-
Calcium silicate-based sealers remnants in isthmuses of mesial roots of mandibular molars: an in vitro evaluation
-
David Saldanha de Brito Alencar, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Francisco Haiter Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Marina Angélica Marciano
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e25. Published online July 15, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e25
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
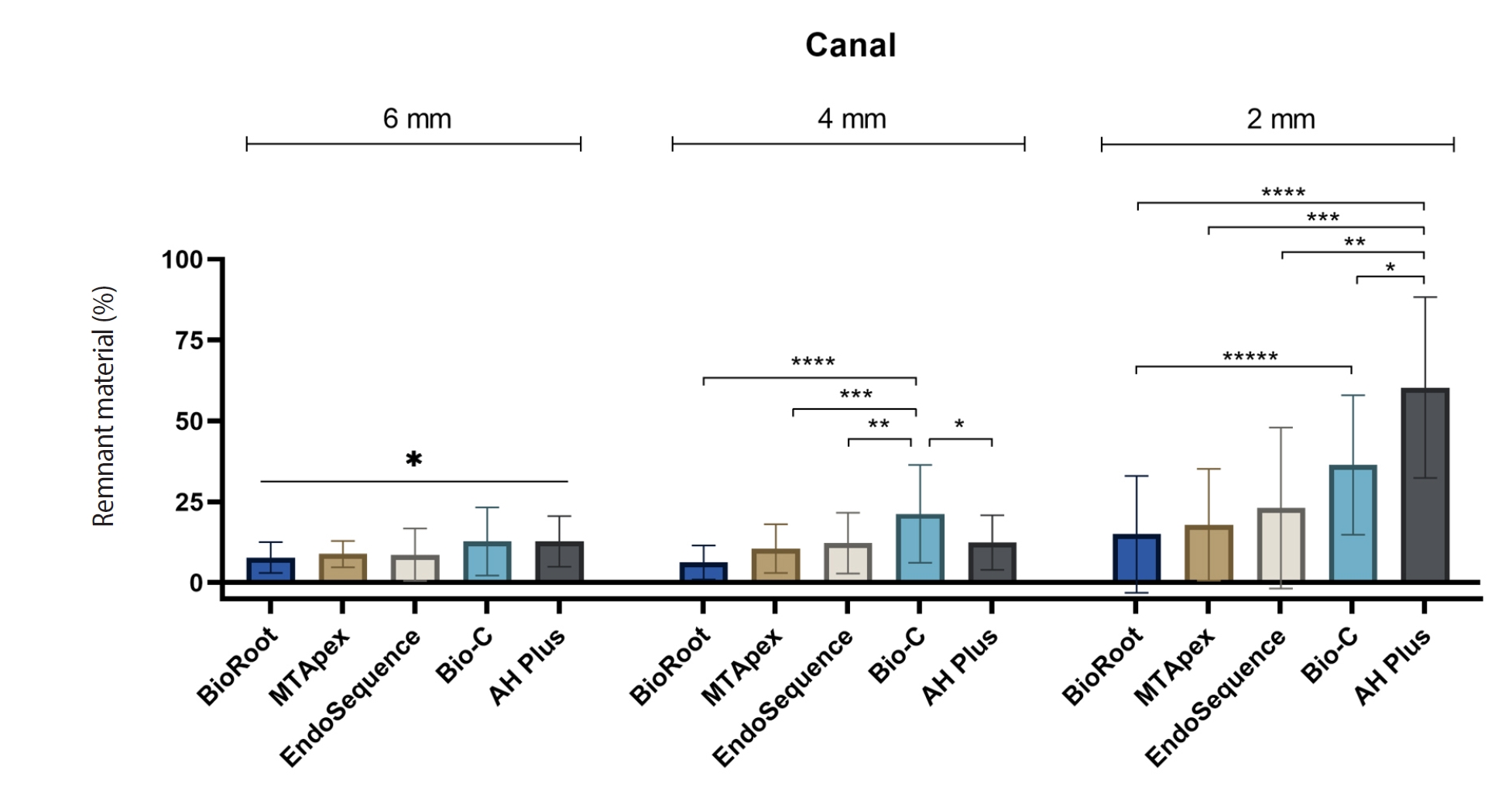
Endodontic retreatment aims to address treatment failure through the removal of root canal filling materials. This in vitro study evaluated the presence of filling material remnants in the mesial root canals, specifically focusing on the isthmuses, of mandibular molars after retreatment.
Methods
One hundred extracted mandibular molar mesial roots with isthmuses were prepared with an R25 file, obturated with one of five calcium silicate-based sealers (BioRoot RCS [Septodont], MTApex [Ultradent Products Inc.], EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow [Brasseler USA], Bio-C Sealer [Angelus]) or an epoxy resin-based sealer (AH Plus Jet [Dentsply Maillefer]), all stained with rhodamine B, and stored at 37ºC for 30 days to allow for setting. Retreatment was subsequently performed using R40 and XP-endo Finisher R instruments (FKG Dentaire) with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite irrigation. The presence of remaining filling material was then assessed using confocal microscopy, and setting times were tested per ISO 6876:2012.
Results
AH Plus Jet showed the most remnants at 2 mm and the longest retreatment time. Calcium silicate-based sealers exhibited prolonged setting times under dry conditions, with EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow showing a particularly extended setting period.
Conclusions
Despite retreatment, residues remained in all canals and isthmus regions, particularly Bio-C Sealer and AH Plus Jet in apical areas, emphasizing the difficulty of complete removal and the persistence of filling material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Bonding effects of mechanical removal of bioceramic sealer residues using glycine or glass microparticles abrasion
Jesus Aranda, Julia de Freitas Ceccato, Eduardo Fernández Godoy, João Felipe Besegato, Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb, Milton Carlos Kuga
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 148: 104289. CrossRef
-
2,038
View
-
113
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
|