Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Radiographic patterns of periosteal bone reactions associated with endodontic lesions
- Poorya Jalali, Jessica Riccobono, Robert A. Augsburger, Mehrnaz Tahmasbi-Arashlow
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e23. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
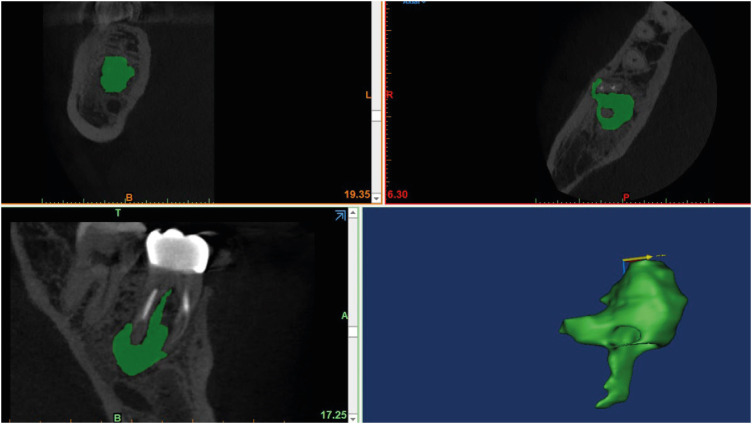
ePub Objectives The formation of new bone by periosteum due to an insult is called periosteal bone reaction (PBR). This study assessed the cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) patterns of periosteal bone reactions associated with periapical inflammatory lesion (apical periodontitis/periapical rarefying osteitis).
Materials and Methods Twenty-two small field of view CBCT images of patients with PBR were selected from a database of a private practice limited to endodontics. The volume of the periapical inflammatory lesion, the presence of cortical fenestration, the distance of the root apices to the affected cortex, and the location, pattern, and longest diameter of the periosteal reaction were recorded. Statistical analysis was performed using Wilcoxon Ranksum, Fischer’s exact, Spearman Correlation Coefficient, and paired
t -test.Results In all cases, periosteal bone reaction manifested as either parallel (90.9%) or irregular (9.1%). No correlation was found between periapical inflammatory lesion volume and the periosteal reaction's longest diameter (
p > 0.05). Cortical fenestration was noted in 72.7% of the cases. In addition, the findings showed that periosteal reactions were located mostly on the buccal and were present 53.8% and 100% of the time in the mandible and maxilla, respectively.Conclusions The periosteal reactions of endodontic origin had a nonaggressive form (
i.e ., parallel or irregular), and none of the lesions resulted in a periosteal reaction with an ominous Codman’s triangle or spicule pattern.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ENDODONTIA E INTERCORRÊNCIAS: COMPREENDENDO OS ACIDENTES E OTIMIZANDO O PROGNÓSTICO
Ana Paula Oliveira Rocha, Flávia Cordeiro Antunes , Millena Alberto Luna , Raissa Danielle Muniz Da Silva , Gustavo Henrique Palma Durães , Juliano Magno de Valadares Bicalho , Lorena Miranda Lima , Barbara Quadros Tonelli
REMUNOM.2026; 2(03): 1. CrossRef - The influence of endodontic treatment quality on periapical lesions' architecture in cone‐beam computed tomography
Ewa Mackiewicz, Tobias Bonsmann, Krzysztof Safranow, Patrycja Nowicka, Janusz Kołecki, Alicja Nowicka
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(1): 36. CrossRef - Novel radiographic pattern of maxillary periostitis induced by endodontic inflammation: A case report
Pai-Chun Huang, I-Hao Su, Meng-Ling Chiang, Jyh-Kwei Chen
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025; 20(3): 1982. CrossRef - Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible managed by nonsurgical re-endodontic treatment
Heegyun Kim, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Soram Oh, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- ENDODONTIA E INTERCORRÊNCIAS: COMPREENDENDO OS ACIDENTES E OTIMIZANDO O PROGNÓSTICO
- 5,250 View
- 85 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Biocompatibility and bioactive potential of the NeoMTA Plus endodontic bioceramic-based sealer
- Roberto Alameda Hoshino, Mateus Machado Delfino, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho, Estela Sasso-Cerri, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e4. Published online December 17, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
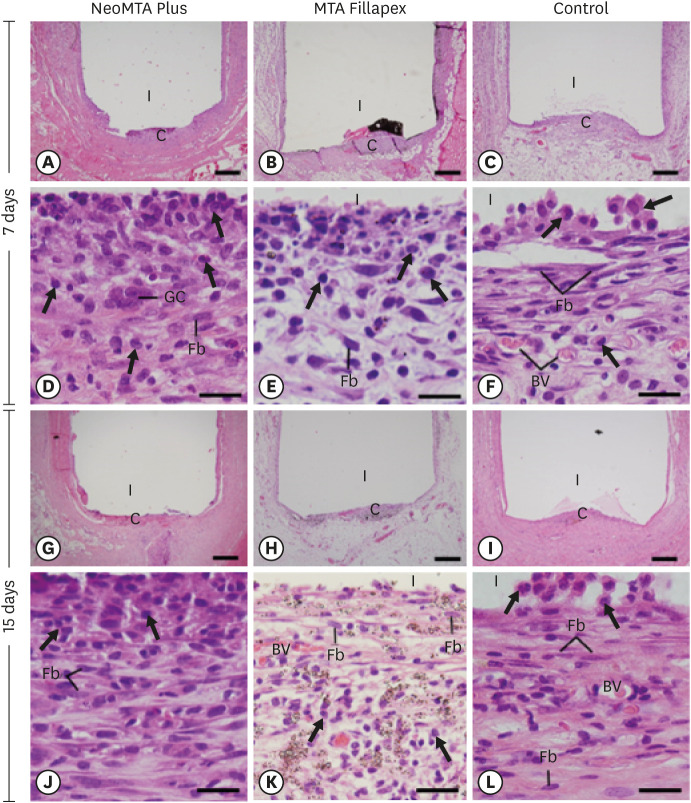
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the biocompatibility and bioactive potential of NeoMTA Plus mixed as a root canal sealer in comparison with MTA Fillapex.
Materials and Methods Polyethylene tubes filled with NeoMTA Plus (
n = 20), MTA Fillapex (n = 20), or nothing (control group, CG;n = 20) were inserted into the connective tissue in the dorsal subcutaneous layer of rats. After 7, 15, 30 and 60 days, the specimens were processed for paraffin embedding. The capsule thickness, collagen content, and number of inflammatory cells (ICs) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) immunolabeled cells were measured. von Kossa-positive structures were evaluated and unstained sections were analyzed under polarized light. Two-way analysis of variance was performed, followed by thepost hoc Tukey test (p ≤ 0.05).Results At 7 days, the capsules around NeoMTA Plus and MTA Fillapex had more ICs and IL-6-immunostained cells than the CG. However, at 60 days, there was no significant difference in the IC number between NeoMTA Plus and the CG (
p = 0.1137) or the MTA Fillapex group (p = 0.4062), although a greater number of IL-6-immunostained cells was observed in the MTA Fillapex group (p = 0.0353). From 7 to 60 days, the capsule thickness of the NeoMTA Plus and MTA Fillapex specimens significantly decreased, concomitantly with an increase in the collagen content. The capsules around root canal sealers showed positivity to the von Kossa stain and birefringent structures.Conclusions The NeoMTA Plus root canal sealer is biocompatible and exhibits bioactive potential.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Retrievability of NeoMTA 2 vs AH Plus Sealer from Retreated Mesial Canals of Mandibular First Molars: A Microcomputed Tomography Ex Vivo Study
Mey A Al-Habib, Mona Alsulaiman
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(5): 493. CrossRef - Effect of calcium silicate-based repair sealers on bone healing in rat skull defects: histological and histomorphometric study
J. M. Sauer, C. E. S. Bueno, R. A. Pelegrine, C. E. Fontana, E. F. Martinez, P. G. Montagner, W. M. Nascimento, A. G. S. Limoeiro, D. G. P. Rocha, M. F. V. Marceliano-Alves, M. P. W. Galhardi, M. Klymus, A. S. Martin
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(3): 433. CrossRef - Biocompatibility and bioactivity of bioceramic endodontic sealer: NeoSealer Flo
Evelin Carine Alves SILVA, Jéssica Arielli PRADELLI, Guilherme Ferreira da SILVA, Paulo Sérgio CERRI, Mario TANOMARU-FILHO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The osteoinductive potential of different root-end filling materials in a rat femur model
Seçkin Aksu, Ebru Delikan, Ayşe Özcan Küçük, Zehra Demiray Asoğlu, Şakir Necat Yılmaz
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical outcomes of nonsurgical root canal treatment using NeoSealer Flo and Endosequence BC Sealer: A retrospective analysis with short-term follow-up
Christian Lepure, Ryan M. Walsh, Sayeed Attar, Casey L. Turner, Joshua Crawford, Poorya Jalali
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Biocompatibility and bioactive potential of NeoPUTTY calcium silicate‐based cement: An in vivo study in rats
Evelin Carine Alves Silva, Jéssica Arielli Pradelli, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Paulo Sérgio Cerri, Mario Tanomaru‐Filho, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(6): 713. CrossRef - Carbon Nanotubes Induce Mineralization of Human Cementoblasts
Ting-Hsuan Wang, Kiyoko Watanabe, Koichiro Muromachi, Nobushiro Hamada, Nobuyuki Tani-Ishii
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(8): 1117. CrossRef - Tissue repair capacity of bioceramic endodontic sealers in rat subcutaneous tissue
George Sampaio Bonates dos Santos, Ceci Nunes Carvalho, Rudys Rodolfo de Jesus Tavares, Paulo Goberlânio de Barros Silva, George Táccio de Miranda Candeiro, Etevaldo Matos Maia Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(3): 25. CrossRef - Participation of fibroblast growth factor‐1 and interleukin‐10 in connective tissue repair following subcutaneous implantation of bioceramic materials in rats
Mateus Machado Delfino, José Leandro de Abreu Jampani, Camila Soares Lopes, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho, Estela Sasso‐Cerri, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(3): 385. CrossRef - Biocompatibility and bioactive potential of an experimental tricalcium silicate‐based cement in comparison with Bio‐C repair and MTA Repair HP materials
Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Rafaela N. H. Inada, José Leandro de Abreu Jampani, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Estela Sasso‐Cerri, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(2): 259. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Sealer Dentinal Tubule Penetration—A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Israa Ashkar, José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner, María Melo
Materials.2023; 16(7): 2734. CrossRef - Bioactivity Potential of Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Scoping Review
Mauro Schmitz Estivalet, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Felipe Immich, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Nadia de Souza Ferreira, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva
Life.2022; 12(11): 1853. CrossRef - Tricalcium silicate cement sealers
Anita Aminoshariae, Carolyn Primus, James C. Kulild
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2022; 153(8): 750. CrossRef - Bioactive potential of Bio‐C Pulpo is evidenced by presence of birefringent calcite and osteocalcin immunoexpression in the rat subcutaneous tissue
Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Camila Soares Lopes, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Estela Sasso‐Cerri, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2022; 110(10): 2369. CrossRef - An Updated Review on Properties and Indications of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements in Endodontic Therapy
Fateme Eskandari, Alireza Razavian, Rozhina Hamidi, Khadije Yousefi, Susan Borzou, Zohaib Khurshid
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Retrievability of NeoMTA 2 vs AH Plus Sealer from Retreated Mesial Canals of Mandibular First Molars: A Microcomputed Tomography Ex Vivo Study
- 2,666 View
- 36 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Effect of phytic acid as an endodontic chelator on resin adhesion to sodium hypochlorite-treated dentin
- Mohannad Nassar, Noriko Hiraishi, Md. Sofiqul Islam, Maria JRH. Romero, Masayuki Otsuki, Junji Tagami
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e44. Published online August 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
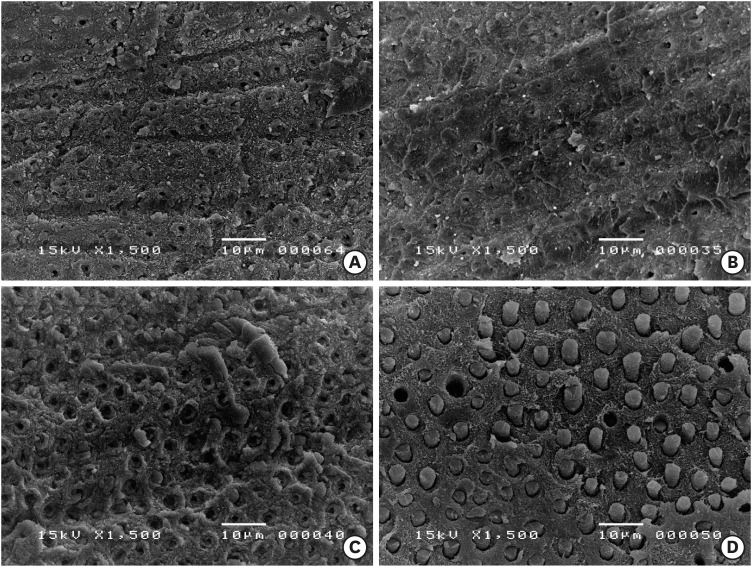
ePub Objectives Phytic acid (IP6), a naturally occurring agent, has been previously reported as a potential alternative to ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). However, its effect on adhesion to sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl)-treated dentin and its interactions with NaOCl have not been previously reported. Thus, in this study, the effects of IP6 on resin adhesion to NaOCl-treated dentin and the failure mode were investigated and the interactions between the used agents were analyzed.
Materials and Methods Micro-tensile bond strength (µTBS) testing was performed until failure on dentin treated with either distilled water (control), 5% NaOCl, or 5% NaOCl followed with chelators: 17% EDTA for 1 minute or 1% IP6 for 30 seconds or 1 minute. The failed specimens were assessed under a scanning electron microscope. The reaction of NaOCl with EDTA or IP6 was analyzed in terms of temperature, pH, effervescence, and chlorine odor, and the effects of the resulting mixtures on the color of a stained paper were recorded.
Results The µTBS values of the control and NaOCl with chelator groups were not significantly different, but were all significantly higher than that of the group treated with NaOCl only. In the failure analysis, a distinctive feature was the presence of resin tags in samples conditioned with IP6 after treatment with NaOCl. The reaction of 1% IP6 with 5% NaOCl was less aggressive than the reaction of the latter with 17% EDTA.
Conclusions IP6 reversed the adverse effects of NaOCl on resin-dentin adhesion without the chlorine-depleting effect of EDTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Chemical Surface Modification on the Repair Bond Strength of Resin Composite: An In Vitro Study
Md Sofiqul Islam, Shadi El Bahra, Smriti Aryal A C, Vivek Padmanabhan, Abdulaziz Al Tawil, Ihab Saleh, Muhammed Mustahsen Rahman, Upoma Guha
Polymers.2025; 17(4): 513. CrossRef - Advancing Adhesive Strategies for Endodontically Treated Teeth—Part I: Impact of Endodontic Irrigation Protocols on the Chemical Composition and Structural Integrity of Coronal Dentin
Joana A. Marques, Rui I. Falacho, Sara Fateixa, Francisco Caramelo, João Miguel Santos, João Rocha, Markus B. Blatz, João Carlos Ramos, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(7): 1848. CrossRef - Effect of collagen crosslinkers on sodium hypochlorite treated dentin bond strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Weiqing Zhou, Shuting Feng, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing Adhesive Strategies for Endodontically Treated Teeth—Part II: Dentin Sealing Before Irrigation Increases Long‐Term Microtensile Bond Strength to Coronal Dentin
Joana A. Marques, Rui I. Falacho, Gabriela Almeida, Francisco Caramelo, João Miguel Santos, João Rocha, Markus B. Blatz, João Carlos Ramos, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(7): 1865. CrossRef - Effects of phytic acid and etidronic acid using continuous and sequential chelation on the removal of smear layer, dentin microhardness, and push-out bond strength of calcium silicate-based cement
Ecehan Hazar, Ahmet Hazar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of free available chlorine in sodium hypochlorite solutions admixed with novel chelating agents
Somya Tyagi, Sonali Taneja, Kandasamy Nagarajan, Divya Chowdhary
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 188. CrossRef - Effect of different chelating agents, with and without activation, including XP-endo Finisher, on root dentin microhardness: An in vitro study
Mahmoud Mohamed A. Sherif, Mai Hamdy Ragab, Marwa ElSayed Sharaan
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(3): 282. CrossRef - Oracle of phytic acid in dental panacea – Insight into properties, therapeutic effect, regeneration, materials interaction and oral physiology
Ummey Salma, C. Pushpalatha, SV. Sowmya, Dominic Augustine, Ahmed Alamoudi, Bassam Zidane, Nassreen Hassan Mohammad Albar, Shilpa Bhandi
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(8): 1093. CrossRef - In Vitro Bond Strength of Dentin Treated with Sodium Hypochlorite: Effects of Antioxidant Solutions
Guillermo Grazioli, Elisa de León Cáceres, Romina Tessore, Rafael Lund, Ana Monjarás-Ávila, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Carlos Cuevas-Suárez
Antioxidants.2024; 13(9): 1116. CrossRef - Is a mix – A fix? “A microscopic analysis of depth of penetration of three combinations of irrigants”
Yantrapragada Lakshmi Sunanda, Krishna Prasad Parvathaneni, T. B. V. G. Raju, Abitha Seshadri, Nadimpalli Mahendra Varma, Gowtam Dev Dondapati
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(2): 186. CrossRef - Effect of phytic acid on dentinal collagen solubilization and its binding and debinding potentials to dentin
Diletta Forgione, Mohannad Nassar, Roda Seseogullari-Dirihan, Ahmed Jamleh, Arzu Tezvergil-Mutluay
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 128: 104361. CrossRef - Application of Inositol Hexaphosphate and Inositol in Dental Medicine: An Overview
Ana Druzijanic, Mare Kovic, Marija Roguljic, Livia Cigic, Martina Majstorovic, Ivana Vucenik
Biomolecules.2023; 13(6): 913. CrossRef - Ex-vivo study about antimicrobial effectiveness of phytic acid against Enterococcus faecalis into root canals
Giulia BOSCHI, Giorgio PICCINELLI, Carlo BONFANTI, Stefano A. SALGARELLO
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of phytic acid on bond strength and interfacial integrity of universal adhesive to deep dentin
Ahmed Mostafa Attia, Ahmed Fawzy Abo-Elezz, Rehab Khalil Safy
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(5): 116. CrossRef - Resin-Based Cement Applied to Enamel and Dentin Pre-Treated with Phytic Acid: An In Vitro Study
Mohannad Nassar, Md. Sofiqul Islam, Smriti Aryal A C, Hatem Mostafa El-Damanhoury, Salvatore Sauro, Noriko Hiraishi
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(24): 11976. CrossRef - Postspace pretreatment with 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 7% maleic acid, and 1% phytic acid on bond strength of fiber posts luted with a self-adhesive resin cement
PriyaC Yadav, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(6): 558. CrossRef - Phytic Acid: Properties and Potential Applications in Dentistry
Mohannad Nassar, Rania Nassar, Husain Maki, Abdullah Al-Yagoob, Mahmood Hachim, Abiola Senok, David Williams, Noriko Hiraishi
Frontiers in Materials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Effect of Chemical Surface Modification on the Repair Bond Strength of Resin Composite: An In Vitro Study
- 2,336 View
- 19 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Evaluation of the rat tissue reaction to experimental new resin cement and mineral trioxide aggregate cement
- Won-Kyung Yang, Hyun-Jung Ko, Mi-Ri Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):194-200. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.194
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives New resin cement (NRC) has been developed as a root repairing material and the material is composed of organic resin matrix and inorganic powders. The aim of this study was to compare the rat subcutaneous tissue response to NRC and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) cement and to investigate the tissue toxicity of both materials.
Materials and Methods Sixty rats received two polyethylene tube-implants in dorsal subcutaneous regions, MTA and NRC specimens. Twenty rats were sacrificed respectively at 1, 4 and 8 wk after implantation and sectioned to 5 µm thickness and stained with Hematoxylin-Eosin (H-E) or von-Kossa staining. The condition of tissue adjacent to the implanted materials and the extent of inflammation to each implant were evaluated by two examiners who were unaware of the type of implanted materials in the tissues. Data were statistically analyzed with paired
t -test (p < 0.05).Results In specimens implanted with both NRC and MTA, severe inflammatory reactions were present at one wk, which decreased with time. At eighth wk, MTA implanted tissue showed mild inflammatory reaction, while there were moderate inflammatory reactions in NRC implanted tissue, respectively. In NRC group, von-Kossa staining showed more calcification materials than MTA group at eighth wk.
Conclusions It was concluded that the calcium reservoir capability of NRC may contribute to mineralization of the tissues.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomineralization of three calcium silicate-based cements after implantation in rat subcutaneous tissue
Ranjdar Mahmood Talabani, Balkees Taha Garib, Reza Masaeli, Kavosh Zandsalimi, Farinaz Ketabat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Genotoxicity of root canal sealers: a literature review
Fábio Miguel dos Santos Costa, Maria Helena Fernandes, Silvia Regina Batistuzzo de Medeiros
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(10): 3347. CrossRef - Marginal adaptation, solubility and biocompatibility of TheraCal LC compared with MTA-angelus and biodentine as a furcation perforation repair material
M. A. Alazrag, A. M. Abu-Seida, K. M. El-Batouty, S. H. El Ashry
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation in vivo of biocompatibility of differents resin-modified cements for bonding orthodontic bands
JANAINA A. MESQUITA, ROGÉRIO LACERDA-SANTOS, GÊISA A.M. SAMPAIO, GUSTAVO P. GODOY, CASSIANO F.W. NONAKA, POLLIANNA M. ALVES
Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências.2017; 89(3 suppl): 2433. CrossRef - A preliminary report on histological outcome of pulpotomy with endodontic biomaterials vs calcium hydroxide
Ali Nosrat, Ali Peimani, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 227. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of root-end filling materials: recent update
Payal Saxena, Saurabh Kumar Gupta, Vilas Newaskar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 119. CrossRef
- Biomineralization of three calcium silicate-based cements after implantation in rat subcutaneous tissue
- 1,370 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Comparison of gene expression profiles of human dental pulp cells treated with mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium hydroxide
- Yong-Beom Kim, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Ho Baek, Kwang-Shik Bae
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):397-408. Published online September 14, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.397
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract Objectives: This study investigated changes in gene expressions concerning of differentiation, proliferation, mineralization and inflammation using Human-8 expression bead arrays when white Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and calcium hydroxide-containing cement were applied
in vitro to human dental pulp cells (HDPCs).Materials and Methods: wMTA (white ProRoot MTA, Dentsply) and Dycal (Dentsply Caulk) in a Teflon tube (inner diameter 10 mm, height 1 mm) were applied to HDPCs. Empty tube-applied HDPCs were used as negative control. Total RNA was extracted at 3, 6, 9 and 24 hr after wMTA and Dycal application. The results of microarray were confirmed by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction.
Results: Out of the 24,546 genes, 43 genes (e.g., BMP2, FOSB, THBS1, EDN1, IL11, COL10A1, TUFT1, HMOX1) were up-regulated greater than two-fold and 25 genes (e.g., SMAD6, TIMP2, DCN, SOCS2, CEBPD, KIAA1199) were down-regulated below 50% by wMTA. Two hundred thirty nine genes (e.g., BMP2, BMP6, SMAD6, IL11, FOS, VEGFA, PlGF, HMOX1, SOCS2, CEBPD, KIAA1199) were up-regulated greater than two-fold and 358 genes (e.g., EDN1, FGF) were down-regulated below 50% by Dycal.
Conclusions: Both wMTA and Dycal induced changes in gene expressions related with differentiation and proliferation of pulp cells. wMTA induced changes in gene expressions related with mineralization, and Dycal induced those related with angiogenesis. The genes related with inflammation were more expressed by Dycal than by wMTA. It was confirmed that both wMTA and Dycal were able to induce gene expression changes concerned with the pulp repair in different ways.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of gene expression during odontogenic differentiation of cultured human dental pulp cells
Min-Seock Seo, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Hyongbum Kim, Seung-Ho Baek
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(3): 142. CrossRef
- Analysis of gene expression during odontogenic differentiation of cultured human dental pulp cells
- 1,390 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


