Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Comparison of remineralization in caries-affected dentin using calcium silicate, glass ionomer cement, and resin-modified glass ionomer cement: an in vitro study
- Kwanchanok Youcharoen, Onwara Akkaratham, Papichaya Intajak, Pipop Saikaew, Sirichan Chiaraputt
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e37. Published online November 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study evaluated the ability of calcium silicate cement (CSC) as a remineralizing agent compared with conventional glass ionomer cement (GIC) and resin-modified GIC (RMGIC) to remineralize artificial caries-affected dentin.
Methods
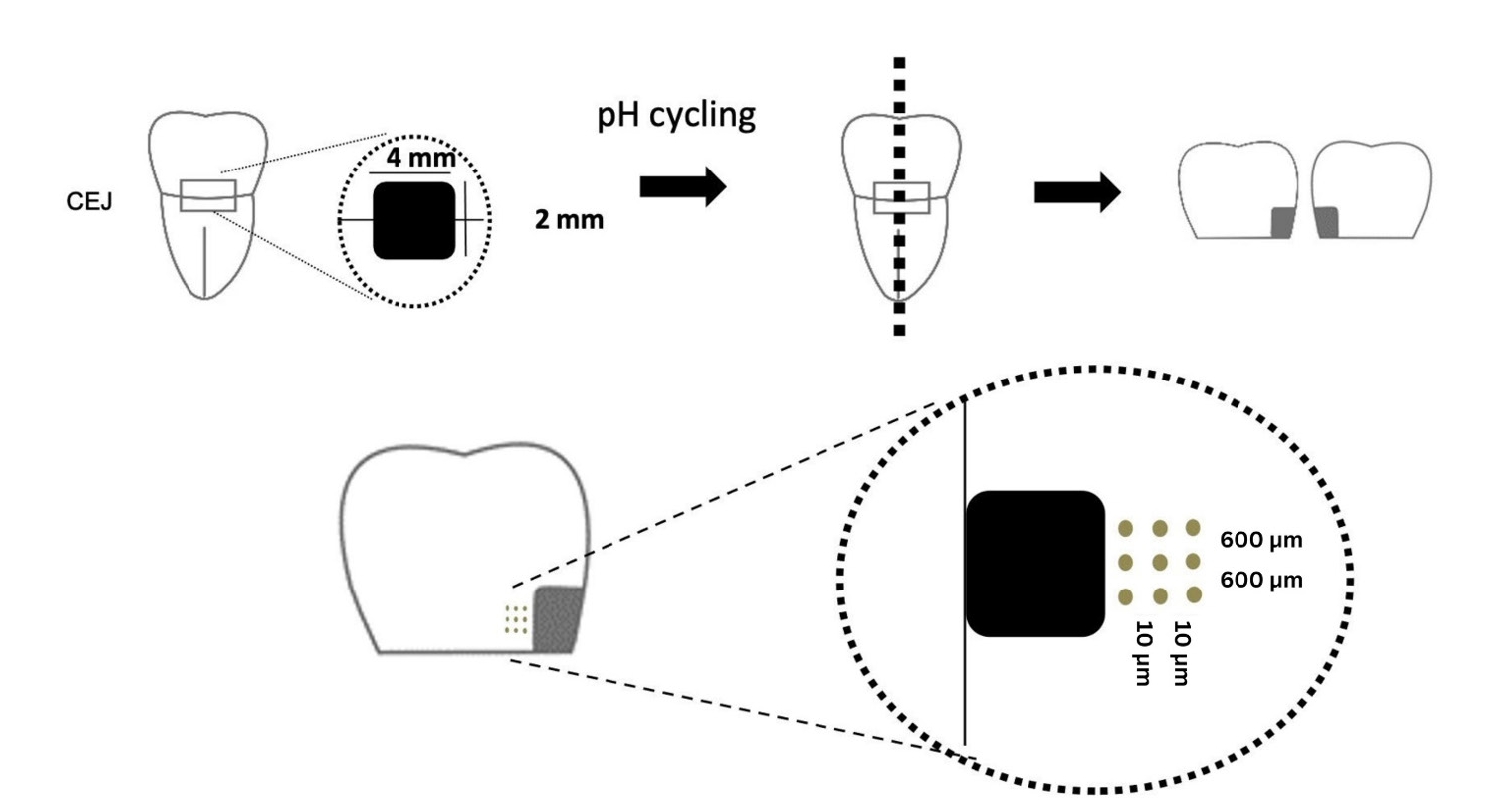
Twenty-five class V cavities were prepared on extracted human third molars. Twenty teeth underwent artificial caries induction. The remaining five teeth with sound dentin serve as the positive control. The twenty demineralized teeth were subdivided into four groups (n = 5): carious dentin without restoration (negative control [NC]), carious dentin restored with CSC (Biodentine, Septodont), carious dentin restored with GI (Fuji IX, GC Corporation), and carious dentin restored with RMGIC (Fuji II LC, GC Corporation). Following restoration, the specimens were stored in artificial saliva for 7 days. The elastic modulus was evaluated by a nanoindentation test. The mineral composition was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX), and the mineral composition at the dentin-material interface.
Results
CSC had a higher modulus of elasticity compared to GI, RMGI, and NC groups (p < 0.05). Higher calcium and phosphorus content was observed under CSC restorations, as indicated by SEM-EDX examination, which may lead to better remineralization.
Conclusions
Compared to GI and RMGI, CSC showed the best remineralization and mechanical reinforcement in caries-affected dentin, indicating CSC for use in minimally invasive restorative dentistry.
- 1,806 View
- 213 Download

- Effects of dentin surface preparations on bonding of self-etching adhesives under simulated pulpal pressure
- Chantima Siriporananon, Pisol Senawongse, Vanthana Sattabanasuk, Natchalee Srimaneekarn, Hidehiko Sano, Pipop Saikaew
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e4. Published online December 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of different smear layer preparations on the dentin permeability and microtensile bond strength (µTBS) of 2 self-etching adhesives (Clearfil SE Bond [CSE] and Clearfil Tri-S Bond Universal [CTS]) under dynamic pulpal pressure.
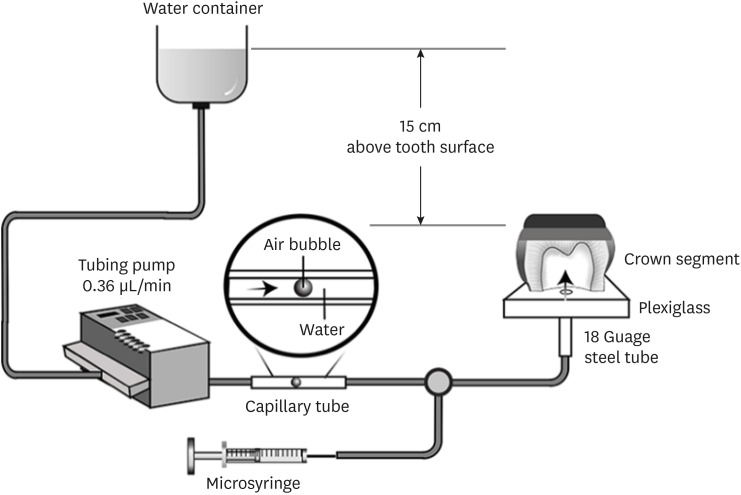
Materials and Methods Human third molars were cut into crown segments. The dentin surfaces were prepared using 4 armamentaria: 600-grit SiC paper, coarse diamond burs, superfine diamond burs, and carbide burs. The pulp chamber of each crown segment was connected to a dynamic intra-pulpal pressure simulation apparatus, and the permeability test was done under a pressure of 15 cmH2O. The relative permeability (%P) was evaluated on the smear layer-covered and bonded dentin surfaces. The teeth were bonded to either of the adhesives under pulpal pressure simulation, and cut into sticks after 24 hours water storage for the µTBS test. The resin-dentin interface and nanoleakage observations were performed using a scanning electron microscope. Statistical comparisons were done using analysis of variance and
post hoc tests.Results Only the method of surface preparation had a significant effect on permeability (
p < 0.05). The smear layers created by the carbide and superfine diamond burs yielded the lowest permeability. CSE demonstrated a higher µTBS, with these values in the superfine diamond and carbide bur groups being the highest. Microscopic evaluation of the resin-dentin interface revealed nanoleakage in the coarse diamond bur and SiC paper groups for both adhesives.Conclusions Superfine diamond and carbide burs can be recommended for dentin preparation with the use of 2-step CSE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of different adhesive strategies and diamond burs on dentin bond strength of universal resin cements
Chavakorn Atsavathavornset, Pipop Saikaew, Choltacha Harnirattisai, Hidehiko Sano
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Universal adhesive systems in dentistry: A narrative review
Svetlana N. Razumova, Anzhela S. Brago, Oxana R. Ruda, Zoya A. Guryeva, Elvira V. Adzhieva
Russian Journal of Dentistry.2024; 28(5): 512. CrossRef - Delayed light activation of resin composite affects the bond strength of adhesives under dynamic simulated pulpal pressure
Nattaporn Sukprasert, Choltacha Harnirattisai, Pisol Senawongse, Hidehiko Sano, Pipop Saikaew
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(11): 6743. CrossRef
- The effect of different adhesive strategies and diamond burs on dentin bond strength of universal resin cements
- 3,094 View
- 48 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


