Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Influence of the root canal filling technique on the success rate of primary endodontic treatments: a systematic review
- Daniel Feijolo Marconi, Giovana Siocheta da Silva, Theodoro Weissheimer, Isadora Ames Silva, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Leonardo Thomasi Jahnke, Jovito Adiel Skupien, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e40. Published online October 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
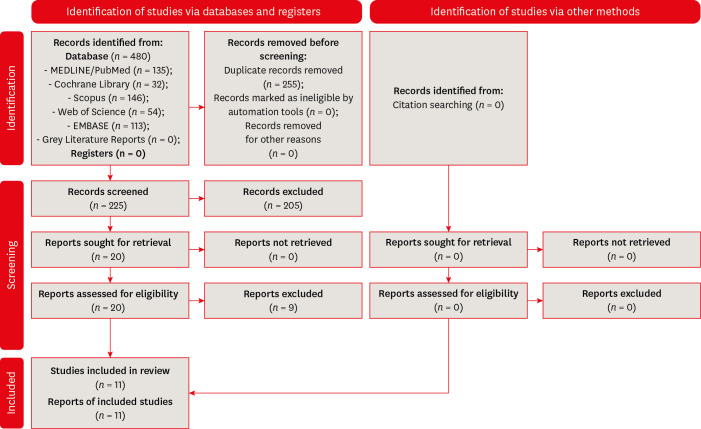
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the influence of different obturation techniques compared to cold lateral compaction on the success rate of primary non-surgical endodontic treatments.
Materials and Methods Systematic searches were performed for studies published up to May 17th, 2022 in MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scopus, EMBASE, and Grey Literature Reports. Randomized clinical trials and nonrandomized (nonrandomized clinical trials, prospective or retrospective) studies that evaluated the success rate of primary non-surgical endodontic treatments obturated with the cold lateral compaction (control) and other obturation techniques were included. The revised Cochrane risk of bias tools for randomized trials (RoB 2) and nonrandomized studies of interventions (ROBINS-I) were used to evaluate the risk of bias. The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) tool was used to evaluate the certainty of evidence.
Results Eleven studies (4 randomized clinical trials (RCTs), 4 prospective, and 3 retrospectives) were included. Two RCTs were classified as having some concerns risk of bias and 2 as a low risk of bias. Two nonrandomized studies were classified as having a critical risk of bias and 5 as having a moderate risk of bias. The GRADE analysis demonstrated a very low to moderate certainty of evidence.
Conclusions This systematic review generally evidenced no differences in the success rate of primary non-surgical endodontic treatments when the cold lateral compaction technique and other obturation techniques are performed. Further well-designed studies are still necessary.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing Sealing Ability of C-Root SP Strontium Silicate Sealer With Different Obturation Techniques: An in vitro Study
Suixin Hu, Jianshe Li, Meng Xu, Laiqing Xu, Yangming Yin, Peng Xue, Liping Dong, Lin Wang, Huixia He, Ying Liu, Qiang Luo, Fei Chen
International Dental Journal.2026; 76(1): 109283. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis Of Obturation Techniques In Endodontics: Lateral Vs. Thermoplasticized. Thermoplasticized
Juan Esteban Díaz Pacheco , Rómulo Guillermo López Torres , Verónica Alejandra Salame Ortíz
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología.2025; 5: 1626. CrossRef - Effect of ultrasonic activation of endodontic sealers on root canal filling quality during the single-cone obturation procedure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory-based studies
Shuting Feng, Weiqing Zhou, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Odontology.2025; 113(4): 1380. CrossRef - In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of a New Experimental Polydimethylsiloxane-Based Endodontic Sealer
Fabiola Cardoso Maldonado, Cesar Gaitan Fonseca, Carlos Bermudez Jimenez, Luis Alejandro Aguilera Galaviz, Margarita L. Martinez-Fierro, Lorena Troncoso Vazquez, Martha Eugenia Reyes Ortiz
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(11): 402. CrossRef - Evaluation of three obturation techniques in 3D-printed models of oval canals with standardized prepared morphology: a micro-CT study
Wenjun Xia, Qisheng Gu, Yingshuang Song, Yunjia Liu, Xuetao Deng, Wenhao Qian
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Radiographic Failure of Nonsurgical Endodontic Treatment and Retreatment Using Single-cone Technique With Calcium Silicate-based Sealers: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Mohammad A. Sabeti, Negah Karimpourtalebi, Arash Shahravan, Omid Dianat
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(6): 735. CrossRef - Method of microbial decontamination of endodontic absorbent paper points: a randomised experimental study
O. A. Pavlovskaya, O. A. Kachanova, V. V. Volobuev, M. N. Mitropanova, A. R. Gazarova, V. Y. Zobenko, A. G. Uvarova
Pediatric dentistry and dental prophylaxis.2024; 24(2): 157. CrossRef - The Push-Out Bond Strength, Surface Roughness, and Antimicrobial Properties of Endodontic Bioceramic Sealers Supplemented with Silver Nanoparticles
Karla Navarrete-Olvera, Nereyda Niño-Martínez, Idania De Alba-Montero, Nuria Patiño-Marín, Facundo Ruiz, Horacio Bach, Gabriel-Alejandro Martínez-Castañón
Molecules.2024; 29(18): 4422. CrossRef - Clinical outcome of non-surgical root canal treatment using different sealers and techniques of obturation in 237 patients: A retrospective study
Mateusz Radwanski, Krystyna Pietrzycka, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Assessing Sealing Ability of C-Root SP Strontium Silicate Sealer With Different Obturation Techniques: An in vitro Study
- 7,066 View
- 103 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Surgical management of an accessory canal in a maxillary premolar: a case report
- Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e30. Published online July 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
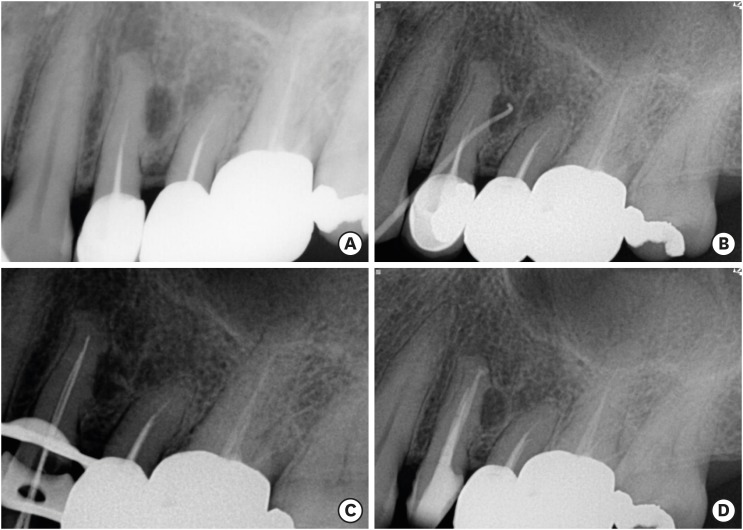
ePub We report the surgical endodontic treatment of a maxillary first premolar with a lateral lesion that originated from an accessory canal. Although lesions originating from accessory canals frequently heal with simple conventional endodontic therapy, some lesions may need additional and different treatment. In the present case, conventional root canal retreatment led to incomplete healing with the need for further treatment (
i.e. , surgery). Surgical endodontic management with a fast-setting calcium silicate cement was performed on the accessory canal using a dental operating microscope. At the patient's 9-month recall visit, the lesion was resolved upon radiography.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictive analysis of root canal morphology in relation to root canal treatment failures: a retrospective study
Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Vishnu Priya Veeraraghavan, P. J. Nagarathna, Sudhir Rama Varma, Jayaraj Kodangattil Narayanan, Santosh R. Patil
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic management of internal replacement resorption of two maxillary central incisors with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography as the diagnostic tool: a case report and review of literature
Fatemeh Eskandari, Safoora Sahebi, Negar Ghorbani Jahandizi, Hossein Mofidi
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Main and Accessory Canal Filling Quality of a Premixed Calcium Silicate Endodontic Sealer According to Different Obturation Techniques
Su-Yeon Ko, Hae Won Choi, E-Deun Jeong, Vinicius Rosa, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2020; 13(19): 4389. CrossRef
- Predictive analysis of root canal morphology in relation to root canal treatment failures: a retrospective study
- 1,671 View
- 17 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Quality of root canal fillings using three gutta-percha obturation techniques
- Edith Siu Shan Ho, Jeffrey Wen Wei Chang, Gary Shun Pan Cheung
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):22-28. Published online January 4, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
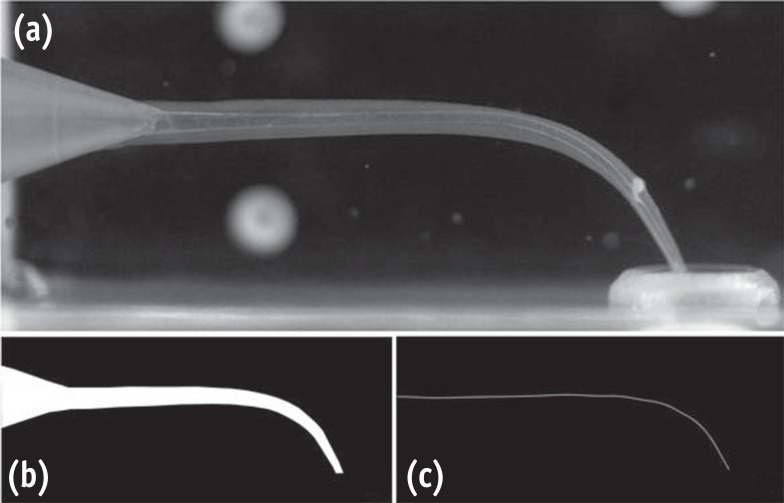
ePub Objectives The goal of this study was to compare the density of gutta-percha root fillings obturated with the following techniques: cold lateral (CL) compaction, ultrasonic lateral (UL) compaction, and warm vertical (WV) compaction.
Materials and Methods Thirty-three extracted mandibular first molars, with two separate mesial canals in each, were selected. After instrumentation, the canals were stratified into three groups based on canal length and curvature, and underwent obturation with one of the techniques. No sealer was used in order to avoid masking any voids. The teeth were imaged pre- and post-obturation using micro-computed tomography. The reconstructed three-dimensional images were analyzed volumetrically to determine the amount of gutta-percha present in every 2 mm segment of the canal.
P values < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.Results The overall mean volume fraction of gutta-percha was 68.51 ± 6.75% for CL, 86.56 ± 5.00% for UL, and 88.91 ± 5.16% for WV. Significant differences were found between CL and UL and between CL and WV (
p < 0.05), but not between UL and WV (p = 0.526). The gutta-percha density of the roots treated with WV and UL increased towards the coronal aspect, but this trend was not noted in the CL group.Conclusions WV compaction and UL compaction produced a significantly denser gutta-percha root filling than CL compaction. The density of gutta-percha was observed to increase towards the coronal aspect when the former two techniques were used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of quality of radiographs taken during root canal treatment on technical quality of root canal fillings and endodontic outcome
Jia Min Ng, Yan Yee Lee, Prashanti Chippagiri, Elaheh Ahanin, Abhishek Parolia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(1): e3. CrossRef - Restorative and endodontic clinical strategies during COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic: a revision of the literature
Manuele MANCINI, Flavio PALAZZI, Francesco IACONO
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the tubular penetration of two different types of nanoparticle root canal sealers over apically separated files: a scanning electron microscopic study (in vitro study)
Alaa H. Nagdi, Nayera A. Mokhless, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Different strategies for treating intracanal fractured instruments in a single tooth: A case report
Rong Chai, Xinpei Jiang, Ruixia Ma, Qiang Zhang, E Yang, Ansheng Zhang
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An Experimental Anatomic CBCT Study on the Correlations Between MB1 and MB2 of the Mesio-Vestibular Root of the Upper First Molars
Luca Fiorillo, Cesare D’Amico, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Francesco Calanna, Alfio Pappalardo, Eugenio Pedullà
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2024; 35(2): 672. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Different Obturation Techniques for Root Canal Filling of Permanent Teeth: An In-Vitro Study
Adhishree S Chib, Neeta S Padmawar, Sonali Waghmare, Durgesh A Tiwari, Shahinwaz Mulani, Megna Bhatt
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Root canal treatment of a rhizomegaly tooth 36 mm long right permanent maxillary canine – A case report
Anita Kapri, Kiran Reddy, Varun Rana, Oliver Jacob, Pushpa Kumari
IP Annals of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 10(1): 59. CrossRef - Thermal and volumetric assessment of endodontic filling techniques using infrared thermography and micro-CT
Fernanda Clotilde M. Suassuna, Débora Ketley M. de Araújo, Ana Marly A. M. Amorim, Saulo Leonardo S. Melo, Richard J. Heck, Antonio Celso D. Antonino, Patrícia M. Bento, Diego Filipe B. Silva, Daniela P. de Melo
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(1): 34. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Efficacy of Various Obturating Techniques for the Presence of Voids
Rehan Ahmad Khan, Shailja Singh, Shazia Siddiqui, Mariyam Khan, Arfat Ahmad, Parul Shakarwal
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2023; 15(Suppl 2): S895. CrossRef - Influence of the root canal filling technique on the success rate of primary endodontic treatments: a systematic review
Daniel Feijolo Marconi, Giovana Siocheta da Silva, Theodoro Weissheimer, Isadora Ames Silva, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Leonardo Thomasi Jahnke, Jovito Adiel Skupien, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Current trends in bio‐based elastomer materials
Shuai Tang, Jiao Li, Runguo Wang, Jichuan Zhang, Yonglai Lu, Guo‐Hua Hu, Zhao Wang, Liqun Zhang
SusMat.2022; 2(1): 2. CrossRef - Carrier-Based Obturation: Effect of Sonication Technique on Sealer Penetration in Dentinal Tubules: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope Study
Riccardo Tonini, Matteo Salvadori, Marco Bartoli, Jacopo Francinelli, Paolo Bertoletti, Maria Luisa Garo, Stefano Salgarello
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(17): 8877. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - The effect of two endodontic sealers and interval before post-preparation and cementation on the bond strength of fiber posts
He Yuanli, Wu Juan, Ji Mengzhen, Chen Xuan, Xiong Kaixin, Yang Xueqin, Qiao Xin, Hu Hantao, Gao Yuan, Zou Ling
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(11): 6211. CrossRef - Complete Obturation—Cold Lateral Condensation vs. Thermoplastic Techniques: A Systematic Review of Micro-CT Studies
Shilpa Bhandi, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Abdulaziz S. Abumelha, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Mohamed Jamal, Hitesh Chohan, A. Thirumal Raj, Luca Testarelli, Rodolfo Reda, Shankargouda Patil
Materials.2021; 14(14): 4013. CrossRef - Root canal filling quality of mandibular molars with EndoSequence BC and AH Plus sealers: A micro‐CT study
Rafael Nigri Roizenblit, Fabiola Ormiga Soares, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Heloisa Gusman
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(1): 82. CrossRef - Effect of four different root canal obturation techniques on marginal adaptation of bioceramic sealer: An in vitro scanning electron microscopic study
NawalA Al-Sabawi, MahaM Yahya, NjwanF Shehab
Journal of International Oral Health.2020; 12(5): 455. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantification of the tug-back by measuring the pulling force and micro computed tomographic evaluation
Su-Jin Jeon, Young-Mi Moon, Min-Seock Seo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 273. CrossRef
- Effect of quality of radiographs taken during root canal treatment on technical quality of root canal fillings and endodontic outcome
- 2,792 View
- 30 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Management of apicomarginal defect in esthetic region associated with a tooth with anomalies
- Vinayak Venkoosa Meharwade, Dipali Yogesh Shah, Pradyna Prabhakar Mali, Vidya Vinayak Meharwade
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):314-321. Published online June 24, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.314
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Tooth related factors such as palatoradicular groove can be one of the causes for localized periodontal destruction. Such pathological process may result in apicomarginal defect along with inflammation of pulp. This creates challenging situation which clinician must be capable of performing advanced periodontal regenerative procedures for the successful management. This case report discusses clinical management of apicomarginal defect associated with extensive periradicular destruction in a maxillary lateral incisor, along with histopathologic aspect of the lesion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical treatment of apico-marginal defect associated with maxillary incisor teeth with a large periapical lesion using sticky bone & platelet rich fibrin membrane – A case report
Snigdho Das, Parthasarathi Mondal, Dipanjan Das, Kurchi Mandal, Kallol Kumar Saha
IP Annals of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 10(3): 250. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of sticky bone with guided tissue regeneration and platelet-rich fibrin membranes in healing of apicomarginal defects with periapical pathology: An in-vivo study
D. Das, P. Mondal, K. K. Saha, S. Das, D. Karmakar, A. Bhagawati
Endodontics Today.2024; 22(4): 335. CrossRef
- Surgical treatment of apico-marginal defect associated with maxillary incisor teeth with a large periapical lesion using sticky bone & platelet rich fibrin membrane – A case report
- 1,456 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Surgical endodontic management of infected lateral canals of maxillary incisors
- Ji-Hyun Jang, Jung-Min Lee, Jin-Kyu Yi, Sung-Baik Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):79-84. Published online October 10, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.79
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This case report presents surgical endodontic management outcomes of maxillary incisors that were infected via the lateral canals. Two cases are presented in which endodontically-treated maxillary central incisors had sustained lateral canal infections. A surgical endodontic treatment was performed on both teeth. Flap elevation revealed vertical bone destruction along the root surface and infected lateral canals, and microscopy revealed that the lateral canals were the origin of the lesions. After the infected lateral canals were surgically managed, both teeth were asymptomatic and labial fistulas were resolved. There were no clinical or radiographic signs of surgical endodontic management failure at follow-up visits. This case report highlights the clinical significance and surgical endodontic management of infected lateral canal of maxillary incisor. It is important to be aware of root canal anatomy variability in maxillary incisors. Maxillary central incisors infected via the lateral canal can be successfully managed by surgical endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical Management of Radicular Cyst with Platelet-rich Fibrin Placement followed by Nonvital Bleaching of a Discolored Maxillary Left Central Incisor (21)
Sagarika Sortey, Gautam Badole, Pratima Shenoi, Rajesh Kubde, Shriya Shahu, Ankita Ramteke, Varsha Uttarwar
Bharati Vidyapeeth Journal of Dentistry and Allied Sciences.2025; 2(1): 31. CrossRef - Apical Surgery of a Maxillary Left Central Tooth Using NeoPutty After Retreatment Failure: A Case Report
Sajedeh Namaei Ghasemi, Zakieh Kheradmand, Siavash Moushekhian, Zeinab Ghasemi
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone Beam Computed Tomography as a Diagnostic Tool in the Diagnosis of an Iatrogenic Root Defect of a Root Canal Treated Maxillary Central Incisor with Periapical Lesion and Its Management by Re-apicectomy
Swathi Aravelli, Uday Kumar, Gunnam Sai Nishitha, K. Mallika Yadav, P. Sivaram, Nimeshika Ramachandruni
Bharati Vidyapeeth Journal of Dentistry and Allied Sciences.2025; 2(4): 155. CrossRef - On the Causes of Persistent Apical Periodontitis. Findings From Endodontic Microsurgery: A Case Report
Mateo José Pesántez-Ibarra, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco, Jeimmy Katherine Molina-Barrera, Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Rafael Fernández-Grisales
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Expert consensus on difficulty assessment of endodontic therapy
Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Jingping Liang, Junqi Ling, Zhuan Bian, Qing Yu, Benxiang Hou, Xinmei Chen, Jiyao Li, Ling Ye, Lei Cheng, Xin Xu, Tao Hu, Hongkun Wu, Bin Guo, Qin Su, Zhi Chen, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Zhengwei Huang, Jinhua Yu, Zhen
International Journal of Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical endodontic treatment of maxillary incisors: Case report
Moazzy I. Almansour
Clinical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Resective and Regenerative Approach for an Unresolved Periapical Lesion: A Surgical Case Report With 24-Month Follow-Up
Anchu R Thomas, Melwin Mathew, Sunil K Nettemu, Anoop Mayya
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An in vitro endodontic model to quantify the accessory canal filling potential of the vertical and lateral condensation techniques
Thomas Gerhard Wolf, Louisa Willems, Benjamín Briseño‐Marroquín
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(2): 245. CrossRef - Application of a new system for classifying root and canal anatomy in studies involving micro‐computed tomography and cone beam computed tomography: Explanation and elaboration
H. M. A. Ahmed, N. Ibrahim, N. S. Mohamad, P. Nambiar, R. F. Muhammad, M. Yusoff, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(7): 1056. CrossRef - German Dentists’ Preferences for the Treatment of Apical Periodontitis: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Jonas Conrad, Jan Retelsdorf, Sameh Attia, Christof Dörfer, Mohamed Mekhemar
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7447. CrossRef - Surgical management of an accessory canal in a maxillary premolar: a case report
Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A new system for classifying accessory canal morphology
H. M. A. Ahmed, P. Neelakantan, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 164. CrossRef - Effects of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy and surgical endodontic treatment on the bacterial load reduction and periapical lesion healing. Three years follow up
Aguinaldo S. Garcez, Julio G. Arantes-Neto, Debora P. Sellera, Eduardo Rodrigues Fregnani
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2015; 12(4): 575. CrossRef
- Surgical Management of Radicular Cyst with Platelet-rich Fibrin Placement followed by Nonvital Bleaching of a Discolored Maxillary Left Central Incisor (21)
- 1,955 View
- 14 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
- Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):253-257. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.253
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Maxillary lateral incisors usually exhibit a single root with a single canal. However, maxillary lateral incisor teeth with unusual morphology of root canal system are frequently reported. These cases of variable root canal anatomy can be treated well by nonsurgical endodontic methods. A detailed description of root canal morphology is fundamental for successful endodontic treatment. Treatment using an operating microscope, radiographs from different angles, and cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT) can produce more predictable endodontic outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An upper left lateral incisor with double roots and double root canals: A case report
Zhou-Bin Xia, Jing Ren, Jia-Xiang Chen, Yu Wei, Yan Yan, Liang-Ju Cao
Medicine.2025; 104(26): e42815. CrossRef - Retreatment of Mandibular Incisors Associated With Root Canal Variations and Periapical Cyst: A Case Report With 3‐Year Follow‐Up
Kai Chen, Ni Li
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodnontic Management of a Maxillary Lateral Incisor with Two Roots
Pujan Kranti Kayastha, Merina Shakya, Laxman Poudel
Journal of Interdisciplinary Dentistry.2022; 12(1): 32. CrossRef - Non-surgical management of dens invaginatus type IIIB in maxillary lateral incisor with three root canals and 6-year follow-up: A case report and review of literature
Suraj Arora, Gurdeep Singh Gill, Shahabe Abullais Saquib, Priyanka Saluja, Suheel M Baba, Shafait Ullah Khateeb, Anshad M Abdulla, Shashit Shetty Bavabeedu, Ahmed Babiker Mohamed Ali, Mohamed Fadul A Elagib
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(33): 12240. CrossRef - Endodontic management and follow-up of two rooted maxillary lateral incisor with open apex – A case report
R AnithaKumari, Sneha Jeetendra, Siddharth Rai, Sudhanva Eregowda
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2020; 5(4): 200. CrossRef - Geminated Maxillary Lateral Incisor with Two Root Canals
Nayara Romano, Luis Eduardo Souza-Flamini, Isabela Lima Mendonça, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Antonio Miranda Cruz-Filho
Case Reports in Dentistry.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Surgical management with intentional replantation on a tooth with palato-radicular groove
Jorge Forero-López, Luis Gamboa-Martínez, Laura Pico-Porras, Javier Laureano Niño-Barrera
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 166. CrossRef - Use of cone-beam computed tomography and three-dimensional modeling for assessment of anomalous pulp canal configuration: a case report
Alper Sinanoglu, Dilek Helvacioglu-Yigit, Ibrahim Mutlu
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 161. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report
Rosaline Hannah, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Nachimuthu Jayaprakash
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 132. CrossRef
- An upper left lateral incisor with double roots and double root canals: A case report
- 3,188 View
- 28 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Treatment of a lateral incisor anatomically complicated with palatogingival groove
- Moon-Sun Choi, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):238-242. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.238
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Palatogingival groove is a developmental anomaly that starts near the cingulum of the tooth and runs down the cementoenamel junction in apical direction, terminating at various depths along the roots. While frequently associated with periodontal pockets and bone loss, pulpal necrosis of these teeth may precipitate a combined endodontic-periodontal lesion. This case presents a case of a lateral incisor anatomically complicated with palatogingival groove.
Methods Two patients with lesion associated with the palatogingival groove were chosen for this report. Palatogingival grooves were treated with different restoration materials with endodontic treatment.
Conclusions Maxillary lateral incisor with a palatogingival groove may occur the periodontal disease with pulpal involvement. Elimination of groove may facilitate the periodontal re-attachment and prevent the recurrence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 253. CrossRef
- Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
- 1,154 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The role of Type 2 Diabetes as a predisposing risk factor on the pulpo-periapical pathogenesis: review article
- Jin-Hee Kim, Kwang-shik Bae, Deog-Gyu Seo, Sung-Tae Hong, Yoon Lee, Sam-Pyo Hong, Kee-Yeon Kum
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):169-176. Published online May 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a syndrome accompanied with the abnormal secretion or function of insulin, a hormone that plays a vital role in controlling the blood glucose level (BGL). Type 1and 2 DM are most common form and the prevalence of the latter is recently increasing. The aim of this article was to assess whether Type 2 DM could act as a predisposing risk factor on the pulpo-periapical pathogenesis. Previous literature on the pathologic changes of blood vessels in DM was thoroughly reviewed. Furthermore, a histopathologic analysis of artificially-induced periapical specimens obtained from Type 2 diabetic and DM-resistant rats was compared. Histopathologic results demonstrate that the size of periapical bone destruction was larger and the degree of pulpal inflammation was more severe in diabetic rats, indicating that Type 2 DM itself can be a predisposing risk factor that makes the host more susceptible to pulpal infection. The possible reasons may be that in diabetic state the lumen of pulpal blood vessels are thickened by atheromatous deposits, and microcirculation is hindered. The function of polymorphonuclear leukocyte is also impaired and the migration of immune cells is blocked, leading to increased chance of pulpal infection. Also, lack of collateral circulation of pulpal blood vessels makes the pulp more susceptible to infection. These decrease the regeneration capacity of pulpal cells or tissues, delaying the healing process. Therefore, when restorative treatment is needed in Type 2 DM patients, dentists should minimize irritation to the pulpal tissue un der control of BGL.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pulp necrosis following luxated injury to teeth in a patient with uncontrolled type II diabetes mellitus: a case report
Haneol Shin, Seung-Jong Lee, Il-Young Jung, Chan-Young Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 61. CrossRef
- Pulp necrosis following luxated injury to teeth in a patient with uncontrolled type II diabetes mellitus: a case report
- 1,190 View
- 12 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Microleakage of resilon: Effects of several self-etching primer
- Jong-Hyeon O, Se-Hee Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(2):133-140. Published online March 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.2.133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the apical microleakage in root canal filled with Resilon by several self-etching primers and methacrylate-based root canal sealer. Seventy single-rooted human teeth were used in this study. The canals were instrumented by a crown-down manner with Gate-Glidden drills and .04 Taper Profile to ISO #40. The teeth were randomly divided into four experimental groups of 15 teeth each according to root canal filling material and self-etching primers and two control groups (positive and negative) of 5 teeth each as follows: group 1 - gutta percha and AH26® sealer; group 2 - Resilon, RealSeal™ primer and RealSeal™ sealer; group 3 - Resilon, Clearfil SE Bond® primer and RealSeal™ sealer group 4 - Resilon, AdheSe® primer and RealSeal™ sealer. Apical leakage was measured by a maximum length of linear dye penetration of roots sectioned longitudinally by diamond disk. Statistical analysis was performed using the One-way ANOVA followed by Scheffe's test. There were no statistical differences in the mean apical dye penetration among the groups 2, 3 and 4 of self-etching primers. And group 1, 2 and 3 had also no statistical difference in apical dye penetration. But, there was statistical difference between group 1 and 4 (p < 0.05). The group 1 showed the least dye penetration. According to the results of this study, Resilon with self-etching primer was not sealed root canal better than gutta precha with AH26® at sealing root canals. And there was no significant difference in apical leakage among the three self-etching primers.
- 799 View
- 1 Download

- Obturation efficiency of non-standardized gutta-percha cone in curved root canals prepared with 0.06 taper nickel-titanium instruments
- Eun-Ah Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(2):79-85. Published online March 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.2.079
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the obturation efficiency of a non-standardized gutta-percha cone in curved root canals prepared with 0.06 taper nickel-titanium instruments.
Sixty simulated curved root canals in clear resin blocks were prepared with crown-down technique using 0.06 taper rotary ProTaper™ and ProFile (Dentsply-Maillefer) until apical canal was size 30. Root canals were randomly divided into 4 groups of 15 blocks and obturated with cold-laterally compacted gutta-percha technique by using either a non-standardized size medium gutta-percha cone or an ISO-standardized size 30 one as a master cone. Gutta-percha area ratio were calculated at apical levels of 1, 3, and 5 mm using AutoCAD 2000 after cross-sectioning, and the data were analyzed with one-way and two-way ANOVAs and Duncan's multiple range test.
Non-standardized size medium cone groups showed significantly higher gutta-percha area ratio than standardized cone groups at all apical levels (
p < 0.01).Non-standardized cone groups used significantly less accessory cones than standardized cone groups (
p < 0.01).-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficiency of Using Different Greater Taper Gutta-Percha Cones in Continuous Warm Vertical Condensation: An Ex Vivo Study
Mamata Hebbal, Reem Barakat, Rahaf Almohareb, Ghada Alaskar, Lama Alghufaily, Nouf AlFarraj, Alia Albaz
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(1): 56. CrossRef
- Efficiency of Using Different Greater Taper Gutta-Percha Cones in Continuous Warm Vertical Condensation: An Ex Vivo Study
- 1,794 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of plugger penetration depth on the apical extrusion of root canal sealer in Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique
- Ho-Young So, Young-Mi Lee, Kwang-Keun Kim, Ki-Ok Kim, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(5):439-445. Published online January 14, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.439
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of plugger penetration depth on the apical extrusion of root canal sealer during root canal obturation with Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique.
Root canals of forty extracted human teeth were divided into four groups and were prepared up to size 40 of 0.06 taper with ProFile. After drying, canals of three groups were filled with Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique with System B™ and different plugger penetration depths of 3, 5, and 7 mm from the apex. Canals of one group were filled with cold lateral compaction technique as a control. Canals were filled with non-standardized master gutta-percha cones and 0.02 mL of Sealapex. Apical extruded sealer was collected in a container and weighed. Data was analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Duncan’s Multiple Range Test. 3 and 5 mm penetration depth groups in Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique showed significantly more extrusion of root canal sealer than 7 mm penetration depth group (
p < 0.05). However, there was no significant difference between 7 mm depth group in Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique and cold lateral compaction group (p < 0.05).The result of this study demonstrates that deeper plugger penetration depth causes more extrusion of root canal sealer in root canal obturation by Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique. Therefore, special caution is needed when plugger penetration is deeper in the canal in Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique to minimize the amount of sealer extrusion beyond apex.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of plugger penetration depth on the area of the canal space occupied by gutta-percha
Young Mi Lee, Ho-young So, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 66. CrossRef
- Influence of plugger penetration depth on the area of the canal space occupied by gutta-percha
- 1,411 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


