-
Phase transformation temperatures influence the reduction ratio of fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium reciprocating files at body temperature: an in vitro experimental study
-
Walid Nehme, Alfred Naaman, Lola Pedèches, Sylvie Lê, Marie Georgelin-Gurgel, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Franck Diemer
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e35. Published online November 5, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e35
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
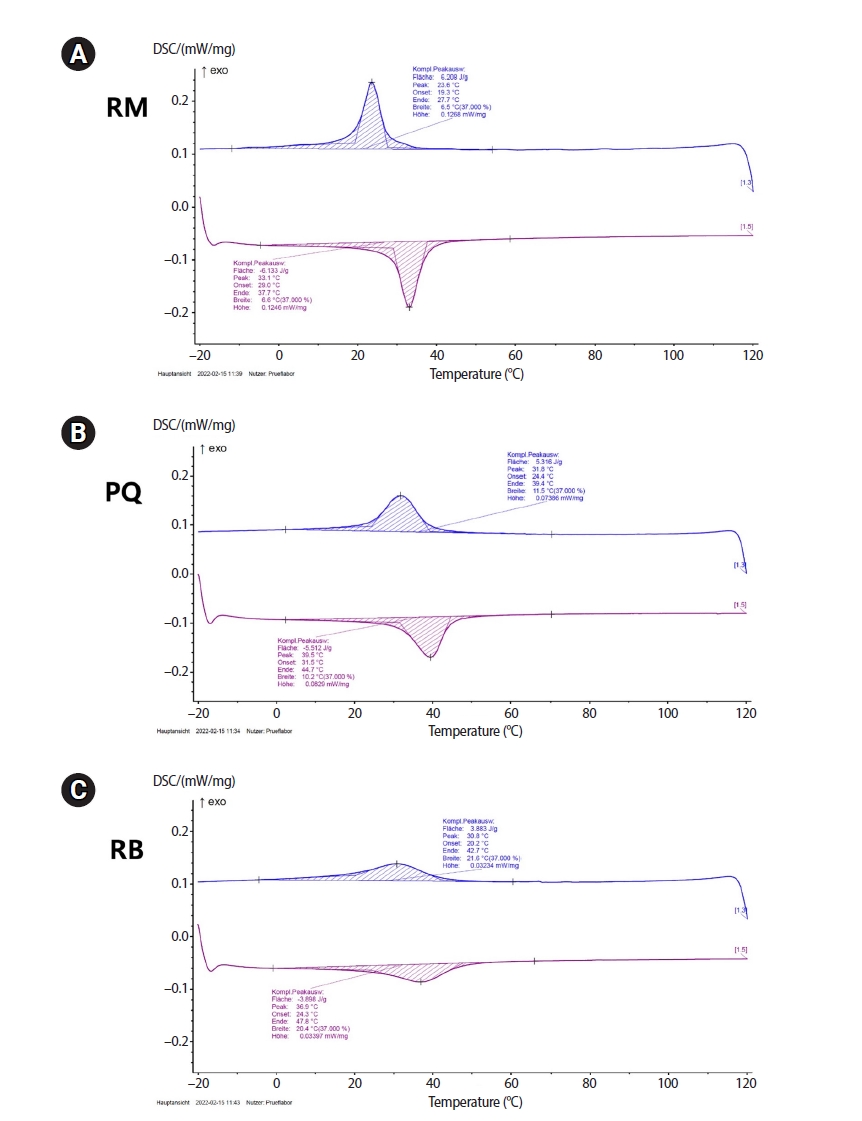
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of transformational temperatures on the cyclic fatigue resistance at body temperature of reciprocating file systems: R motion (RM), Procodile Q (PQ), and Reciproc Blue.
Methods
Resistance test was done in a custom-made device at room (20°C ± 1°C) and body (37°C ± 1°C) temperatures within a 60° angle of curvature and 5 mm radius of the artificial canal. The time to fracture (TTF) was recorded. The scanning electron microscope observation and differential scanning calorimetry analyses were performed. Two-way analysis of variance and Tukey post-hoc comparison were applied at a significance level of 0.05.
Results
The results showed a significant influence of temperature on instrumental breakage, regardless of the file systems (p < 0.05). The TTF is significantly decreased at body temperature (p < 0.05). PQ showed the longest TTF in both temperature conditions (p < 0.05). RM demonstrated a significantly higher TTF reduction ratio compared to the other files (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Within the limitations of this study, the heat-treated files with reciprocating kinetics may have different reduction ratios of the fatigue resistance of the file systems under different temperature conditions. This characteristic is an important point of consideration when clinicians select the file system to reduce potential file fracture.
-
Influence of disinfecting solutions on the surface topography of gutta-percha cones: a systematic review of in vitro studies
-
Lora Mishra, Gathani Dash, Naomi Ranjan Singh, Manoj Kumar, Saurav Panda, Franck Diemer, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Barbara Lapinska, Abdul Samad Khan
-
Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e42. Published online November 1, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e42
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The surface integrity of gutta-percha cones is a crucial factor in the success of endodontic procedures. Disinfecting solutions play a pivotal role in sterilizing gutta-percha cones, but their influence on gutta-percha surface topography remains a subject of concern. This systematic review aimed to present a qualitative synthesis of available laboratory studies assessing the influence of disinfecting solutions on the surface topography of gutta-percha and offers insights into the implications for clinical practice. The present review followed PRISMA 2020 guidelines. An advanced database search was performed in PubMed, Google Scholar, Embase, Scopus, LILAC, non-indexed citations and reference lists of eligible studies in May 2024. Laboratory studies, in English language, were considered for inclusion. The quality (risk of bias) of the included studies was assessed using parameters for in vitro studies. A total of 28 studies were included in the qualitative synthesis. Based on the included in vitro studies, surface deposits and alterations in the physical properties of gutta-percha cones were observed after the disinfection protocol. A comprehensive review of the available literature indicates that the choice of disinfecting solution, its concentration, and immersion time significantly affect the surface topography of gutta-percha cones. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - In Vitro Evaluation of Disinfectants on Gutta-Percha Cones: Antimicrobial Efficacy Against Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans
Tringa Kelmendi, Donika Bajrami Shabani, Aida Meto, Hani Ounsi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(19): 6846. CrossRef
-
4,049
View
-
197
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
|