Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Bonding effects of cleaning protocols and time-point of acid etching on dentin impregnated with endodontic sealer
- Tatiane Miranda Manzoli, Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, João Felipe Besegato, Flávia Angélica Guiotti, Andréa Abi Rached Dantas, Milton Carlos Kuga
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e21. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
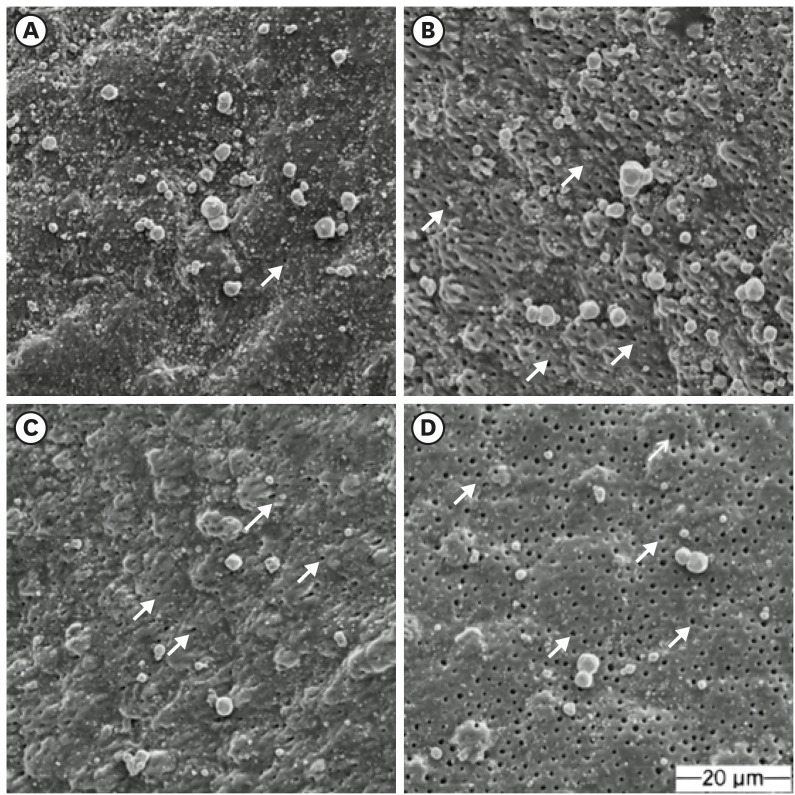
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the bonding effects of cleaning protocols on dentin impregnated with endodontic sealer residues using ethanol (E) or xylol (X). The effects of dentin acid etching immediately (I) or 7 days (P) after cleaning were also evaluated. For bonding to dentin, universal adhesive (Scotchbond Universal; 3M ESPE) was used. The persistence of sealer residues, hybrid layer formation and microshear bond strength were the performed analysis.
Materials and Methods One hundred and twenty bovine dentin specimens were allocated into 4 groups (
n = 10): G1 (E+I); G2 (X+I); G3 (E+P); and G4 (X+P). The persistence of sealer residues was evaluated by SEM. Confocal laser scanning microscopy images were taken to measure the formed hybrid layer using the Image J program. For microshear bond strength, 4 resin composite cylinders were placed over the dentin after the cleaning protocols. ANOVA followed by Tukey test and Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn test were used for parametric and non-parametric data, respectively (α = 5%).Results G2 and G4 groups showed a lower persistence of residues (
p < 0.05) and thicker hybrid layer than the other groups (p < 0.05). No bond strength differences among all groups were observed (p > 0.05).Conclusions Dentin cleaning using xylol, regardless of the time-point of acid etching, provided lower persistence of residues over the surface and thicker hybrid layer. However, the bond strength of the universal adhesive system in etch-and-rinse strategy was not influenced by the cleaning protocols or time-point of acid etching.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of Post-Endodontic Access Cavity Cleaning Techniques: A Randomized Clinical Study
Ayse Karadayi, Elif Irem Altintas, Ezgi Tüter Bayraktar, Bora Korkut
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 166. CrossRef - Does cleaning of post space before cementation of fiber reinforced post affect the push-out bond strength to resin cement?
Maher S. Hajjaj, Khalid A. Alghamdi, Abdulrahman A. Alshehri, Hassan A. Almusallam, Nabeel M. Munshi, Osamah A. Alsulimani, Naseeba H. Khouja, Yousef A. Alnowailaty, Saeed J. Alzahrani
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of the Use of a Mixed Solution of Equal Amounts of Amyl Acetate, Acetone, and Ethanol on the Cleaning of Endodontic Sealer Residues on the Bond Strength of the Fiber Post Cementation System: A Laboratory Investigation
Antonia Patricia Oliveira Barros, Ana Paula Aparecida Raimundo Alves Freitas, Frederico Guilherme Otto Kokol, Elizangela Maria Pereira de Souza, Adirson Jorge Junior, Cristiane de Melo Alencar, Marcelo Ferrarezi de Andrade, Milton Carlos Kuga
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the application protocol and bonding strategy of the universal adhesive on dentin previously impregnated with bioceramic sealer
Antonia Patricia Oliveira Barros, Joatan Lucas de Sousa Gomes Costa, Jardel Camilo do Carmo Monteiro, Lucas David Galvani, Marcelo Ferrarezi de Andrade, José Roberto Cury Saad, Milton Carlos Kuga
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2024; 134: 103765. CrossRef - Influência do protocolo de remoção de resíduos de cimentos à base de resina epóxi sobre a interface de adesão com o adesivo universal, utilizado na estratégia condiciona-e-lava
Paulo Firmino Da Costa Neto, Mariana Bena Gelio, Elisângela Maria Pereira De Souza, Jardel Camilo do Carmo Monteiro, Adirson Jorge Júnior, Thais Piragine Leandrin, José Roberto Cury Saad, Milton Carlos Kuga
Cuadernos de Educación y Desarrollo.2023; 15(5): 4802. CrossRef
- Efficacy of Post-Endodontic Access Cavity Cleaning Techniques: A Randomized Clinical Study
- 2,289 View
- 40 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- The influence of nanofillers on the properties of ethanol-solvated and non-solvated dental adhesives
- Leonardo Bairrada Tavares da Cruz, Marcelo Tavares Oliveira, Cintia Helena Coury Saraceni, Adriano Fonseca Lima
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e28. Published online July 24, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
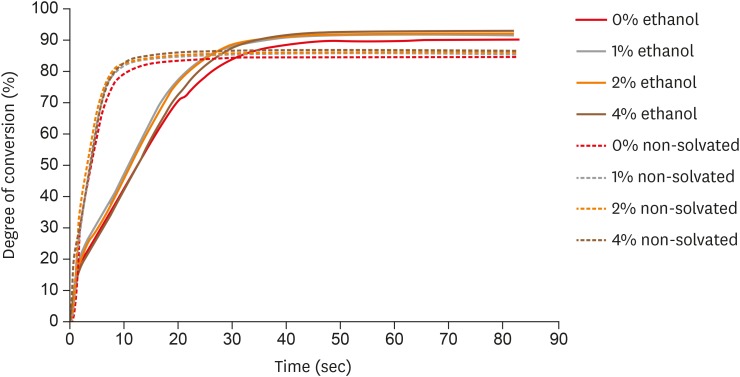
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of different concentrations of nanofillers on the chemical and physical properties of ethanol-solvated and non-solvated dental adhesives.
Materials and Methods Eight experimental adhesives were prepared with different nanofiller concentrations (0, 1, 2, and 4 wt%) and 2 solvent concentrations (0% and 10% ethanol). Several properties of the experimental adhesives were evaluated, such as water sorption and solubility (
n = 5, 20 seconds light activation), real-time degree of conversion (DC;n = 3, 20 and 40 seconds light activation), and stability of cohesive strength at 6 months (CS;n = 20, 20 seconds light activation) using the microtensile test. A light-emitting diode (Bluephase 20i, Ivoclar Vivadent) with an average light emittance of 1,200 mW/cm2 was used.Results The presence of solvent reduced the DC after 20 seconds of curing, but increased the final DC, water sorption, and solubility of the adhesives. Storage in water reduced the strength of the adhesives. The addition of 1 wt% and 2 wt% nanofillers increased the polymerization rate of the adhesives.
Conclusions The presence of nanofillers and ethanol improved the final DC, although the DC of the solvated adhesives at 20 seconds was lower than that of the non-solvated adhesives. The presence of ethanol reduced the strength of the adhesives and increased their water sorption and solubility. However, nanofillers did not affect the water sorption and strength of the tested adhesives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In Vitro Comparison of Gingival Epithesis Materials: Color Stability, Surface Properties, and Microbial Adhesion After Staining
Ellen Pick, Andrea Gubler, Thomas Attin, Patrick R. Schmidlin
Dentistry Journal.2026; 14(3): 142. CrossRef - Effect of boric acid on the color stability and mechanical properties of 3D-printed permanent resins
Dalndushe Abdulai, Rafat Sasany, Raghib Suradi, Mehran Moghbel, Seyed Ali Mosaddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Boron Nitride-Filled Dental Adhesive System
Senthilguru Kulanthaivel, Jeremiah Poppen, Sandra Ribeiro Cunha, Benjamin Furman, Kyumin Whang, Erica C. Teixeira
Polymers.2023; 15(17): 3512. CrossRef - Analyses of Experimental Dental Adhesives Based on Zirconia/Silver Phosphate Nanoparticles
Abdul Khan, Yasmin Alhamdan, Hala Alibrahim, Khalid Almulhim, Muhammad Nawaz, Syed Ahmed, Khalid Aljuaid, Ijlal Ateeq, Sultan Akhtar, Mohammad Ansari, Intisar Siddiqui
Polymers.2023; 15(12): 2614. CrossRef - Mechanical characterization and adhesive properties of a dental adhesive modified with a polymer antibiotic conjugate
Camila Sabatini, Russell J. Aguilar, Ziwen Zhang, Steven Makowka, Abhishek Kumar, Megan M. Jones, Michelle B. Visser, Mark Swihart, Chong Cheng
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2022; 129: 105153. CrossRef
- In Vitro Comparison of Gingival Epithesis Materials: Color Stability, Surface Properties, and Microbial Adhesion After Staining
- 1,501 View
- 9 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of solvent volatilization time on the bond strength of etch-and-rinse adhesive to dentin using conventional or deproteinization bonding techniques
- José Aginaldo de Sousa Júnior, Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Fabricio Eneas Diniz de Figueiredo, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):202-208. Published online March 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.202
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study determined the effect of the air-stream application time and the bonding technique on the dentin bond strength of adhesives with different solvents. Furthermore, the content and volatilization rate of the solvents contained in the adhesives were also evaluated.
Materials and Methods Three adhesive systems with different solvents (Stae, SDI, acetone; XP Bond, Dentsply De Trey, butanol; Ambar, FGM, ethanol) were evaluated. The concentrations and evaporation rates of each adhesive were measured using an analytical balance. After acid-etching and rinsing, medium occlusal dentin surfaces of human molars were kept moist (conventional) or were treated with 10% sodium hypochlorite for deproteinization. After applying adhesives over the dentin, slight air-stream was applied for 10, 30 or 60 sec. Composite cylinders were built up and submitted to shear testing. The data were submitted to ANOVA and Tukey's test (α = 0.05).
Results Stae showed the highest solvent content and Ambar the lowest. Acetone presented the highest evaporation rate, followed by butanol. Shear bond strengths were significantly affected only by the factors of 'adhesive' and 'bonding technique' (
p < 0.05), while the factor 'duration of air-stream' was not significant. Deproteinization of dentin increased the bond strength (p < 0.05). Stae showed the lowest bond strength values (p < 0.05), while no significant difference was observed between XP Bond and Ambar.Conclusions Despite the differences in content and evaporation rate of the solvents, the duration of air-stream application did not affect the bond strength to dentin irrespective of the bonding technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of solvent evaporation and photo-irradiation strategy of contact-cure adhesive system on bonding to root canal
Wahyuni Suci Dwiandhany, Kittisak Sanon, Yasushi Shimada, Ahmed Abdou
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of adhesive air-drying time on bond strength to dentin: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohamed M. Awad, Ali Alrahlah, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hamdi Hosni Hamama
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2019; 90: 154. CrossRef
- Effect of solvent evaporation and photo-irradiation strategy of contact-cure adhesive system on bonding to root canal
- 1,649 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effect of ethylene glycol analogs on mechanical properties of moist demineralized dentin matrix
- Kyung-Ha Lee, Young-Gon Cho, Kwang-Won Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):290-299. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of ethylene glycol analogs on modulus of elasticity and ultimate tensile strength of moist, demineralized dentin matrix.
Methods Dentin disks 0.5 mm thick were prepared from mid-coronal dentin of extracted, unerupted, human third molars. "I" beam and hour-glass shaped specimens were prepared from the disks, the ends protected with nail varnish and the central regions completely demineralized in 0.5M EDTA for 5 days. Ultimate tensile stress (UTS) and low strain modulus of elasticity (E) were determined with specimens immersed for 60 min in distilled water (H2O), ethylene glycol (HO-CH2-CH2-OH), 2-methoxyethanol (H3CO-CH2-CH2-OH), and 1,2-dimethoxyethane (H3CO-CH2-CH3-OCH3) prior to testing in those same media. Modulus of elasticity was measured on the same specimens in a repeated measures experimental design. The results were analyzed with a one-way ANOVA on ranks, followed by Dunn's test at α = 0.05. Regression analysis examined the relationship between UTS or E and hoy's solubility parameter for hydrogen bonding (δh) of each solvent.
Results The UTS of demineralized dentin in water, ethylene glycol, 2-methoxyethanol, and 1,2-dimethoxyethane was 24 (3), 30 (5), 37 (6), and 45 (6) MPa, × (SD) N = 10. Low strain E for the same media were 16 (13), 23 (14), 52 (24), and 62 (22) MPa. Regression analysis of UTS vs δh revealed a significant (p < 0.0001, r = -0.99, R2 = 0.98) inverse, exponential relationship. A similar inverse relationship was obtained between low strain E vs δh (p < 0.0005, r = -0.93, R2 = 0.86).
Significance The tensile properties of demineralized dentin are dependent upon the hydrogen bonding ability of polar solvents (δh). Solvents with low δh values may permit new interpeptide H-bonding in collagen that increases its tensile properties. Solvents with high δh values prevent the development of these new interpeptide H-bonds.
- 784 View
- 0 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


