Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The influence of bioactive glass (BGS-7) on enamel remineralization: an in vitro study
- Chaeyoung Lee, Eunseon Jeong, Kun-Hwa Sung, Su-Jung Park, Yoorina Choi
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e33. Published online October 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
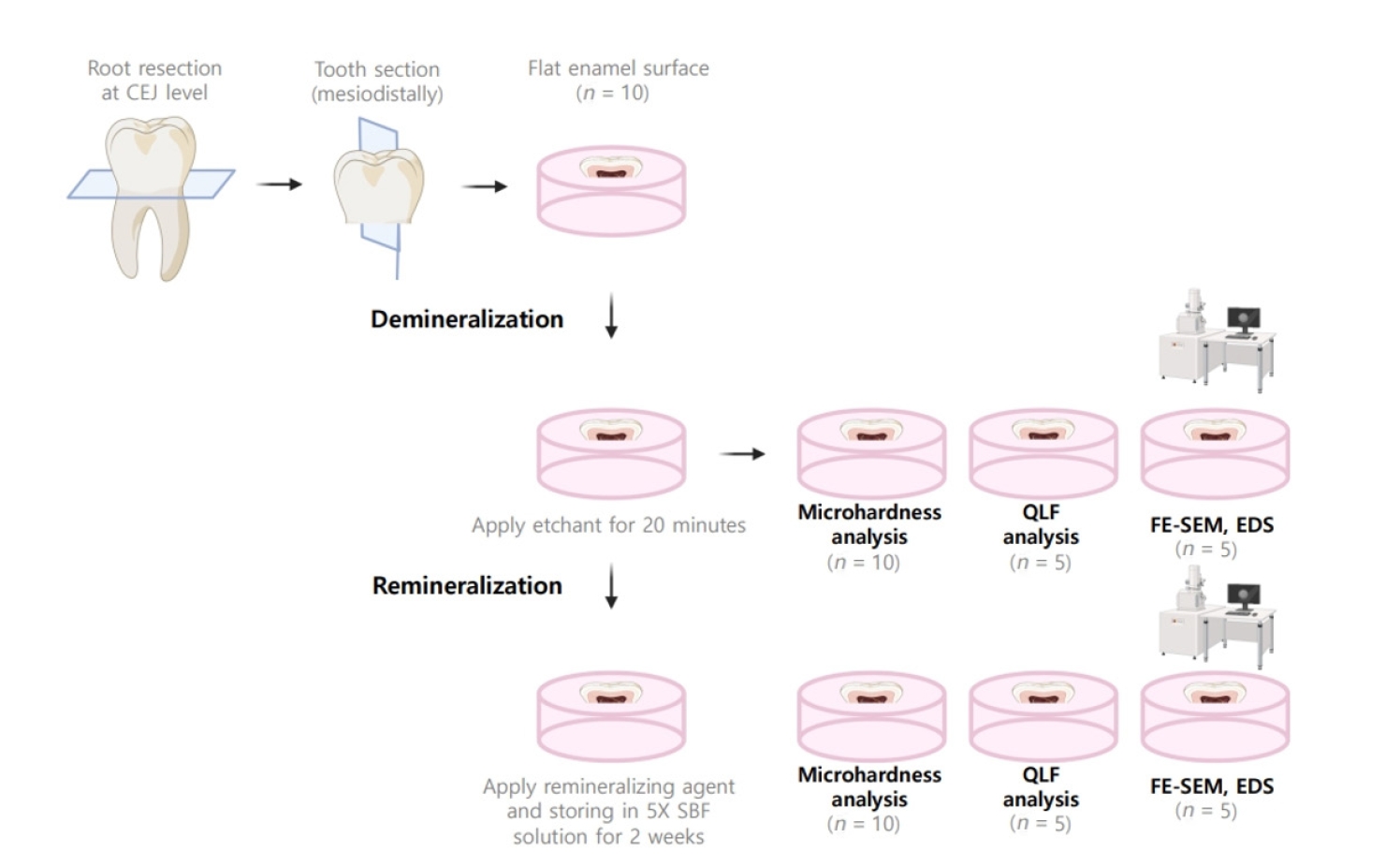
The aim of this study was to compare the remineralizing capacity of bioactive glass (BGS-7, CGBIO) with other agents.
Methods
Twenty caries-free third molars were sectioned and demineralized. Specimens were divided into four groups: (1) control, (2) Clinpro XT varnish (Solventum), (3) 1.23% acidulated phosphate fluoride gel, and (4) a new type of CaO-SiO2-P2O5-B2O3 system of bioactive glass ceramics (BGS-7). Agents were applied and stored in simulated body fluid at 37℃ for 2 weeks. Microhardness was measured using the Vickers hardness testing method. Five specimens per group were analyzed using quantitative light-induced fluorescence (QLF) to assess mineral loss. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) were used to examine the surface morphology and elemental composition. Data were analyzed using paired t-test and one-way analysis of variance (p < 0.05).
Results
BGS-7 showed the highest microhardness values and the greatest recovery in QLF analysis (p < 0.05). FE-SEM revealed granular precipitates on demineralized enamel in the BGS-7 group. EDS confirmed the presence of newly formed silicon and fluoride layers.
Conclusions
BGS-7 demonstrated superior remineralization capacity compared to other agents, suggesting its potential as an effective remineralizing material. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bacterial ghosts (BGs): A promising approach as candidate vaccine
Helal F. Hetta, Ibraheem M. Mwafey, Noura H. Abd Ellah, Fawaz E. Alanazi, Yasmin N. Ramadan
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Bacterial ghosts (BGs): A promising approach as candidate vaccine
- 1,696 View
- 194 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of an aluminum chloride hemostatic agent on the dentin shear bond strength of a universal adhesive
- Sujin Kim, Yoorina Choi, Sujung Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e14. Published online March 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
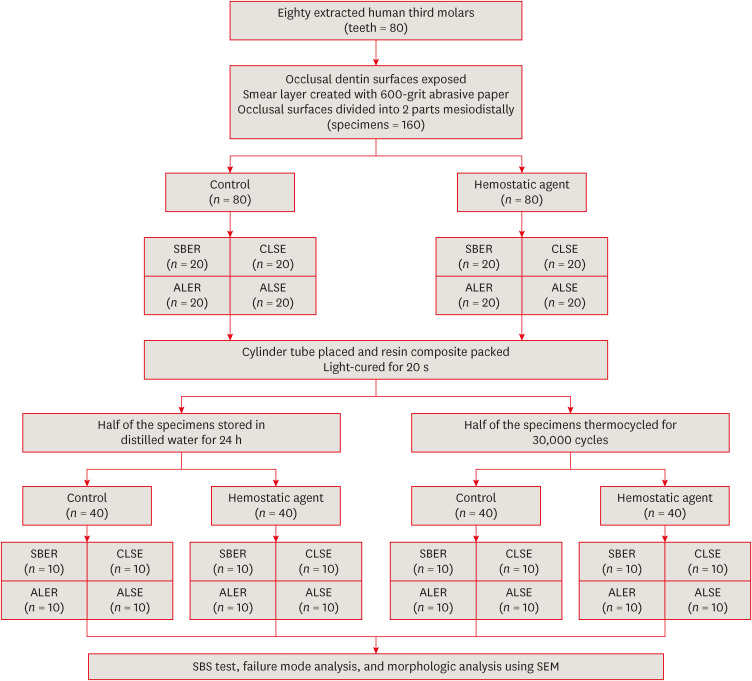
ePub Objectives This study investigated the effect of an aluminum chloride hemostatic agent on the shear bond strength (SBS) of a universal adhesive to dentin.
Materials and Methods Eighty extracted human molars were trimmed at the occlusal dentin surfaces and divided mesiodistally. According to hemostatic agent application, specimens were randomly allocated into control (C) and hemostatic agent (Traxodent; H) groups. Each group was divided into 4 subgroups according to the adhesive system (
n = 20): Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (SBER), Clearfil SE Bond (CLSE), All-Bond Universal etch-and-rinse mode (ALER), and All-Bond Universal self-etch mode (ALSE). SBS was measured for half of the specimens at 24 hours, and the other half were thermocycled in water baths (group T). Fracture surfaces were examined to determine the failure mode. The SBS was measured, and data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance, the Student’st -test, and the Tukey honestly significant difference test (p = 0.05).Results No significant differences in SBS were found between groups C and H for any adhesive system at 24 hours. After thermocycling, a statistically significant difference was observed between CT+ALSE and HT+ALSE (
p < 0.05). When All-Bond Universal was applied to hemostatic agent-contaminated dentin, the SBS of H+ALSE was significantly lower than that of H+ALER (p < 0.05). The SBER subgroups showed no significant differences in SBS regardless of treatment and thermocycling.Conclusions When exposed dentin was contaminated by an aluminum chloride hemostatic agent before dentin adhesive treatment, application of All-Bond Universal in etch-and-rinse mode was superior to self-etch mode.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nature-driven blue-emissive N, S-CDs: Harnessing sequential "switch-off-on" fluorescence signals for detection of chrysin and Al³⁺ along with cellular imaging versatility
Maha Mohammad Abdel-Monem, Mohamed I. Walash, Asmaa Kamal El-Deen
Talanta Open.2025; : 100466. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Shear Bond Strength of Self-Adhesive and Glass Ionomer Cement to Dentin After Removal of Hemostatic Agents Using Different Cleansing Protocols: An In Vitro Study
Hemashree Namburajan, Mathew Chalakuzhiyil Abraham, Vidhyasankari N, Rajkumar K, Abhinayaa Suthagar, Vishnupriya Venkatasubramanian, Sindhuja Nagarajan
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Emalje- og dentinadhesiver: Avgjørende faser i klinisk behandling
Torgils Lægreid, Tom Paulseth, Arne Lund
Den norske tannlegeforenings Tidende.2024; 134(8): 604. CrossRef
- Nature-driven blue-emissive N, S-CDs: Harnessing sequential "switch-off-on" fluorescence signals for detection of chrysin and Al³⁺ along with cellular imaging versatility
- 3,330 View
- 70 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Recognition and management of palatogingival groove for tooth survival: a literature review
- Hee-Jin Kim, Yoorina Choi, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):77-86. Published online April 12, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Palatogingival groove (PGG) is an anomaly in the maxillary anterior teeth, often accompanied by the area of bony destruction adjacent to the teeth with no carious or traumatic history. The hidden trap in the tooth can harbor plaque and bacteria, resulting in periodontal destruction with or without pulpal pathologic change. Related diseases can involve periodontal destruction, combined endodontic-periodontal lesions, or separate endodontic and periodontal lesions. Disease severity and prognosis related to PGG depend on several factors, including location, range, depth, and type of the groove. Several materials have been used and recommended for cases of extensive periodontal destruction from PGG to remove and block the inflammatory source and recover the health of surrounding periodontal tissues. Even in cases of severe periodontal destruction, several studies have reported favorable treatment outcomes with proper management. With new options in diagnosis and treatment, clinicians need a detailed understanding of the characteristics, treatment, and prognosis of PGG to successfully manage the condition.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of Palatal Grooves on Maxillary Anterior Teeth Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Oscar Lozano González, Marco Felipe Salas Orozco, Nuria Patiño Marín, Paul V. Abbott, Marc Garcia-Font, Francesc Abella Sans
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(1): 14. CrossRef - Endodontic bioceramics: current and futurity aspects
Roma M, Karthik Shetty, Laxmish Mallya, Krishna Prasad Shetty
Frontiers in Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A Unified Deep Learning Framework for Visual Diagnosis of Palatal Radicular Grooves in CBCT Scans: A Multicenter Validation Study
Qikui Zhu, Weitao Fu, Yeyu Lin, Jiaxing Li, Wenhui Tang, Ying Zhang, Rui Zhang, Guanfan Lu, Yao Lin, Jing Shen, Zhuan Bian, Liuyan Meng
Journal of Endodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic and Periodontal Treatment of a Two‐Rooted Maxillary Lateral Incisor With a Type III Palatoradicular Groove: A Case Report With 2‐Year Follow‐Up
Katsuhiro Takeda, Tomoya Naruse, Yohei Takahashi, Reina Kawai, Kimiaki Yuhi, Hideki Shiba, Barbara Lapinska
Case Reports in Dentistry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Three-year follow-up case report: root canal treatment combined with intentional replantation for treating type III palatogingival groove in a maxillary lateral incisor
Jixu Jia, Miao Cheng, Sumeng Shi, Yanchun Qiao
Frontiers in Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of palatogingival groove and its association with periapical lesions and periodontal bone loss: a cone beam computed tomography study
Dilan Pelin Yildirim, Selin Goker Kamali
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Morphology and Prevalence of Palatoradicular Grooves on Affected Maxillary Anterior Teeth Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography: An Institutional Retrospective Study
Dilara Baştuğ, Leyla Benan Ayrancı
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(14): 8031. CrossRef - Sulco palato-gengival e suas consequências: Revisão de literatura
Marielli de Paula Gonçalves, Maria Júlia Ribeiro Chalita Vieira, Mikaelly Kawany Martins da Silva, Fabiana Tavares Lunardi Palhari, Maria Isabel Gonçalves Fialho
Research, Society and Development.2025; 14(8): e5014849388. CrossRef - Credibility of Intentional Reimplantation Techniques for Periodontally Compromised Teeth: A Report of Two Cases
Satarupa Suklabaidya, Ilakiya Mathi, Kennedy Babu, Gandhimadhi D, Manoj Margabandhu
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of Palatal Radicular Groove in upper Lateral Incisors: A CBCT study at Isfahan Azad dental school
Amirreza Zefreh, Azadeh Torkzadeh, Hajar Shekarchizadeh, Maryam Zare Jahromi, Rojin Ardalani
Contemporary Orofacial Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A classification of radicular grooves from the perspective of periodontology
Huxiao Li, Zhaowei Tai, Jiachen Dong, Zhongchen Song
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in Root Canal Therapy: Translational Innovations and the Role of Nanoparticles in Endodontic Treatment
Noha M. Badawi, Mohamed M. Kataia, Hadeel A. Mousa, Mozhgan Afshari
Journal of Nanotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation to estimate the prevalence of palatogingival groove in the maxillary anterior teeth and its radiographic characteristics: An institutional retrospective study
Mousumi Biswas, Dibyendu Mazumdar, Binayak Saha, Siddhi Agarwala, Kallol Kumar Saha, Kuntal Chowdhury
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(3): 233. CrossRef - A Three-Dimensional Assessment of a Type I Shallow Palatogingival Groove by Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Case Report
Ramachandra Reddy Gowda Venkatesha, Karthik Rajaram Mohan, Saramma Mathew Fenn, Sabitha Gokulraj, Kumar Appusamy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Approaches of Palatogingival Groove: A Systematic Review
Greta Venskutė
Journal of Dental Health and Oral Research.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Palatal groove associated with periodontal lesions: a systematic review illustrated by a decisional tree for management
Yvan Gaudex, Vianney Gandillot, Isabelle Fontanille, Philippe Bouchard, Stephane Kerner, Maria Clotilde Carra
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Palatogingival Groove: The Known–unknown Devourer
Sandeep Tandon, Rinku Mathur, Ambika S Rathore, Tripti S Rai, Kanchan Kumari Dhaker, Sumedha Gupta
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(S1): S95. CrossRef - Nomogram to predict radicular grooves in maxillary lateral incisors in preoperative orthodontic population
Xiuneng Zhou, Jie Deng, Nianke Liu, Chunhui Yang, Shiyu Li, Yaling Song
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Palatogingival Groove in Maxillary Lateral Incisor: A Report of a Rare Case With a Brief Review of Literature
Irfan Ansari, Sanjay Miglani, Vijay Yadav, Shamimul Hasan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of palatogingival groove affecting maxillary anterior teeth in Saudi subpopulation: A cone-beam computed tomographic study with literature review
Ali Ibrahim Aljuailan, Roqayah Aljuailan, Rahul N. Gaikwad, Shaul Hameed Kolarkodi, Nasser Rufaydan Alamri
The Saudi Dental Journal.2023; 35(8): 1039. CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Interdisciplinary approach for diagnosis and management of the tooth with type III palatogingival groove
Harakh Chand Baranwal, Jyoti Yadav
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(2): 211. CrossRef - Progress in Diagnosis and Treatment of Palatogingival Groove
倩 郑
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(04): 2723. CrossRef - Palatogingival grooves associated with periodontal bone Loss of maxillary incisors in a Chinese population
Rui Zhang, Jie Xiong, Markus Haapasalo, Ya Shen, Liuyan Meng
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(2): 313. CrossRef - Surgical management of lateral lesions with intentional replantation in single-rooted mandibular first premolars with radicular groove
Ya-Hsin Yu, Minje Kim, Samuel Kratchman, Bekir Karabucak
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2022; 153(4): 371. CrossRef - Management of the palato-radicular groove with a periodontal regenerative procedure and prosthodontic treatment: A case report
Dan-Hua Ling, Wei-Ping Shi, Yan-Hong Wang, Dan-Ping Lai, Yan-Zhen Zhang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(17): 5732. CrossRef - Combined Periodontal and Endodontic Management of Palatal Radicular Groove with Platelet‐Rich Fibrin and Biodentine®
Arjun Hari Rijal, Bhageshwar Dhami, Pratistha Ghimire, Konstantinos Michalakis
Case Reports in Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intentional replantation combined root resection therapy for the treatment of type III radicular groove with two roots: A case report
Dan Tan, Shi-Ting Li, Hao Feng, Zhong-Chao Wang, Cai Wen, Min-Hai Nie
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(20): 6991. CrossRef - DENTAL DEFECTS WITH SUBGINGIVAL EXTENSION: A RESTORATIVE CONUNDRUM
Seema Yadav
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2021; : 20. CrossRef - Misdiagnosis or Missed Diagnosis? Cone-Beam Computed Tomography-Aided Multidisciplinary Management of Maxillary Central Incisor with Palatogingival Groove
R. Kurinji Amalavathy, K.M. Vidya, Sonali Nabil Sarooshi, Hrudi Sundar Sahoo
Indian Journal of Dental Sciences.2021; 13(1): 46. CrossRef - Root and Root Canal Morphology: Study Methods and Classifications
Duaa M Shihab , Anas F Mahdee
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2021; 33(4): 11. CrossRef - Prevalence and radiological characteristics of palatogingival groove: A retrospective cone-beam computed tomography study in an Indian cohort
MS Lekshmi, Sheetal Sharma, ShaliniR Gupta, Sidhartha Sharma, Vijay Kumar, Amrita Chawla, Ajay Logani
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(4): 359. CrossRef - Successful Multidisciplinary Management of an Endodontic‐Periodontal Lesion Associated With a Palato‐Radicular Groove: A Case Report
Diksha Katwal, Jennifer K. Fiorica, Jane Bleuel, Stephen J. Clark
Clinical Advances in Periodontics.2020; 10(2): 88. CrossRef - Anatomical, microbiological, and genetic considerations in treatment of Chinese periodontal patients
Edwin X. J. Goh, Marianne M. A. Ong
Journal of Investigative and Clinical Dentistry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A new system for classifying tooth, root and canal anomalies
H. M. A. Ahmed, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(4): 389. CrossRef
- Prevalence of Palatal Grooves on Maxillary Anterior Teeth Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 8,199 View
- 173 Download
- 35 Crossref

- Mandibular bone necrosis after use of paraformaldehyde-containing paste
- Chi-hwan Lee, Yoorina Choi, Sujung Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):332-337. Published online November 8, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Paraformaldehyde has been used in the past as a pulpotomy agent. However, it has a severe cytotoxic effect and may cause alveolar bone necrosis. Depulpin, a devitalizing agent containing 49% paraformaldehyde, is no longer used frequently due to its severe side effects. In the two cases described in the present study, Depulpin was used as a devitalizing agent during root canal treatment. It caused a gradual loss of sensibility in adjacent teeth, gingival necrosis, and osteomyelitis. This case report demonstrates the serious side effects of using a paraformaldehyde-containing paste as a devitalizing agent for pulp, particularly mandibular bone necrosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Numb chin syndrome caused by paraformaldehyde-containing devitalizing agent – Case report
Jyh-Kwei Chen, Yeung-Yi Hsu, Chun-Pin Chiang, Meng-Ling Chiang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(2): 955. CrossRef - Non-radiation and non-drug–induced maxillary osteomyelitis: Study of underlying risk factors, presentation, management and treatment outcomes
Kumar Nilesh, Pankaj Patil, Digvijay Patil, Monica Patil
Medical Journal Armed Forces India.2022; 78: S145. CrossRef - Acute toxicity potential and impact on periodontal and periapical tissue of Pulp Out: A paste contained jatropha, sidaguri, and melittin
Maria Tanumihardja, A.M. Windha, N. Musfirah, G.K. Punggawa, Andi Fatima, A.H.M. Nur Fadhila, Esfandiary, Nurhayaty Natsir, Husni Cangara, Lukman Muslimin
Toxicology Reports.2022; 9: 1788. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the effect of two pulpal medicaments on pain and bleeding status of mandibular molars with irreversible pulpitis post-failure of inferior alveolar nerve block: a double-blind, randomized, clinical trial
Naomi Ranjan Singh, Lora Mishra, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Nike Kurniawati, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum
PeerJ.2022; 10: e13397. CrossRef - Dental implant restoration of mandibular bone necrosis defects caused by use of paraformaldehyde-containing paste: A case report
Won-Pyo Lee, Ho-Keel Hwang, Hyoung-Hoon Jo
Oral Biology Research.2019; 43(1): 110. CrossRef - Is Panoramic Radiography an Accurate Imaging Technique for the Detection of Endodontically Treated Asymptomatic Apical Periodontitis?
Cosimo Nardi, Linda Calistri, Giulia Grazzini, Isacco Desideri, Chiara Lorini, Mariaelena Occhipinti, Francesco Mungai, Stefano Colagrande
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(10): 1500. CrossRef - A case of high density abnormality in x-ray findings of mandible caused by leakage of root canal filling paste
Haruko Kashiwamura, Kyoko Oka, Yoko Tuchihashi, Hanako Yoshioka, Mayumi Kato, Atsuko Baba, Toyohiro Kagawa, Kazuhiko Okamura, Masao Ozaki
Pediatric Dental Journal.2017; 27(3): 162. CrossRef
- Numb chin syndrome caused by paraformaldehyde-containing devitalizing agent – Case report
- 2,883 View
- 20 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of proanthocyanidin, a crosslinking agent, on physical and biological properties of collagen hydrogel scaffold
- Yoorina Choi, Hee-Jin Kim, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):296-303. Published online October 4, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.296
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the effects of proanthocyanidin (PAC), a crosslinking agent, on the physical properties of a collagen hydrogel and the behavior of human periodontal ligament cells (hPDLCs) cultured in the scaffold.
Materials and Methods Viability of hPDLCs treated with PAC was measured using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The physical properties of PAC treated collagen hydrogel scaffold were evaluated by the measurement of setting time, surface roughness, and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The behavior of the hPDLCs in the collagen scaffold was evaluated by cell morphology observation and cell numbers counting.
Results The setting time of the collagen scaffold was shortened in the presence of PAC (
p < 0.05). The surface roughness of the PAC-treated collagen was higher compared to the untreated control group (p < 0.05). The thermogram of the crosslinked collagen exhibited a higher endothermic peak compared to the uncrosslinked one. Cells in the PAC-treated collagen were observed to attach in closer proximity to one another with more cytoplasmic extensions compared to cells in the untreated control group. The number of cells cultured in the PAC-treated collagen scaffolds was significantly increased compared to the untreated control (p < 0.05).Conclusions Our results showed that PAC enhanced the physical properties of the collagen scaffold. Furthermore, the proliferation of hPDLCs cultured in the collagen scaffold crosslinked with PAC was facilitated. Conclusively, the application of PAC to the collagen scaffold may be beneficial for engineering-based periodontal ligament regeneration in delayed replantation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of collagen crosslinkers on sodium hypochlorite treated dentin bond strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Weiqing Zhou, Shuting Feng, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Proliferative Effect of Proanthocyanidins on HGF-1 and HPDLF Cells: An In Vitro Study
Evelina Alkimavičienė, Nomeda Basevičienė, Arvydas Strazdauskas, Rasa Banienė, Nijolė Savickienė
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2098. CrossRef - A highly biocompatible CE-crosslinked collagen implant with exceptional anti-calcification and collagen regeneration capabilities for aging skin rejuvenation
Qi Wang, Huiyu Yan, Linyan Yao, Wenhua Li, Jianxi Xiao
Journal of Materials Chemistry B.2024; 12(18): 4467. CrossRef - Dexamethasone release from hyaluronic acid microparticle and proanthocyanidin-gelatin hydrogel in sciatic tissue regeneration
Kazem Javanmardi, Hamideh Shahbazi, Ava Soltani Hekmat, Mehdi Khanmohammadi, Arash Goodarzi
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - New Materials Based on Collagen and Taxifolin Derivatives: Production and Properties
Yu. V. Shatalin, M. I. Kobyakova, V. S. Shubina
Биологические мембраны Журнал мембранной и клеточной биологии.2024; 41(1): 82. CrossRef - Modulation of Adhesion and Migration of NIH/3T3 Cells in Collagen Materials by Taxifolin Derivatives
Yu. V. Shatalin, M. I. Kobyakova, V. S. Shubina
Biochemistry (Moscow), Supplement Series A: Membrane and Cell Biology.2023; 17(S1): S85. CrossRef - Development and characterization of crosslinked k-carrageenan/sericin blend with covalent agents or thermal crosslink for indomethacin extended release
Wedja Timóteo Vieira, Meuris Gurgel Carlos da Silva, Laura de Oliveira Nascimento, Melissa Gurgel Adeodato Vieira
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 246: 125558. CrossRef - New Challenges and Prospective Applications of Three-Dimensional Bioactive Polymeric Hydrogels in Oral and Craniofacial Tissue Engineering: A Narrative Review
Gamal Abdel Nasser Atia, Hany K. Shalaby, Naema Goda Ali, Shaimaa Mohammed Morsy, Mohamed Mohamady Ghobashy, Hager Abdel Nasser Attia, Paritosh Barai, Norhan Nady, Ahmad S. Kodous, Hasi Rani Barai
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(5): 702. CrossRef - Polyphenols: Bioavailability, Microbiome Interactions and Cellular Effects on Health in Humans and Animals
Michael B. Scott, Amy K. Styring, James S. O. McCullagh
Pathogens.2022; 11(7): 770. CrossRef - Advances of Hydrogel Therapy in Periodontal Regeneration—A Materials Perspective Review
Maoxue Li, Jiaxi Lv, Yi Yang, Guoping Cheng, Shujuan Guo, Chengcheng Liu, Yi Ding
Gels.2022; 8(10): 624. CrossRef - Collagen stabilization by natural cross-linkers: A qualitative and quantitative FTIR study on ultra-thin dentin collagen model
Rong WANG, Tyler STANLEY, Xiaomei YAO, Hang LIU, Yong WANG
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(3): 440. CrossRef - Cross-Linking Agents for Electrospinning-Based Bone Tissue Engineering
Dong-Jin Lim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(10): 5444. CrossRef - Dense lamellar scaffold, biomimetically inspired, for reverse cardiac remodeling: Effect of proanthocyanidins and glutaraldehyde
Thais Alves, Juliana Ferreira Souza, Venancio Alves Amaral, Alessandra Candida Rios, Tais Costa, Kessi Crescencio, Fernando Batain, Denise Grotto, Renata Lima, Lindemberg Silveira Filho, Jose Oliveira Junior, Patricia Severino, Norberto Aranha, Marco Chau
Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology.2021; 42(2): 248. CrossRef - The effect of the cross-linker ratio used in gellan gum biomaterial synthesis on biomineralization
Serbülent TÜRK, Burak ÜNLÜ, Mahmut ÖZACAR
Bulletin of Biotechnology.2021; 2(2): 27. CrossRef - The recent advances in scaffolds for integrated periodontal regeneration
Hyun Nyun Woo, Young Joon Cho, Solaiman Tarafder, Chang H. Lee
Bioactive Materials.2021; 6(10): 3328. CrossRef - Plant based cross-linkers for tissue engineering applications
Abhishek Indurkar, Ashish Pandit, Ratnesh Jain, Prajakta Dandekar
Journal of Biomaterials Applications.2021; 36(1): 76. CrossRef - Plant-based biomaterials in tissue engineering
Abhishek Indurkar, Ashish Pandit, Ratnesh Jain, Prajakta Dandekar
Bioprinting.2021; 21: e00127. CrossRef - Traditional Chinese Medicine and orthopedic biomaterials: Host of opportunities from herbal extracts
Huijuan Tang, Andrell Hosein, Monica Mattioli-Belmonte
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2021; 120: 111760. CrossRef - Adsorption of Gold Ions onto Sericin and Alginate Particles Chemically Crosslinked by Proanthocyanidins: a Complete Fixed-Bed Column Study
Nilza Tatiane das Graças Santos, Richard Landers, Meuris Gurgel Carlos da Silva, Melissa Gurgel Adeodato Vieira
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.2020; 59(1): 318. CrossRef - Proanthocyanidin as a crosslinking agent for fibrin, collagen hydrogels and their composites with decellularized Wharton’s-jelly-extract for tissue engineering applications
Elham Hasanzadeh, Narges Mahmoodi, Arefeh Basiri, Faezeh Esmaeili Ranjbar, Zahra Hassannejad, Somayeh Ebrahimi-Barough, Mahmoud Azami, Jafar Ai, Vafa Rahimi-Movaghar
Journal of Bioactive and Compatible Polymers.2020; 35(6): 554. CrossRef - Hydrogels for the Delivery of Plant-Derived (Poly)Phenols
Nicola Micale, Andrea Citarella, Maria Sofia Molonia, Antonio Speciale, Francesco Cimino, Antonella Saija, Mariateresa Cristani
Molecules.2020; 25(14): 3254. CrossRef - Natural biopolymer‐based hydrogels for use in food and agriculture
Miri Klein, Elena Poverenov
Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture.2020; 100(6): 2337. CrossRef - Grape Seed-Inspired Smart Hydrogel Scaffolds for Melanoma Therapy and Wound Healing
Hongshi Ma, Quan Zhou, Jiang Chang, Chengtie Wu
ACS Nano.2019; 13(4): 4302. CrossRef - Improvement of the Physical Properties of Guided Bone Regeneration Membrane from Porcine Pericardium by Polyphenols-Rich Pomace Extract
Nazario Russo, Clara Cassinelli, Elisa Torre, Marco Morra, Giorgio Iviglia
Materials.2019; 12(16): 2564. CrossRef - Novel Biomedical Applications of Crosslinked Collagen
Lisha Gu, Tiantian Shan, Yu-xuan Ma, Franklin R. Tay, Lina Niu
Trends in Biotechnology.2019; 37(5): 464. CrossRef - The prospects of collagen as a basis for curable and activated osteoplastic materials
N. L. Fatkhudinova, A. V. Vasilyev, T. B. Bukharova, E. O. Osidak, N. V. Starikova, S. P. Domogatsky, D. V. Goldshtein, A. A. Kulakov
Stomatologiya.2018; 97(6): 78. CrossRef
- Effect of collagen crosslinkers on sodium hypochlorite treated dentin bond strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- 1,886 View
- 8 Download
- 26 Crossref

-
In vitro evaluation of a newly produced resin-based endodontic sealer - Yoo-Seok Song, Yoorina Choi, Myung-Jin Lim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Chan-Ui Hong, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):189-195. Published online July 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives A variety of root canal sealers were recently launched to the market. This study evaluated physicochemical properties, biocompatibility, and sealing ability of a newly launched resin-based sealer (Dia-Proseal, Diadent) compared to the existing root canal sealers (AHplus, Dentsply DeTrey and ADseal, Metabiomed).
Materials and Methods The physicochemical properties of the tested sealers including pH, solubility, dimensional change, and radiopacity were evaluated. Biocompatibility was measured using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. For microleakage test, single-rooted teeth were instrumented, and obturated with gutta-percha and one of the sealers (
n = 10). After immersion in 1% methylene blue solution for 2 weeks, the specimens were split longitudinally. Then, the maximum length of staining was measured. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey test (p = 0.05).Results Dia-Proseal showed the highest pH value among the tested sealers (
p < 0.05). ADseal showed higher dimensional change compared to AHplus and Dia-Proseal (p < 0.05). The solubility values of AHplus and Dia-Proseal were similar, whereas ADseal had the lowest solubility value (p < 0.05). The flow values of sealer in increasing order were AHplus, DiaProseal, and ADseal (p < 0.05). The radiopacity of AHplus was higher than those of ADseal and Dia-Proseal (p < 0.05). The cell viability of the tested materials was statistically similar throughout the experimental period. There were no significant differences in microleakage values among the tested samples.Conclusions The present study indicates that Dia-Proseal has acceptable physicochemical properties, biocompatibility, and sealing ability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
Amira Galal Ismail, Manar M. Galal, Tamer M. Hamdy
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2026; 16(2): 101400. CrossRef - Comparison of Apical Sealing Ability of Different Endodontic Sealers – An In Vitro Study
Supriya Patil, Rahul Singh, B Jyothi Lekshmi, Sameer Ahmed Khan, H Shalini, Prashanth Kumar Katta
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 1): S513. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of ICON resin infiltration and bioactive glass adhesive for managing initial caries lesions using quantitative light-induced fluorescence: a randomized clinical trial
Zakereyya S.M. Albashaireh, Susan N. Al-Khateeb, Malak K. Altallaq
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 159: 105853. CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparison of Epoxy Resin Sealer Removal During Endodontic Retreatment
Prashant A Bondarde, Aditi S Patkar, Aishwarya R Pawar, Rukmini Pande, Akshata Deshpande, Rachana S Agrawal, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Stereomicroscopic evaluation of sealing ability of four different root canal sealers: an in-vitro study
Sonam Sah, Panna Mangat, Ajay Kumar, Neha Sah, Ganiga Channaiah Shivakumar, Marco Di Blasio, Gabriele Cervino, Giuseppe Minervini
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Physicochemical properties of AH plus bioceramic sealer, Bio-C Sealer, and ADseal root canal sealer
Tamer M. Hamdy, Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Shehabeldin Saber
Head & Face Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Biological investigation of resinous endodontic sealers containing calcium hydroxide
Carlos Roberto Emerenciano Bueno, Francine Benetti, Marina Tolomei Sandoval Cury, Ana Maria Veiga Vasques, Leopoldo Cosme-Silva, Índia Olinta de Azevedo Queiroz, Ana Cláudia Rodrigues da Silva, Rogério de Castilho Jacinto, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, E
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(7): e0287890. CrossRef - Comparison of the apical seal obtained by Adseal, Proseal, and AH26 sealers in root canal obturation with lateral compaction technique
Akam Saeidi, Romina Hajipour, Elham Mahmoudi, Farideh Feizi, Soraya Khafri
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Cytotoxicity of Calcium Silicate-based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Sealers: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Nezar Boreak, Mazen Ahmed Qadi, Faisal Hadi Khormi, Luay Mutaen Faqiri, Sadeem Omar Zaylai, Yaser Ali Jad, Bassam Ali Hamdi, Asayil Juraybi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 24(8): 610. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of push-out bond strength of bioceramic and epoxy sealers after using various final irrigants: An in vitro study
Chandrasekhar Veeramachaneni, Swathi Aravelli, Sreeja Dundigalla
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(2): 145. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Reinforcement Using MTA-based, Epoxy Resin-based, and Silicone-based Endodontic Sealers in Canals Instrumented with Single-file Rotary System: An In Vitro Study
Reshma Rajasekhar, Varsha Maria Sebastian, Farhat Nasreen, Pramod Junjanna, Azeem Hassan, Venkidesh Hari Maratt
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(10): 1098. CrossRef - The Short-Term Antibacterial Activity of Three Selected Endodontic Sealers against Enterococcus faecalis Bacterial Culture
Matej Rosa, Yuliya Morozova, Roman Moštěk, Pavel Holík, Lucia Somolová, Barbora Novotná, Soňa Zábojníková, Kateřina Bogdanová, Kateřina Langová, Iva Voborná, Lenka Pospíšilová, Josef Paul Kovařík
Life.2022; 12(2): 158. CrossRef - Antimicrobial potential of AH Plus supplemented with bismuth lipophilic nanoparticles on E. faecalis isolated from clinical isolates
Jesús Alejandro Torres-Betancourt, Rene Hernandez-Delgadillo, Jorge Jaime Flores-Treviño, Juan Manuel Solís-Soto, Nayely Pineda-Aguilar, Maria Argelia Akemi Nakagoshi-Cepeda, Rosa Isela Sánchez-Nájera, Shankararaman Chellam, Claudio Cabral-Romero
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectrometry Analysis and Radiopacity of Five Different Root Canal Sealers
Gözde Kandemir Demirci, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Seniha Miçooğulları Kurt, Burcu Serefoglu, Pelin Güneri, Michael Hülsmann, Mehmet Kemal Caliskan
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(5): 1. CrossRef - Ultrasonic vibration and thermo‐hydrodynamic technique for filling root canals: Technical overview and a case series
Yong‐Sik Cho
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1668. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties of Two Generations of MTA-Based Root Canal Sealers
Sawsan Abu Zeid, Hadeel Yaseen Edrees, Abeer Abdulaziz Mokeem Saleh, Osama S. Alothmani
Materials.2021; 14(20): 5911. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiopacity of endodontic materials using two models for conversion to millimeters of aluminum
Victor Manuel OCHOA-RODRÍGUEZ, Jorge Homero WILCHES-VISBAL, Barbara ROMA, Hernán COAGUILA-LLERENA, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO, Andréa GONÇALVES, Rubens SPIN-NETO, Gisele FARIA
Brazilian Oral Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Flow characteristics and alkalinity of novel bioceramic root canal sealers
Anastasios Katakidis, Konstantinos Sidiropoulos, Elisabeth Koulaouzidou, Christos Gogos, Nikolaos Economides
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - SELECTED PROPERTIES OF CONTEMPORARY ENDODONTIC SEALERS: PART 1
M Rosa, Y Morozova, R Moštěk, A Jusku, V Kováčová, L Somolová, I Voborná, T Kovalský
Česká stomatologie a praktické zubní lékařství.2020; 120(4): 107. CrossRef - Calcium phosphates as fillers for methacrylate-based sealer
Flávia Veronezi Rostirolla, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Fabio Rocha Bohns, Fernando Freitas Portella, Susana Maria Werner Samuel, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(12): 4417. CrossRef - Do in vitro solubility studies on endodontic sealers demonstrate a high level of evidence? A systematic review
Ankur Razdan, Ana Raquel Benetti, Lars Bjørndal
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2019; 77(4): 253. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties of two epoxy resin-based sealants: Topseal® and Adseal™. a comparative study
Julio César Cardona-Hidalgo, José Manuel González-Carreño, Julio César Avendaño-Rueda
Revista Facultad de Odontología.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Comparison of Biocompatibility of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Ju Kyung Lee, Sunil Kim, Sukjoon Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Euiseong Kim
Materials.2019; 12(15): 2411. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties of Epoxy Resin-Based and Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers
Ju Kyung Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
- 2,083 View
- 21 Download
- 27 Crossref

- The effect of saliva decontamination procedures on dentin bond strength after universal adhesive curing
- Jayang Kim, Sungok Hong, Yoorina Choi, Sujung Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):299-305. Published online October 2, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.299
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the effectiveness of multiple decontamination procedures for salivary contamination after curing of a universal adhesive on dentin bond strength according to its etch modes.
Materials and Methods Forty-two extracted bovine incisors were trimmed by exposing the labial dentin surfaces and embedded in cylindrical molds. A universal adhesive (All-Bond Universal, Bisco) was used. The teeth were randomly divided into groups according to etch mode and decontamination procedure. The adhesive was applied according to the manufacturer's instructions for a given etch mode. With the exception of the control groups, the cured adhesive was contaminated with saliva for 20 sec. In the self-etch group, the teeth were divided into three groups: control, decontamination with rinsing and drying, and decontamination with rinsing, drying, and adhesive. In the etch-and-rinse group, the teeth were divided into four groups: control, decontamination with rinsing and drying, decontamination with rinsing, drying, and adhesive, and decontamination with rinsing, drying, re-etching, and reapplication of adhesive. A composite resin (Filtek Z350XT, 3M ESPE) was used for filling and was cured on the treated surfaces. Shear bond strength was measured, and failure modes were evaluated. The data were subjected to one-way analysis of variation and Tukey's HSD test.
Results The etch-and-rinse subgroup that was decontaminated by rinse, drying, re-etching, and reapplication of adhesive showed a significantly higher bond strength.
Conclusions When salivary contamination occurs after curing of the universal adhesive, additional etching improves the bond strength to dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of different methods of saliva decontamination on microshear bond strength of composite to composite: An in vitro study
Sara Ordooei Javan, Reza Movahedian, Somayeh Hosseini Tabatabaei
Dental Research Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in Resin-Dentin Bonding: Evaluating Pre-Treatment Techniques for Improved Adhesion
Rim Bourgi
Journal of Dental Health and Oral Research.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Effect of contamination and decontamination methods on the bond strength of adhesive systems to dentin: A systematic review
Rim Bourgi, Carlos Enrique Cuevas‐Suarez, Walter Devoto, Ana Josefina Monjarás‐Ávila, Paulo Monteiro, Khalil Kharma, Monika Lukomska‐Szymanska, Louis Hardan
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(8): 1218. CrossRef - Universal adhesive application to contaminated/non-contaminated dentin with three different protocols: An in vitro shear bond strength and SEM analysis
Tuğçe BALOGLU GONCU, Nasibe Aycan YILMAZ
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(4): 633. CrossRef - Tükürük kontaminasyon/dekontaminasyonunun üniversal adezivlerin dentine bağlanma dayanımına etkisi
Cansu ATALAY, Aybüke USLU, Ece MERAL, Ayşe YAZICI, A. Atila ERTAN
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(3): 611. CrossRef - Bioactive glass ceramic can improve the bond strength of sealant/enamel?
R. E. Silveira, R. G. Vivanco, R. C. de Morais, G. Da Col dos Santos Pinto, F. de C. P. Pires-de-Souza
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2019; 20(4): 325. CrossRef - Universal dental adhesives: Current status, laboratory testing, and clinical performance
Sanket Nagarkar, Nicole Theis‐Mahon, Jorge Perdigão
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2019; 107(6): 2121. CrossRef - Effect of Saliva Decontamination on Bond Strength of 1-step Self-etching Adhesives to Dentin of Primary Posterior Teeth
Junhee Lee, Shin Kim, Taesung Jeong, Jonghyun Shin, Eungyung Lee, Jiyeon Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2019; 46(3): 274. CrossRef - Polymeric materials and films in dentistry: An overview
Dinesh Rokaya, Viritpon Srimaneepong, Janak Sapkota, Jiaqian Qin, Krisana Siraleartmukul, Vilailuck Siriwongrungson
Journal of Advanced Research.2018; 14: 25. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity of Light-Cured Dental Materials according to Different Sample Preparation Methods
Myung-Jin Lee, Mi-Joo Kim, Jae-Sung Kwon, Sang-Bae Lee, Kwang-Mahn Kim
Materials.2017; 10(3): 288. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of different methods of saliva decontamination on microshear bond strength of composite to composite: An in vitro study
- 2,842 View
- 18 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Healing after horizontal root fractures: 3 cases with 2-year follow-up
- Yoorina Choi, Sung-Ok Hong, Seok-Ryun Lee, Kyung-San Min, Su-Jung Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):126-131. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.126
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Among dental traumas, horizontal root fractures are relatively uncommon injuries. Proper initial management and periodical evaluation is essential for the successful treatment of a root-fractured tooth. If pulpal necrosis develops, endodontic treatment is indicated, exclusively for the coronal fragment. Fragment diastases exert a great influence on healing at the fracture line and on pulpal necrosis. An adequately treated root-fractured tooth has a good prognosis. This case report describes the treatment and 2-yr follow up of 3 maxillary central incisors, first with horizontal root fracture, second with horizontal root fracture and avulsion, and third with horizontal root fracture and lateral luxation. All three cases were treated with mineral trioxide aggregate (ProRoot, Dentsply). During 2 yr of follow-up evaluation, the root-fractured teeth of the present patients were well retained in the arch, showing periodontal healing, even after endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Horizontal fracture of the tooth root: 3-year follow up study
Efka Zabokova-Bilbilova, Jasna Simonoska, Emilija Stefanovska, Mirjana Markovska-Arsovska
Acta stomatologica Naissi.2025; 41(91): 3061. CrossRef - Clinical applications of calcium silicate‐based materials: a narrative review
S Küçükkaya Eren
Australian Dental Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in maxillary central incisor with a horizontal mid root fracture after various management protocols
Kavitha Anantula, Bhavana Vankayala, SarjeevSingh Yadav
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(5): 470. CrossRef - : The Use of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate in The Treatment of Horizontal Root Fractures: A Case Presentation and Literature Update
Elif BALLIKAYA, Hamdi GÜNGÖR
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(3): 850. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part II: other clinical applications and complications
M. Torabinejad, M. Parirokh, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(3): 284. CrossRef
- Horizontal fracture of the tooth root: 3-year follow up study
- 2,510 View
- 22 Download
- 5 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


