majeti, Kommineni Harika Chowdary, Lakshmi Bhavani Potru, Anusha Yaragani, Yata Prashanth Kumar, Gagandeep K Sidhu, Navneet S Kathuria
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT ROTARY INSTRUMENT SYSTEMS ON THE AMOUNT OF APICALLY EXTRUDED DEBRIS
Recai ZAN, Bilge LENGER
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2022; 25(2): 172. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Effectiveness of MicroMega Remover, ProTaper Universal Retreatment, Reciproc, and Hedstrom Files in the Retreatment of Curved Root Canals Obturated with Different Techniques: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study
- 2,508 View
- 33 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

-
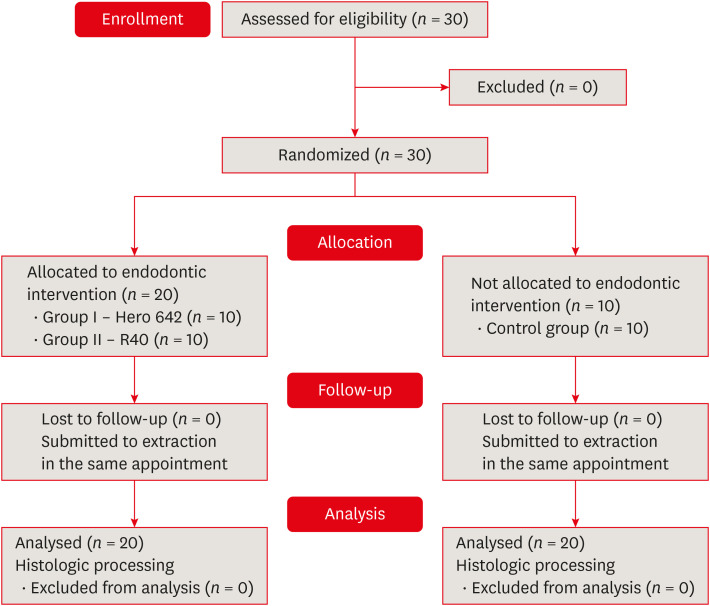
Apical root canal cleaning after preparation with endodontic instruments: a randomized trial
in vivo analysis - Volmir João Fornari, Mateus Silveira Martins Hartmann, José Roberto Vanni, Rubens Rodriguez, Marina Canali Langaro, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Alexandre Augusto Zaia
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e38. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate vital pulp tissue removal from different endodontic instrumentation systems from root canal apical third
in vivo .Materials and Methods Thirty mandibular molars were selected and randomly divided into 2 test groups and one control group. Inclusion criteria were a positive response to cold sensibility test, curvature angle between 10 and 20 degrees, and curvature radius lower than 10 mm. Root canals prepared with Hero 642 system (size 45/0.02) (
n = 10) and Reciproc R40 (size 40/0.06) (n = 10) and control (n = 10) without instrumentation. Canals were irrigated only with saline solution during root canal preparation. The apical third was evaluated considering the touched/untouched perimeter and area to evaluate the efficacy of root canal wall debridement. Statistical analysis usedt -test for comparisons.Results Untouched root canal at cross-section perimeter, the Hero 642 system showed 41.44% ± 5.62% and Reciproc R40 58.67% ± 12.39% without contact with instruments. Regarding the untouched area, Hero 642 system showed 22.78% ± 6.42% and Reciproc R40 34.35% ± 8.52%. Neither instrument achieved complete cross-sectional root canal debridement. Hero 642 system rotary taper 0.02 instruments achieved significant greater wall contact perimeter and area compared to reciprocate the Reciproc R40 taper 0.06 instrument.
Conclusions Hero 642 achieved higher wall contact perimeter and area but, regardless of instrument size and taper, vital pulp during
in vivo instrumentation is not entirely removed.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unveiling the correlation between in vivo endodontic reciprocate instrumentation and crack formation
Mateus Silveira Martins Hartmann, José Roberto Vanni, Karla Rovaris, Lucas Jeziorski Hartmann, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Volmir João Fornari
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 150: 105367. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of stress distribution against the root canal wall at three different levels using novel NiTi rotary files – A finite element analysis
Rimjhim Singh, Sandeep Dubey, Palak Singh, Praveen Singh Samant, Suparna Ganguly Saha
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(1): 62. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Ultrasonic and Sonic Irrigant Activation Systems: Assessing Extrusion Risk, Debridement, and Biofilm Removal in Distinct Apical Preparation Sizes
Sara Paixão, Pedro Sousa Gomes, Maria Helena Fernandes, Cláudia Rodrigues, Liliana Grenho
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(9): 3904. CrossRef - A Short Report on the Effectiveness of Edge Taper Platinum and XP-3D Shaper for the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis Count in the Root Canal System: An Ex Vivo Study
Hanie Moaveni, Parastou Ghahari, Samira Behrad, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Sobhan Rashmee, Somayeh Teimoori
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2024; 16(2): 77. CrossRef - Comparative in Vitro Study on the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Endodontic Sealers Against Common Oral Pathogens
Csaba Dudás, Zsuzsanna Bardocz-Veres, Anita Iulia Gyulai, Silvia Izabella Pop, Melinda Székely, Bernadette Kerekes-Máthé, Mónika Kovács
Dentistry Journal.2024; 13(1): 17. CrossRef - Periradicular repair after single- and two-visit root canal treatments using ultrasonic irrigant activation and calcium hydroxide dressing of teeth with apical periodontitis: study protocol for randomized controlled trials
Gustavo M. Almeida, Vitor Hugo M. Carvalho, Érika B. P. Silva, Marco Antonio F. Cançado, Leonardo S. Barroso, Erica L. Queiroz, Tien Li An, Ana Paula D. Ribeiro, Jacy R. Carvalho-Junior, André F. Leite
Trials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of EndoSeal MTA, iRoot SP, and AH Plus against Planktonic Bacteria
Siew Thong Mak, Xin Fang Leong, In Meei Tew, Endang Kumolosasi, Lishen Wong
Materials.2022; 15(6): 2012. CrossRef - Influence of apical preparation size and final irrigation protocol on the debridement of oval root canals
Carolina Pessoa Stringheta, Rina Andréa Pelegrine, Victor Angelo Martins Montalli, James L Gutmann, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(6): 16. CrossRef
- Unveiling the correlation between in vivo endodontic reciprocate instrumentation and crack formation
- 2,559 View
- 29 Download
- 8 Crossref

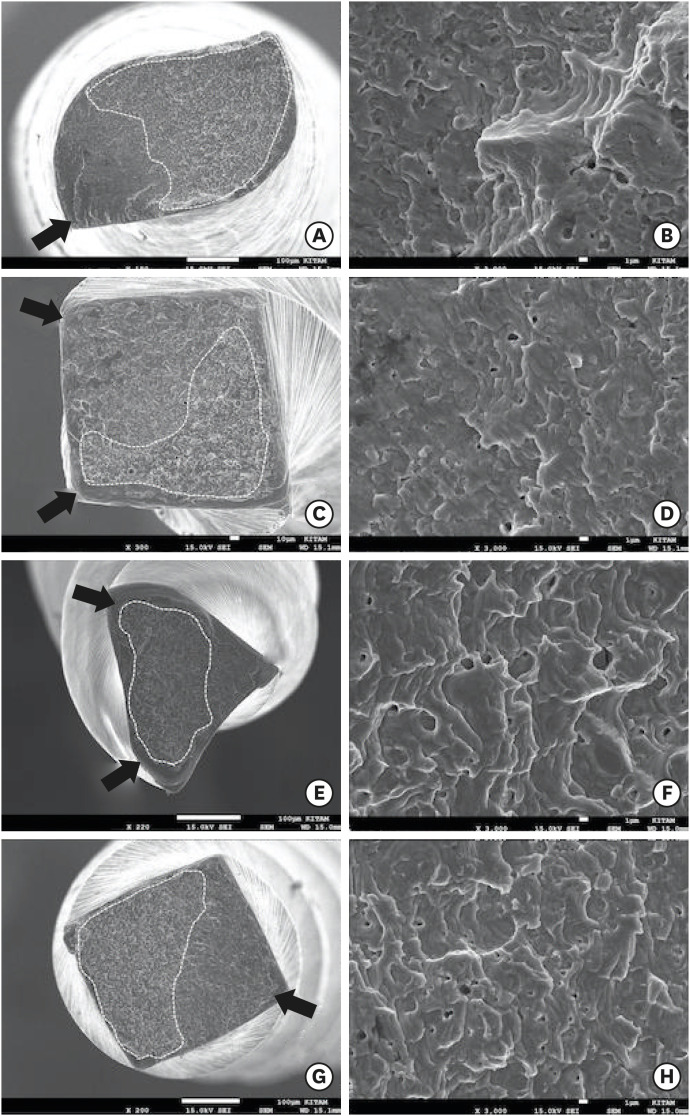
- Comparison of the cyclic fatigue resistance of VDW.ROTATE, TruNatomy, 2Shape, and HyFlex CM nickel-titanium rotary files at body temperature
- Mustafa Gündoğar, Gülşah Uslu, Taha Özyürek, Gianluca Plotino
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e37. Published online June 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aims to compare the cyclic fatigue resistance of VDW.ROTATE, TruNatomy, 2Shape, and HyFlex CM nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files at body temperature.
Materials and Methods In total, 80 VDW.ROTATE (25/0.04), TruNatomy (26/0.04), 2Shape (25/0.04), and HyFlex CM (25/0.04) NiTi rotary files (
n = 20 in each group) were subjected to static cyclic fatigue testing at body temperature (37°C) in stainless-steel artificial canals prepared according to the size and taper of the instruments until fracture occurred. The number of cycles to fracture (NCF) was calculated, and the lengths of the fractured fragments were measured. The data were statistically analyzed using a 1-way analysis of variance andpost hoc Tamhane tests at the 5% significance level (p < 0.05).Results There were significant differences in the cyclic fatigue resistance among the groups (
p < 0.05), with the highest to lowest NCF values of the files as follows: VDW.ROTATE, HyFlex CM, 2Shape, and TruNatomy. There was no significant difference in the lengths of the fractured fragments among the groups. The scanning electron microscope images of the files revealed typical characteristics of fracture due to cyclic fatigue.Conclusions The VDW.ROTATE files had the highest cyclic fatigue resistance, and the TruNatomy and 2Shape files had the lowest cyclic fatigue resistance in artificial canals at body temperature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multimethod Analysis of a Novel NiTi Rotary System: Cyclic Fatigue, Buckling Resistance, and Bending Tests
Alyne Rouse Rocha, Ana Grasiela Limoeiro, Iris Nogueira Seckler, Bárbara Rebeca Alves, Adriana Jesus Soares, Samuel Nogueira Lima, Victor Talarico Vieira, Marília Fagury Videira Marceliano-Alves, Wayne Martins Nascimento, Luis Cardoso Rasquin, Marcos Froz
European Journal of Dentistry.2026; 20(01): 061. CrossRef - Micro‐CT Evaluation of Dentin Preservation by ProTaper Gold and VDW.Rotate in Oval Mandibular Incisors
Wesley Viana de Sousa, Marina da Cunha Isaltino, Christianne Velozo, Silmara de Andrade Silva, Luiza de Almeida Souto Montenegro, Hugo Victor Dantas, Frederico Barbosa de Sousa, Diana Albuquerque, Cristiana Corsi
The Scientific World Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-CT evaluation of dentinal microcrack formation in mesiobuccal canals of maxillary molars following instrumentation with heat-treated rotary and reciprocating systems
Fatemeh Soltaninejad, Yazdan Shantiaee, Babak Zandi, Arsham Moslemi, Seyed Sepehr Mirebeigi-Jamasbi
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue and Physical Properties Testing of Different Small Taper Heat-Treated Reciprocating Files
Ahmed Altuwalah, Taher Al Omari, Riyadh Alroomy, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Hamza Elfarraj, Rubén A. Domínguez-Pérez, Rashid El Abed
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance, number of uses, and morphological/chemical analysis of RCS Rainbow Files, VDW Rotate and ProTaper Ultimate: in vitro study
Tayná Lopes da Silva, Patrícia Carla Lopes, Mírian Galvão Bueno de Rezende, Amjad Abu Hasna
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Efficiency of Different Endodontic File Systems; Protaper Universal, MTWO, Protaper Next, Trunatomy, I-Race in Terms of Remaining Dentin Thickness: An In vitro CBCT Analysis
Anju Retnakaran, Faisal M. A. Gaffoor, Rethi Gopakumar, C Sabari Girish, N. C Sajeena, N Gokul Krishna
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 2): S1409. CrossRef - Analysis of Cutting Capacity, Surface Finishing, and Mechanical Properties of NiTi Instruments 25/.04: ROTATE and LOGIC 2
Ridalton Carlos de Morais, Juliana Delatorre Bronzato, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Marcos Frozoni, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(7): 982. CrossRef - Effect of Temperature on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Phase Transformation Behavior of Three Different NiTi Endodontic Instruments
Esra İrem Yi̇ği̇t, İrem Çetinkaya
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of the Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of a New TruNatomy Glider File after Different Cycles of Use
Lorena Ferreira Rego, Juliana Delatorre Bronzato, Alana Pinto Carôso Souza, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Marcos Frozoni
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 619. CrossRef - Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite and Hypochlorous Acid Solutions on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Waveonegold, K3XF and Hyflex-EDM: A Study of Metallurgical Properties
D. A. Bozkurt, M. Akman, H. B. Karadag, Z. Ovalioglu, Ö.Küçük Keleş
Strength of Materials.2023; 55(1): 191. CrossRef - Effectiveness of conservative instrumentation in root canal disinfection
Sıla Nur Usta, Carmen Solana, Matilde Ruiz-Linares, Pilar Baca, Carmen María Ferrer-Luque, Monica Cabeo, Maria Teresa Arias-Moliz
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 3181. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of different nickel‐titanium instruments in single and double curvature at room and body temperatures: A laboratory study
Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Maria Laura Leotta, Francesco Saverio Canova, Virginia Rosy Romeo, Gabriele Cervino, Luigi Generali, Eugenio Pedullà
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(3): 592. CrossRef - Influence of NiTi Wire Diameter on Cyclic and Torsional Fatigue Resistance of Different Heat-Treated Endodontic Instruments
Eugenio Pedullà, Francesco Saverio Canova, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Alfred Naaman, Franck Diemer, Luigi Generali, Walid Nehme
Materials.2022; 15(19): 6568. CrossRef - Impact of Different Access Cavity Designs and Ni–Ti Files on the Elimination of Enterococcus faecalis from the Root Canal System: An In Vitro Study
Gizem Andac, Atakan Kalender, Buket Baddal, Fatma Basmaci
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(4): 2049. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportations and centering ability of rotary instrument systems with different heat-treated NiTi alloys: An in vitro CBCT study
Mukadder İnci BAŞER KOLCU, Gülter Devrim KAKİ
Turkish Journal of Health Science and Life.2022; 5(2): 81. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of cutting efficiency, cyclic fatigue, corrosion resistance, and autoclave cycle effects of three different file systems: An in-vitro micro-CT and metallurgy analysis
KondasV Venkatesh, EldhoJ Varghese
Journal of International Oral Health.2022; 14(6): 551. CrossRef - Influence of different heat treatments and temperatures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of endodontic instruments with the same design
Walid Nehme, Alfred Naaman, Franck Diemer, Maria Laura Leotta, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Eugenio Pedullà
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(4): 1793. CrossRef - Analysis of cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Next rotary instruments
Nenad Stosic, Jelena Popovic, Marija Andjelkovic-Apostolovic, Aleksandar Mitic, Radomir Barac, Marija Nikolic, Marko Igic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2022; 69(3): 109. CrossRef - Influência do hipoclorito de sódio na resistência à fadiga cíclica em instrumentos rotatórios endodônticos de memória controlada de NiTi: uma avaliação experimental
Marcelo Leite MESQUITA, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira BUENO, Alexandre Sigrist DE MARTIN, Rina Andrea PELEGRINE, Carlos Eduardo FONTANA
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Novel TruNatomy Files with Conventional Endodontic Files: An In Vitro SEM Study
Sabari Murugesan, Vinoth Kumar, Bharath Naga Reddy, Syed Nahid Basheer, Rajeswary Kumar, Saravanan Selvaraj
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(11): 1243. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue of TruNatomy Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument in Single and Double Curvature Canals: A Comparative Study
Sarah A Rashid, Hikmet A AI-Gharrawi
World Journal of Dentistry.2021; 12(1): 28. CrossRef
- Multimethod Analysis of a Novel NiTi Rotary System: Cyclic Fatigue, Buckling Resistance, and Bending Tests
- 3,247 View
- 45 Download
- 21 Crossref

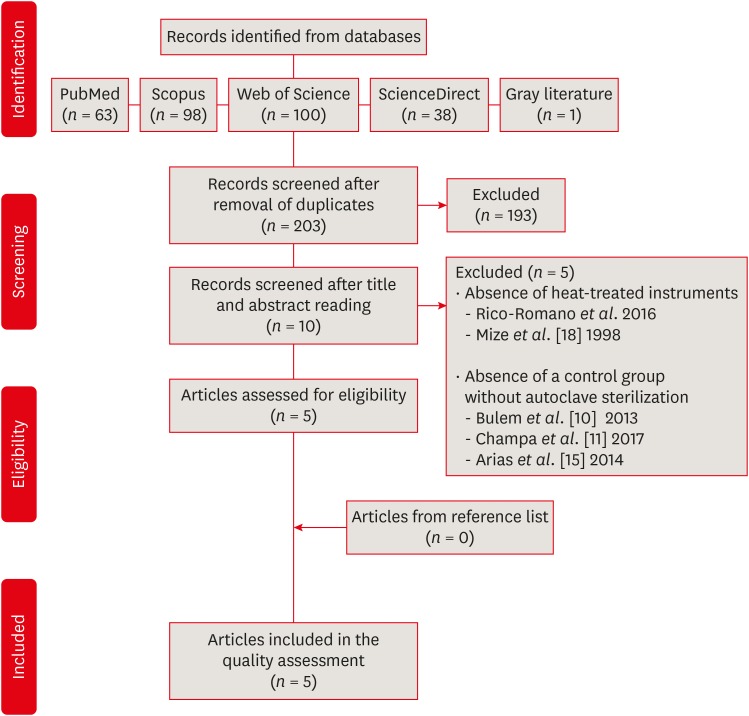
- Influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium instruments: a systematic review
- Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Mayara Zanon, Fernanda Hecksher, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Rafaela Andrade de Vasconcelos, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e25. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This systematic review evaluated the influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments.
Materials and Methods A systematic search without restrictions was conducted in the following electronic databases: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, ScienceDirect, Cochrane, and Open Grey. The hand search was also performed in the main endodontic journals. The eligible studies were submitted to the methodological assessment and data extraction.
Results From 203 abstracts, a total of 10 articles matched the eligible criteria. After reading the full articles, 2 were excluded because of the absence of the heat-treated instruments in the experimental design and 3 due to the lack of a control group using heat-treated instruments without autoclave sterilization. From the 5 included studies, 1 presented a low risk of bias, 3 presented moderate and 1 high risk. It was observed heterogeneous findings in the included studies, with autoclave sterilization cycles increasing, decreasing or not affecting the cyclic fatigue life of heat-treated NiTi instruments. However, the retrieved studies evaluating the cyclic fatigue resistance of endodontic instruments presented different protocols and assessing outcomes, this variability makes the findings less comparable within and also between groups and preclude the establishment of an unbiased scientific evidence base.
Conclusions Considering the little scientific evidence and considerable risk of bias, it is still possible to conclude that autoclave sterilization procedures appear to influence the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated NiTi instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Autoclaving on the Mechanical Performance and Metallurgical Behavior of ProTaper Ultimate, BlueShaper, and ZenFlex Nickel–Titanium Systems
Fatima Bardan, Mohamed El-Kishawi, Ensanya Ali Abou Neel, Saaid Al Shehadat, Rashid El Abed, Ahmed Jamleh
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 292. CrossRef - Impact of Repeated Use on Cyclic and Torsional Fatigue of 3 Rotary Files: Implications for Clinical Safety
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Rafael da Rocha Tavares Duarte, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Leonardo Rigoldi Bonjardim
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 954. CrossRef - EndoMagic Gold M06 Eğelerinde Boyut ve Konikliğin Döngüsel Yorgunluğa Etkisi: Bir İn Vitro Çalışma
Bircan Kuloğlu, Ayşe Çoban, Hatice Büyüközer Özkan
Akdeniz Diş Hekimliği Dergisi.2025; 4(3): 212. CrossRef - Effect of simulated clinical use and sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel titanium files
Mohammad Alajemi, Ammar AbuMostafa
PeerJ.2024; 12: e17418. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue of Different Ni-Ti Endodontic Rotary File Alloys: A Comprehensive Review
Dina Abdellatif, Alfredo Iandolo, Michela Scorziello, Giuseppe Sangiovanni, Massimo Pisano
Bioengineering.2024; 11(5): 499. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Rotary versus Reciprocating Endodontic Files: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ana De Pedro-Muñoz, Cristina Rico-Romano, Patricia Sánchez-Llobet, José María Montiel-Company, Jesús Mena-Álvarez
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(3): 882. CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite on cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel–titanium instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Lucas Guimarães Abreu, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Kiani dos Santos de Paula, Sabrina de Castro Oliveira, Juliana Goto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Francine Benetti
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6291. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of EdgeTaper Platinum, Protaper Gold, and TruNatomy Prime rotary files before and after autoclave sterilization
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem M. Barakat, Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal F. Alkadi
PeerJ.2023; 11: e14656. CrossRef - Effect of calcium hydroxide on fracture resistance and microhardness of dentin in human teeth
Simar Sethi, Alpa Gupta, Ansy Hanna Kurian, Dax Abraham, Parul Chauhan, Kritika Aneja, Sucheta Jala, Arundeep Singh
Endodontology.2022; 34(4): 223. CrossRef - Effect of body temperature on the cyclic fatigue resistance of the nickel”titanium endodontic instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Selventhra Savitha, Sidhartha Sharma, Vijay Kumar, Amrita Chawla, Perumal Vanamail, Ajay Logani
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 338. CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files After Usage and Autoclave Sterilization: An In Vitro Study
Rashid El Abed, Aisha Alshehhi, Yoo Jung Kang, Dana Al Raeesi, Amar H. Khamis, Mohamed Jamal, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(11): 1428. CrossRef - Effect of Autoclaving Cycles on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Race and Race Evo Nickel-Titanium Endodontic Rotary Files: An In Vitro Study
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem Barakat, Aroob Albakri, Manal Altamimi
Metals.2021; 11(12): 1947. CrossRef - Effect of number of uses and sterilization on the instrumented area and resistance of reciprocating instruments
Victor de Ornelas Peraça, Samantha Rodrigues Xavier, Fabio de Almeida Gomes, Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Erick Miranda Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of sterilization procedures on the physical and mechanical properties of rotating endodontic instruments: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Claudia Arena, Diego Sovereto, Riccardo Aiuto, Luigi Laino, Gaetano Illuzzi, Enrica Laneve, Bruna Raddato, Vito Carlo Alberto Caponio, Antonio Dioguardi, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Giuseppe Troiano, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Impact of Autoclaving on the Mechanical Performance and Metallurgical Behavior of ProTaper Ultimate, BlueShaper, and ZenFlex Nickel–Titanium Systems
- 2,702 View
- 47 Download
- 14 Crossref

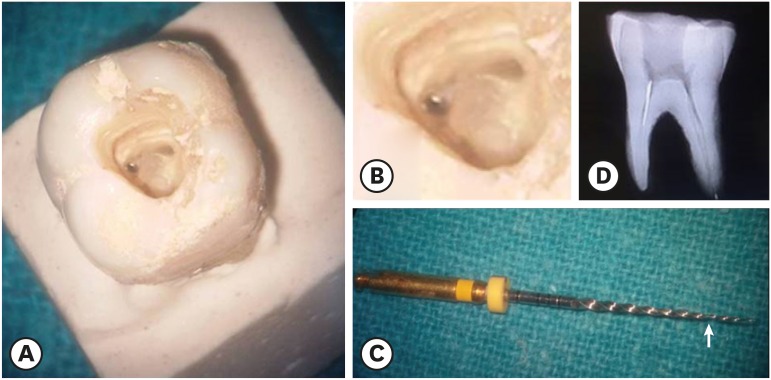
- Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of ultrasonic tips versus the Terauchi file retrieval kit for the removal of separated endodontic instruments
- Preeti Jain Pruthi, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar, Mahesh Verma
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e14. Published online February 6, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective The aim of this study was to perform a comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of ultrasonic tips versus the Terauchi file retrieval kit (TFRK) for the removal of broken endodontic instruments.
Materials and Methods A total of 80 extracted human first mandibular molars with moderate root canal curvature were selected. Following access cavity preparation canal patency was established with a size 10/15 K-file in the mesiobuccal canals of all teeth. The teeth were divided into 2 groups of 40 teeth each: the P group (ProUltra tips) and the T group (TFRK). Each group was further subdivided into 2 smaller groups of 20 teeth each according to whether ProTaper F1 rotary instruments were fractured in either the coronal third (C constituting the PC and TC groups) or the middle third (M constituting the PM and TM groups). Instrument retrieval was performed using either ProUltra tips or the TFRK.
Results The overall success rate at removing the separated instrument was 90% in group P and 95% in group T (
p > 0.05) The mean time for instrument removal was higher with the ultrasonic tips than with the TFRK (p > 0.05).Conclusion Both systems are acceptable clinical tools for instrument retrieval but the loop device in the TFRK requires slightly more dexterity than is needed for the ProUltra tips.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of success rate and operator variability in loop.based versus ultrasonic retrieval of fractured endodontic instruments: An ex vivo study
Tanushree Saxena, Vivek Devidas Mahale, Manish Ranjan, Sanyuta Singh, E. Aparna Mohan, M. Hema
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 73. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of time efficiency and dentin preservation in ultrasonic versus loop retrieval of separated endodontic files: An ex vivo study with pilot nano-computed tomography analysis
Tanushree Saxena, Vivek Devidas Mahale, Manish Ranjan, M. Hema, Sanyukta Singh, E. Aparna Mohan
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 90. CrossRef - Comparison of the pull-out force of different microtube-based methods in fractured endodontic instrument removal: An in-vitro study
Nasim Hashemi, Mohsen Aminsobhani, Mohammad Javad Kharazifard, Fatemeh Hamidzadeh, Pegah Sarraf
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture resistance and volumetric dentin change after management of broken instrument using static navigation – An in vitro study
Shady Atef Adeeb Yassa, Mohamed Nabeel, Ahmed M. Ghobashy, Moataz B. Alkhawas
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 319. CrossRef - Remoção de instrumento fraturado com a técnica do laço: relato de caso
Larissa Sousa Rangel, Ryhan Menezes Cardoso, Thayane Kelly Trajano da Silva, Robeci Alves Macêdo Filho, Andressa Cartaxo de Almeida, Mariana Camilly Tavares Ferreira, Thalles Gabriel Germano Lima, Diana Santana de Albuquerque
Caderno Pedagógico.2025; 22(7): e16332. CrossRef - Would It Necessarily Require Retrieving Endodontic Files on Every Instance? Implementing Separated Files with the Bypass Technique: Report of Three Cases
Mohit S. Zarekar, Apurva S. Satpute, Mohini S. Zarekar
Journal of Primary Care Dentistry and Oral Health.2025; 6(2): 118. CrossRef - Novel electromagnetic device to retrieve fractured stainless steel endodontic files: an in-vitro investigation
Ashraf Mohammed Alhumaidi, Mubashir Baig Mirza, Ahmed A. Alelyani, Raid A. Almnea, Amal S. Shaiban, Ahmed Altuwalah, Riyadh Alroomy, Ahmed Abdullah Al Malwi, Ahmad Jabali, Mohammed M. Al Moaleem
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of Root Canal Treatment Using Loops While Endodontic Treatment: A Clinical Study
Chitharanjan Shetty, Kodithala Sravya, Abhilasha Bhawalkar, Alok Dubey, Tejaswi Kala, Prachi Sethy
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 5): S3735. CrossRef - Efficiency of fractured file retrieval according to different nickel-titanium alloys and fragment lengths
Joon Hyuk Yoon, Yoshitsugu Terauchi, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Broken Instrument Removal Methods with a Minireview of the Literature
Mohsen Aminsobhani, Nasim Hashemi, Fatemeh Hamidzadeh, Pegah Sarraf, Giovanni Mergoni
Case Reports in Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive Assessment of Cyclic Fatigue Strength in Five Multiple-File Nickel–Titanium Endodontic Systems
Jorge N. R. Martins, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Duarte Marques, Francisco M. Braz Fernandes, Marco A. Versiani
Materials.2024; 17(10): 2345. CrossRef - Management of an Intracanal Separated Instrument in the Lower Right First Molar: A Case Report
Pratik Rathod, Aditya Patel, Anuja Ikhar, Manoj Chandak, Joyeeta Mahapatra, Tejas Suryawanshi, Jay Patil, Priti Mahale
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive factors in the retrieval of endodontic instruments: the relationship between the fragment length and location
Ricardo Portigliatti, Eugenia Pilar Consoli Lizzi, Pablo Alejandro Rodríguez
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of two instrument retrieval techniques in removing separated rotary and reciprocating nickel-titanium files in mandibular molars – An in vitro study
S. Jitesh, Smita Surendran, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(12): 1240. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Treatment on Mechanical Properties of Nickel-Titanium Instruments
Eunmi Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Samuel O. Dorn, Ya Shen, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sang Won Kwak
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 213. CrossRef - Efficacy of instrument removal techniques in root canal treatment: a literature review
Rómulo Guillermo López Torres, Jairo Romario Moreno Ochoa, Verónica Alejandra Salame Ortiz
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of the HBW Ultrasonic Ring for retrieval of fragmented manual or rotatory instruments
Jennifer Galván-Pacheco, Verónica Méndez-González, Ana González-Amaro, Heriberto Bujanda-Wong, Amaury Pozos-Guillén, Arturo Garrocho-Rangel
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(4): 278. CrossRef - Retrieving Fragments
Swayangprabha Sarangi, Manoj Ghanshyamdasji Chandak, Kajol Naresh Relan, Payal Sandeep Chaudhari, Pooja Chandak, Anuja Ikhar
Journal of Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences University.2022; 17(2): 429. CrossRef - A novel approach for retrieval of separated endodontic instrument: Two case reports
Tanvi Kohli, Syed Shahid Hilal
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2022; 7(3): 143. CrossRef - A novel endodontic extractor needle for separated instrument retrieval
Saaid Al Shehadat, Colin Alexander Murray, Sunaina Shetty Yadadi
Advances in Biomedical and Health Sciences.2022; 1(2): 116. CrossRef - Present status and future directions: Removal of fractured instruments
Yoshi Terauchi, Wagih Tarek Ali, Mohamed Mohsen Abielhassan
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 685. CrossRef - Ultrasonic Use in Endodontic Management Approach, Review Article
Bakheet Mohammed Al-Ghannam, Khalid Abdulmohsen Almuhrij, Rund Talal Basfar, Raghad Omar Alamoudi, Aseel Mohammed Alqahtani, Ahmed Atef Sait, Ahmed Loay Ghannam, Sultan Khalid Abdoun
World Journal of Environmental Biosciences.2021; 10(1): 61. CrossRef - The Time Taken for Retrieval of Separated Instrument and the Change in Root Canal Volume after Two Different Techniques Using Cbct
Balu Santhosh Kumar, Sridevi Krishnamoorthy, Sandhya Shanmugam, Angambakkam Rajasekharan PradeepKumar
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2021; 32(4): 489. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of success rate and operator variability in loop.based versus ultrasonic retrieval of fractured endodontic instruments: An ex vivo study
- 4,060 View
- 119 Download
- 23 Crossref

-
Cyclic fatigue resistance of M-Pro and RaCe Ni-Ti rotary endodontic instruments in artificial curved canals: a comparative
in vitro study - Hadeer Mostafa El Feky, Khalid Mohammed Ezzat, Marwa Mahmoud Ali Bedier
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e44. Published online November 7, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e44

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
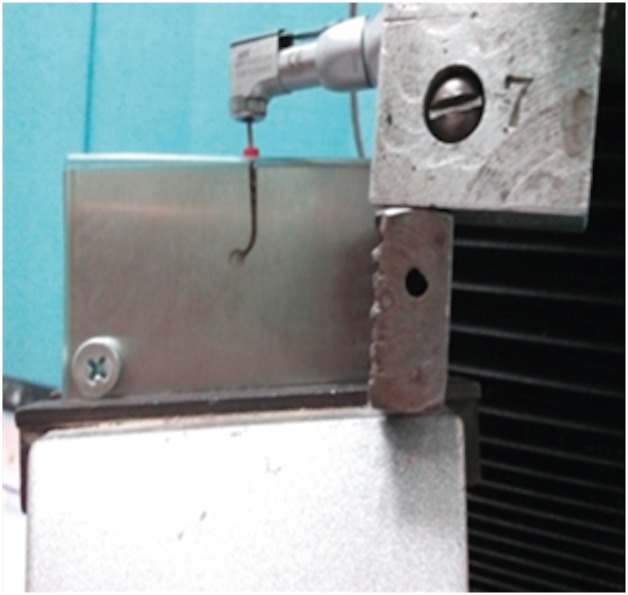
ePub Objectives To compare the flexural cyclic fatigue resistance and the length of the fractured segments (FLs) of recently introduced M-Pro rotary files with that of RaCe rotary files in curved canals and to evaluate the fracture surface by scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
Materials and Methods Thirty-six endodontic files with the same tip size and taper (size 25, 0.06 taper) were used. The samples were classified into 2 groups (n = 18): the M-Pro group (M-Pro IMD) and the RaCe group (FKG). A custom-made simulated canal model was fabricated to evaluate the total number of cycles to failure and the FL. SEM was used to examine the fracture surfaces of the fragmented segments. The data were statistically analyzed and comparisons between the 2 groups for normally distributed numerical variables were carried out using the independent Student's
t -test. Ap value less than 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.Results The M-Pro group showed significantly higher resistance to flexural cyclic fatigue than the RaCe group (
p < 0.05), but there was no significant difference in the FLs between the 2 groups (p ≥ 0.05).Conclusions Thermal treatment of nickel-titanium instruments can improve the flexural cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary endodontic files, and the M-Pro rotary system seems to be a promising rotary endodontic file.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Canal Curvature and Different Manufacturing Processes of Five Different NiTi Rotary Files on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance
Panupat Phumpatrakom, Awiruth Klaisiri, Sukitti Techapatiphandee, Thippawan Saekow, Panuroot Aguilar
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(03): 264. CrossRef - EndoMagic Gold M06 Eğelerinde Boyut ve Konikliğin Döngüsel Yorgunluğa Etkisi: Bir İn Vitro Çalışma
Bircan Kuloğlu, Ayşe Çoban, Hatice Büyüközer Özkan
Akdeniz Diş Hekimliği Dergisi.2025; 4(3): 212. CrossRef - Evaluatation of two nickle-titanium systems’ (Neolix and X Pro Gold) resistance to fracture after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.
Solmaz Araghi, Abbas Delvarani, Faeze dehghan, Parisa Kaghazloo
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 17. CrossRef - Endodontic Ni–Ti Rotary Instruments for Glide-path, Are They Still Necessary and How to Think about the Ideal Instrument?
Shilpa Bhandi, Rodolfo Reda, Luca Testarelli, Elisa Maccari
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(6): 505. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of cyclic fatigue resistance of thermomechanically treated NiTi rotary instruments in simulated curved canals with two different radii of curvature: An in vitro Study
Tahira Hamid, Azhar Malik, Ajay Kumar, Shamim Anjum
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(4): 393. CrossRef - New heat-treated vs electropolished nickel-titanium instruments used in root canal treatment: Influence of autoclave sterilization on surface roughness
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem Barakat, Fatimah Albohairy, Hannes C. Schniepp
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(3): e0265226. CrossRef - The Effect of Taper and Apical Diameter on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Rotary Endodontic Files Using an Experimental Electronic Device
Vicente Faus-Llácer, Nirmine Hamoud Kharrat, Celia Ruiz-Sánchez, Ignacio Faus-Matoses, Álvaro Zubizarreta-Macho, Vicente Faus-Matoses
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(2): 863. CrossRef
- The Effect of Canal Curvature and Different Manufacturing Processes of Five Different NiTi Rotary Files on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance
- 2,300 View
- 10 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Comparison of the shaping ability of novel thermally treated reciprocating instruments
- Cangül Keskin, Murat Demiral, Evren Sarıyılmaz
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e15. Published online March 3, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The present study aimed to evaluate the shaping ability of 2 thermally treated nickel-titanium reciprocating systems in simulated curved canals.
Materials and Methods Forty simulated canals were prepared to apical size 25 using Reciproc Blue R25 (VDW) and WaveOne Gold Primary (Dentsply Sirona) instruments. Standard pre- and post-preparation images were taken and superimposed. The removal of resin material was measured at 5 standard points: the canal orifice, halfway between the canal orifice and the beginning of the curve, the beginning of the curve, the apex of the curve, and the end-point of the simulated canal. The data were analysed using the independent sample
t -test with a 5% significance threshold.Results The canals in which Reciproc Blue R25 was used showed a significantly greater widening than those in which WaveOne Gold was used at 4 of the 5 measurement points (
p < 0.05). The Reciproc Blue R25 instrument removed significantly more resin from the inner aspect of the curve at 2 of the 5 points and similar amounts at the remaining 3 points. At the 2 apical points, there was no significant difference between the Reciproc Blue R25 and WaveOne Gold Primary instruments.Conclusion Both instruments respected the original canal anatomy; however, WaveOne Gold resulted in a more conservative shape with less transportation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Single-File Systems With and Without Glide Path in Extracted Natural Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Indumathi Manoharan, Deblina Basu, Mathan Rajan
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping Ability of the Root Canal System Using Reciproc and Reciproc Blue in Preparation of Artificial Canals
Hawazin Majdi, Khalid Merdad, Tariq Abuhaimed, Lujain Mirdad, Omar Alkhattab, Abdulaziz Bakhsh
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of four different file systems in terms of transportation in S-shaped canals and apically extruded debris
Mustafa Alrahhal, Fatma Tunç
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(4): 226. CrossRef - Assessment of Debris Extrusion in Curved Canals: An In Vitro Analysis of Various Single‐File Endodontic Instrumentation Systems
Muhammad Zubair Ahmad, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping ability of rotary and reciprocating single-file systems in combination with and without different glide path techniques in simulated curved canals
Lu Shi, Yunfei Yang, Jie Wan, Wen Xie, Ruiming Yang, Ying Yao
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(4): 1520. CrossRef - An Investigation of the Accuracy and Reproducibility of 3D Printed Transparent Endodontic Blocks
Martin Smutný, Martin Kopeček, Aleš Bezrouk
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic).2022; 65(2): 59. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of Reciprocating Single-file Systems in Simulated Canals: Reciproc versus Reciproc Blue
İrem ÇETİNKAYA, Mukadder İnci BAŞER KOLCU
SDÜ Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; 28(1): 145. CrossRef - Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Apical extrusion of debris with different rotary and reciprocating single-file endodontic instrumentation systems: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol
Muhammad Zubair Ahmad, Durre Sadaf, Marcy McCall MacBain, Ahmed Nabil Mohamed
BMJ Open.2020; 10(9): e038502. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic assessment of the shaping ability of the One Curve, One Shape, and ProTaper Next nickel-titanium rotary systems
Pelin Tufenkci, Kaan Orhan, Berkan Celikten, Burak Bilecenoglu, Gurkan Gur, Semra Sevimay
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Geometry and Transportation of Root Canals with Severe Curvature Prepared by Different Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Instruments: A Micro–computed Tomographic Study
Daniel José Filizola de Oliveira, Graziela Bianchi Leoni, Rafael da Silva Goulart, Manoel Damião de Sousa-Neto, Yara Teresinha Correa Silva Sousa, Ricardo Gariba Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(6): 768. CrossRef - Several factors can affect the root canal transportation of MB2 canals in extracted maxillary first molars
R. R. Vivan, M. P. Alcalde, E. J de Camargo, V. A. S. Marques, M. V. R. Só, J. A. Duque, M. A. H. Duarte
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(4): 551. CrossRef - Effect of larger apical size on the quality of preparation in curved canals using reciprocating instruments with different heat thermal treatments
J. A. Duque, R. R. Vivan, M. A. H. Duarte, M. P. Alcalde, V. M. Cruz, M. M. B. Borges, C. M. Bramante
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(11): 1652. CrossRef
- Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Single-File Systems With and Without Glide Path in Extracted Natural Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,465 View
- 7 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effect of microleakage of a self-etching primer adhesive according to types of cutting instruments
- Yong-Hee Kim, Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(4):327-334. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.4.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of burs on microleakage of Class V resin restorations when a self-etching primer adhesive was used.
Forty Class V cavities were prepared with four different cutting burs on extracted third molars, and divided into one of four equal groups (n = 10); Group 1-plain cut carbide bur (no. 245), Group 2-cross cut carbide bur (no. 557), Group 3-fine diamond bur (TF-21F), Group 4-standard diamond bur (EX-41).
The occlusal and gingival margin of cavities was located in enamel and dentin, respectively. Cavities were treated with Clearfil SE Bond and restored with Clearfil AP-X. Specimens were thermocycled, immersed in a 2% methylene blue solution for 24 hours, and bisected longitudinally. They were observed leakages at enamel and dentinal margins. Data were analyzed using Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon signed ranked test.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. At enamel margin, microleakage of group 4 was statistically higher than those of group 1, 2 and 3 (p < 0.01).
2. At dentinal margin, microleakage of group 4 was statistically higher than group 3 (p < 0.01), but group 1 and 2 were not statistically different with group 3 and 4.
3. Enamel microleakage was statistically higher than dentinal microleakage in group 1, 2 and 3 (p < 0.05), but statistical difference between the microleakage of enamel and dentinal margin was not in group 4.
In conclusion, the use of coarse diamond bur showed high microleakage at both enamel and dentinal margin when Clearfil SE Bond was used in class V cavity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microshear bond strength of a self-etching primer adhesive to enamel according to the type of bur
Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(6): 477. CrossRef - Effect of cutting instruments on the dentin bond strength of a self-etch adhesive
Young-Gon Lee, So-Ra Moon, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(1): 13. CrossRef
- Microshear bond strength of a self-etching primer adhesive to enamel according to the type of bur
- 1,053 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


