Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 28(2); 2003 > Article
- Original Article Mechanical properties and microleakage of composite resin materials cured by variable light intensities
- Seung-Ryul Han, Kyung-San Min, Dong-Hoon Shin
-
2003;28(2):-145.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.2.134
Published online: March 31, 2003
Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Dankook University, Korea.
- Corresponding author (donyshin@dankook.ac.kr)
Copyright © 2003 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 888 Views
- 2 Download
Abstract
-
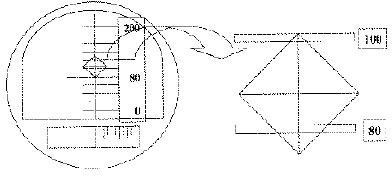
Mechanical properties and microleakage of two composites [conventional hybrid type DenFil (VERICOM Co., Anyang, Korea) / micro matrix hybrid type Esthet X (Dentsply Caulk, Milford, DE, U.S.A.)] were evaluated to assess whether variable light intensity curing is better than conventional curing technique.Curing was done for 40 seconds in two ways of 2 step soft-start technique and 5 step ramping technique. Three kinds of light intensities of 50, 100, 200 mW/cm2 were initially used for 10, 20, 30 seconds each and the maximum intensity of 600 mW/cm2 was used for the rest of curing time in a soft-start curing technique. In a ramping technique, curing was done with the same initial intensities and the light intensity was increased 5 times with the same rate to the maximum intensity of 600 mW/cm2.After determining conditions that showed no different mechanical properties with conventional technique, Esthet X composite was filled in a class V cavity, which dimension was 4×3×1.5 mm and cured under those conditions.Microleakage was evaluated in two ways of dye penetration and maximum gap estimation through SEM observation. ANOVA and Spearman's rho test were used to confirm any statistical significance among groups.The results were as follows:
Several curing conditions of variable light intensities resulted in the similar mechanical properties with a conventional continuous curing technique, except conditions that start curing with an initial light intensity of 50 mW/cm2,
Conventional and ramping techniques were better than soft-start technique in mechanical properties of microhardness and compressive strength.
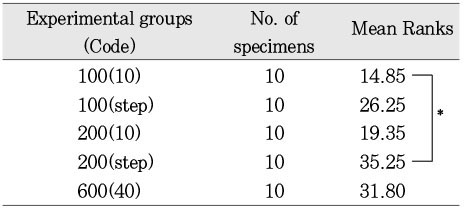
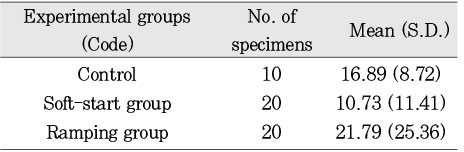
Soft-start group that started curing with an initial light intensity of 100 mW/cm2 for 10 seconds showed the least dye penetration. Soft-start group that started curing with an initial light intensity of 200 mW/cm2 for 10 seconds showed the smallest marginal gap, if there was no difference among groups.
Soft-start technique resulted in better dye-proof margin than conventional technique (p=0.014) and ramping technique(p=0.002).
There was a very low relationship(p=0.157) between the methods of dye penetration and marginal gap determination through SEM evaluation.
From the results of this study, it was revealed that ramping technique would be better than conventional technique in mechanical properties, however, soft-start technique might be better than conventional one in microleakage.It was concluded that much endeavor should be made to find out the curing conditions, which have advantages of both aspects or to solve these kinds of problems through a novel idea of polymerization.
- 1. Buonocore MG. A simple method of increasing the adhesion of acrylic materials to enamel surfaces. J Dent Res. 1955;34: 849-853.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Harrington E, Wilson HJ, Shortall AC. Light-activated restorative materials: a method of determining effective radiation times. J Oral Rehabil. 1996;23(3):210-218.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Silikas N, Eliades G, Watts DC. Light intensity effects on resin-composite degree of conversion and shrinkage strain. Dent Mater. 2000;16(4):292-296.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Sakaguchi RL, Sasik CT, Bunczak MA, Douglas WH. Strain gauge method for measuring polymerization contraction of composite restoratives. J Dent. 1991;19(5):312-326.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Mehl A, Hickel R, Kunzelmann KH. Physical properties and gap formation of light-cured composites with and without 'soft-start polymerization'. J Dent. 1997;25(3-4):321-330.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Goracci G, Mori G, Casa de'Martinis L. Curing light intensity and marginal leakage of resin composite restorations. Quint Int. 1996;27: 355-362.
- 7. Suh BI, Cripe CA, Yin R. Light intensity and exposure time effects on light cured composites. J Dent Res. 1998;77(Special issue B):Abst. No. #73.
- 8. Dennison JB, Yaman P, Seir R, Hamilton JC. Effect of variable light intensity on composite shrinkage. J Prosthet Dent. 2000;84(5):499-505.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Fan PL, Wozniak WT, Reyes WD, Stanford JW. Irradiance of visible light-curing units and voltage variation effects. J Am Dent Assoc. 1987;115(3):442-445.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Feilzer AJ, Dooren LH, de Gee AJ, Davidson CL. Influence of light intensity on polymerization shrinkage and integrity of restorative-cavity interface. Eur J Oral Sci. 1995;103(5):322-326.PubMed
- 11. Unterbrink GL, Muessner R. Influence of light intensity on two restorative systems. J Dent. 1995;23(3):183-189.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Peutzfeldt A, Sahafi A, Asmussen E. Characterization of resin composites polymerized with plasma arc curing units. Dent Mater. 2000;16(5):330-336.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Stritikus J, Owens B. An in vitro study of microleakage of occlusal composite restorations polymerized by a conventional curing light and a PAC curing light. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2000;24(3):221-227.PubMed
- 14. Park SM, Shin DH. Microhardness and microleakage of composite resin according to the change of curing light intensity. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2001;26(5):363-371.
- 15. Yap AU, Seneviratne C. Influence of light energy density on effectiveness of composite cure. Oper Dent. 2001;26(5):460-466.PubMed
- 16. Uno S, Asmussen E. Marginal adaptation of a restorative resin polymerized at reduced rate. Scand J Dent Res. 1991;99: 440-444.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Burgess JO, DeGoes M, Walker R, Ripps AH. An evaluation of four light-curing units comparing soft and hard curing. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent. 1999;11(1):125-133.PubMed
- 18. Koran P, Kurschner R. Effect of sequential versus continuous irradiation of a light-cured resin composite on shrinkage, viscosity, adhesion, and degree of polymerization. Am J Dent. 1998;11(1):17-22.PubMed
- 19. Yap AU, Ng SC, Siow KS. Soft-start polymerization: influence on effectiveness of cure and post-gel shrinkage. Oper Dent. 2001;26(3):260-266.PubMed
- 20. Yap AU, Soh MS, Siow KS. POst-gel shrinkage with pulse activation and soft-start polymerization. Oper Dent. 2002;27(1):81-87.PubMed
- 21. Friedl KH, Schmalz G, Hiller KA, Markl A. Marginal adaption of Class V restorations with and without "soft-start polymerization". Oper Dent. 2000;25(1):26-32.PubMed
- 22. Price RB, Bannerman RA, Rizkalla AS, Hall GC. Effect of stepped vs. continuous light curing exposure on bond strengths to dentin. Am J Dent. 2000;13(3):123-128.PubMed
- 23. Asmussen E, Peutzfeldt A. Influence of pulse-delay curing on softening of polymer structures. J Dent Res. 2001;80(6):1570-1573.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. St-Georges AJ, Swift EJ Jr, Thompson JY, Heymann HO. Curing light intensity effects on wear resistance of two resin composites. Oper Dent. 2002;27(4):410-417.PubMed
- 25. Bouschlicher MR, Rueggeberg FA, Boyer DB. Effect of stepped light intensity on polymerization force and conversion in a photoactivated composite. J Esthet Dent. 2000;12(1):23-32.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Lim BS, Ferracane JL, Sakaguchi RL, Condon JR. Reduction of polymerization contraction stress for dental composites by two-step light-activation. Dent Mater. 2002;18(6):436-444.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Obici AC, Sinhoreti MA, de Goes MF, Consani S, Sobrinho LC. Effect of the photo-activation method on polymerization shrinkage of restorative composites. Oper Dent. 2002;27(2):192-198.PubMed
- 28. Sakaguchi RL, Berge HX. Reduced light energy density decreases post-gel contraction while maintaining degree of conversion in composites. J Dent. 1998;26(8):695-700.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Yoshikawa T, Burrow MF, Tagami J. A light curing method for improving marginal sealing and cavity wall adaptation of resin composite restorations. Dent Mater. 2001;17(4):359-366.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations


Fig. 1
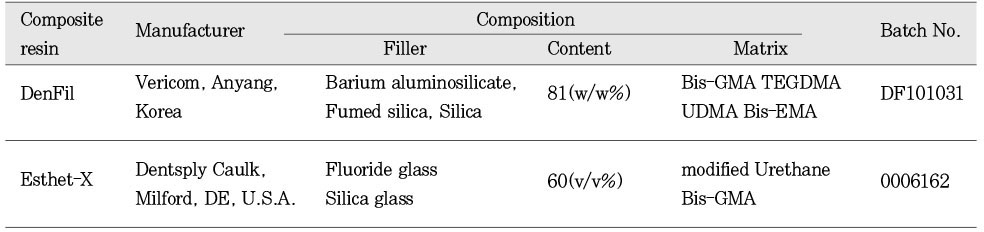
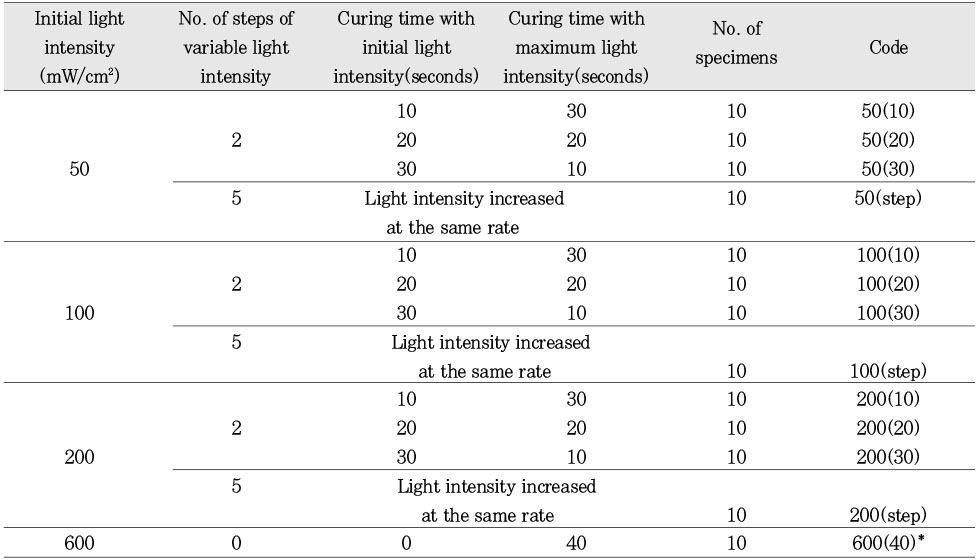
Experimental materials
Classification of experimental groups according to curing conditions
600(40)*:Control group
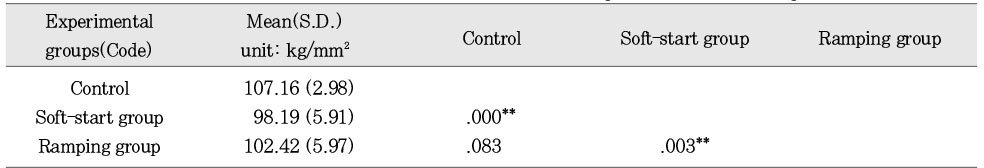
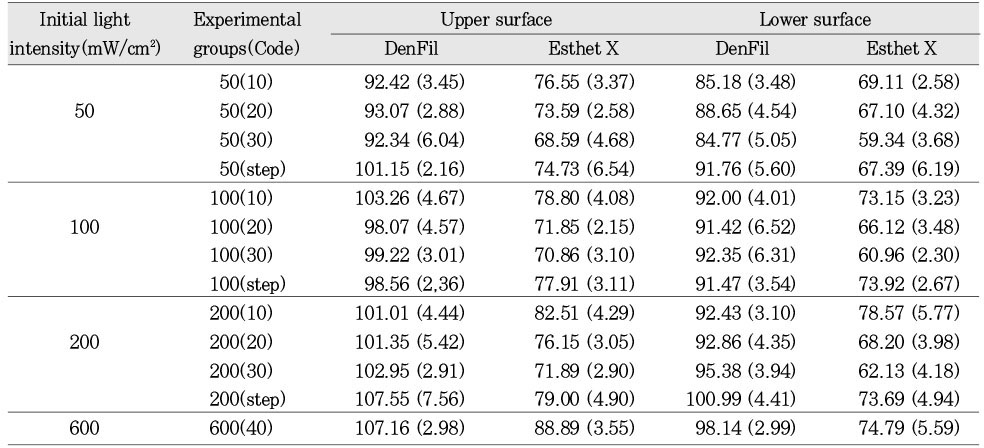
Vickers hardness [Mean (S.D.)] (unit: kg/mm2)
Mean hardness value and statistics of the upper surface according to ways of variable light intensity (DenFil)
**:p < 0.01
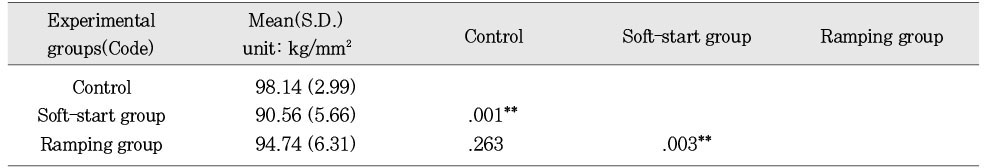
Mean hardness value and statistics of the lower surface according to ways of variable light intensity (DenFil)
**:p < 0.01
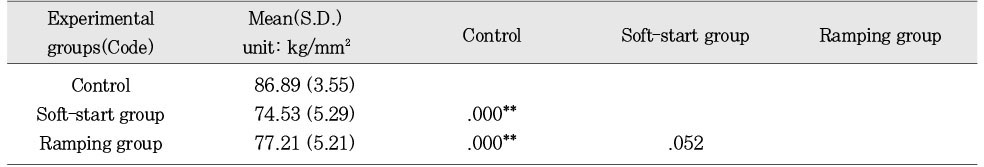
Mean hardness value and statistics of the upper surface according to ways of variable light intensity (Esthet X)
**:p < 0.01
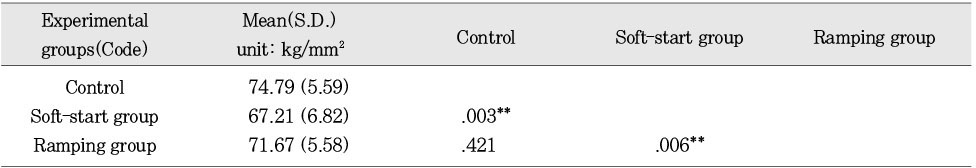
Mean hardness value and statistics of the lower surface according to ways of variable light intensity (Esthet X)
**:p < 0.01
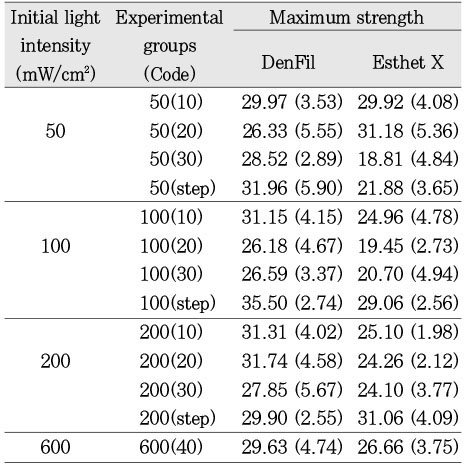
Maximum compressive strength (kg/mm2)
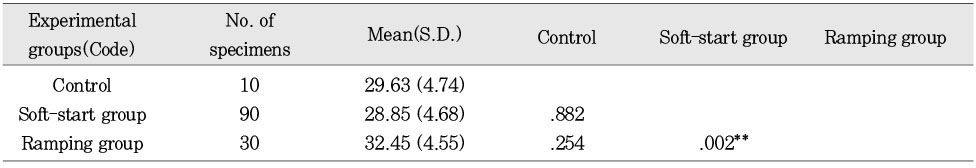
Mean maximum compressive strength and statistics of DenFil according to ways of variable light intensity (unit: kgf/mm2)
**:p < 0.01
Mean maximum compressive strength and statistics of Esthet X according to ways of variable light intensity (unit: kgf/mm2)
*:p < 0.05
Mean degree of dye penetration
Mean ranks of degree of dye penetration (Kruskal-Wallis test)
*:p < 0.05
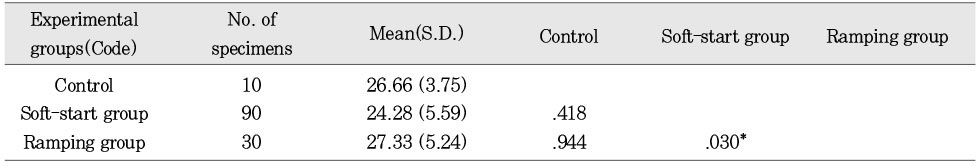
Mean degree of dye penetration and ranks at gingival margin according to ways of variable light intensity
*:p < 0.05 **:p < 0.01
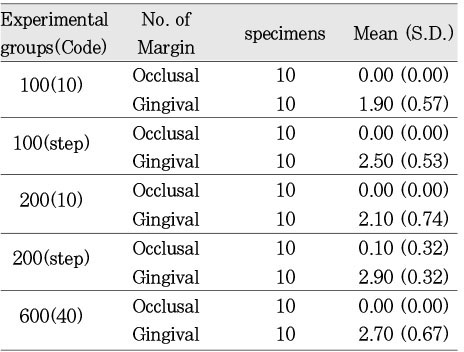
Maximum gap (unit: µm)
Mean maximum gap at gingival margin according to ways of variable light intensity (unit: µm)
600(40)*:Control group
**:p < 0.01
**:p < 0.01
**:p < 0.01
**:p < 0.01
**:p < 0.01
*:p < 0.05
*:p < 0.05
*:p < 0.05 **:p < 0.01

 KACD
KACD


 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

