Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Pulp stones: any relevance with the levels of serum calcium, parathyroid hormone, vitamin D and uric acid
- Ceyda Gürhan, Ercan Saruhan
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e17. Published online March 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of serum calcium, parathyroid hormone (PTH), vitamin D, and uric acid levels on pulp stone formation.
Materials and Methods Patients who were admitted to the Muğla Sıtkı Koçman University, Faculty of Dentistry, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology for dental complaints were registered. Among these patients, individuals who had routine biochemical tests at the same period in the Outpatient Clinics of Muğla Sıtkı Koçman University Training and Research Hospital were included in the study. The patients with at least 1 pulp stone on panoramic radiographs recorded as the “pulp stone group” while patients without any pulp stones were the “control group”. Demographic data and serum levels of calcium, PTH, vitamin D, and uric acid were retrospectively evaluated in both groups. Student
t -test or Mann-WhitneyU test was used to evaluate the differences between the groups.Results Among 151 patients, dental pulp stone was detected in 53.6% of patients, and 82.7% of these patients were female. Female sex and pulp stone formation were significantly associated (
p = 0.001). The mean age of the pulp stone group was 43.9, while it was 39.9 in the control group, without any significant correlation between age and pulp stone (p > 0.05). Similarly, there were no significant differences in serum levels of PTH, vitamin D, uric acid and calcium between groups (p > 0.05).Conclusions According to the present study, the effect of dental factors rather than systemic factors should be considered primarily in pulp stone formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A novel deep learning-based pipeline architecture for pulp stone detection on panoramic radiographs
Ceyda Gürhan, Hasan Yiğit, Selim Yılmaz, Cihat Çetinkaya
Oral Radiology.2025; 41(2): 285. CrossRef - Vitamin D deficiency and oral health: a systematic review of literature
Saida Ziada, Aws Wishahe, Najet Mabrouk, Souad Sahtout
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between pulp stones and systemic diseases: a retrospective study using digital panoramic radiographs in a Turkish population
Buket Beytaş Alğan, Mustafa Murat Koçak, Sibel Koçak, Baran Can Sağlam
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- A novel deep learning-based pipeline architecture for pulp stone detection on panoramic radiographs
- 3,667 View
- 104 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Evaluation of the relation between the pulp stones and direct restorations using cone beam computed tomography in a Turkish subpopulation
- Güzide Pelin Sezgin, Sema Sönmez Kaplan, Tuna Kaplan
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e34. Published online June 8, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
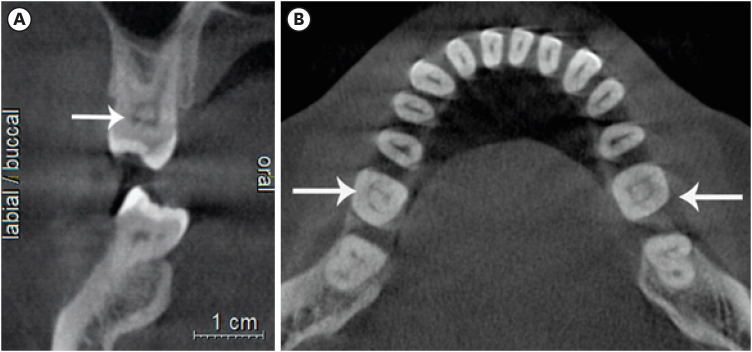
ePub Objectives This study aimed to assess the presence of pulp stones through an examination of cone beam computed tomography images and correlate their prevalence with age, sex, dental arch and side, tooth type, and restoration type and depth.
Materials and Methods Cone beam computed tomography images obtained from 673 patients and archival data on 11,494 teeth were evaluated. The associations of pulp stones with age, sex, dental arch and side, tooth type, and restoration type and depth were noted. All the measurements were subjected to a χ2 test and one sample χ2 test (
p < 0.05).Results In the study group, 163 (24.2%) patients and 379 (3.3%) teeth had at least one pulp stone. The pulp stone frequency in those aged 30–39 years was significantly greater than in those aged 18–29 and ≥ 60 years, and the frequency was higher in females than in males (
p < 0.05). The highest prevalence of pulp stones was found in maxillary dental arches and molar teeth (p < 0.05). Pulp stones were significantly more common in medium-depth restorations (p < 0.05).Conclusions Maxillary molar teeth, medium-depth restorations, individuals aged 30–39 years and females had a greater percentage of pulp stones.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Assessment of the Prevalence and Association of Pulp Calcification with Dental and Periodontal Pathology: A Descriptive Study
José Luis Sanz, Lucía Callado, Stefana Mantale, Jenifer Nicolás, James Ghilotti, Carmen Llena
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(4): 1373. CrossRef - Prevalence of mineralization in the pulp chamber in patients according to CBCT data
V. A. Molokova, I. N. Antonova, V. A. Osipova
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(2): 188. CrossRef - Could carotid artery calcifications and pulp stones be an alarm sign for diabetes mellitus? A retrospective observational study
Motahare Baghestani, Mohadese Faregh, Seyed Hossein Razavi, Fatemeh Owlia
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Distribution and influencing factors of pulp stones based on CBCT: a retrospective observational study from southwest China
Wantong Zhang, Yao Wang, Lin Ye, Yan Zhou
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Association of Calcified Pulp Stones with Periodontitis: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study in Saudi Arabian Population
Abdullah Saad Alqahtani
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 1): S644. CrossRef - The Prevalence And Distribution Of Pulp Stones: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study İn A Group Of Turkish Patients
Mujgan Firincioglulari, Seçil Aksoy, Melis Gülbeş, Umut Aksoy, Kaan Orhan
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2024; 13(3): 496. CrossRef - Radiographical examination of pulp stone distribution by cone beam computed tomography
Fatma Tunç, Emre Çulha, Muazzez Naz Baştürk
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2024; 7(4): 472. CrossRef - Cone-Beam Computed Tomography-Based Investigation of the Prevalence and Distribution of Pulp Stones and Their Relation to Local and Systemic Factors in the Makkah Population: A Cross-Sectional Study
Laila M Kenawi, Haytham S Jaha, Mashael M Alzahrani, Jihan I Alharbi, Shahad F Alharbi, Taif A Almuqati, Rehab A Alsubhi, Wahdan M Elkwatehy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone beam computed tomography assessment of the prevalence and association of pulp calcification with periodontitis
Lingling Xiang, Botao Wang, Yuan Zhang, Jintao Wang, Peipei Wu, Jian Zhang, Liangjun Zhong, Rui He
Odontology.2023; 111(1): 248. CrossRef - Three-dimensional analysis for detection of pulp stones in a Saudi population using cone beam computed tomography
Hassan H. Kaabi, Abdullah M. Riyahi, Nassr S. Al-Maflehi, Saleh F. Alrumayyan, Abdullah K. Bakrman, Yazeed A. Almutaw
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(4): 257. CrossRef
- Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Assessment of the Prevalence and Association of Pulp Calcification with Dental and Periodontal Pathology: A Descriptive Study
- 2,247 View
- 26 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


