-
Calcium silicate-based sealers remnants in isthmuses of mesial roots of mandibular molars: an in vitro evaluation
-
David Saldanha de Brito Alencar, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Francisco Haiter Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Marina Angélica Marciano
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e25. Published online July 15, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e25
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
Endodontic retreatment aims to address treatment failure through the removal of root canal filling materials. This in vitro study evaluated the presence of filling material remnants in the mesial root canals, specifically focusing on the isthmuses, of mandibular molars after retreatment.
Methods
One hundred extracted mandibular molar mesial roots with isthmuses were prepared with an R25 file, obturated with one of five calcium silicate-based sealers (BioRoot RCS [Septodont], MTApex [Ultradent Products Inc.], EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow [Brasseler USA], Bio-C Sealer [Angelus]) or an epoxy resin-based sealer (AH Plus Jet [Dentsply Maillefer]), all stained with rhodamine B, and stored at 37ºC for 30 days to allow for setting. Retreatment was subsequently performed using R40 and XP-endo Finisher R instruments (FKG Dentaire) with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite irrigation. The presence of remaining filling material was then assessed using confocal microscopy, and setting times were tested per ISO 6876:2012.
Results
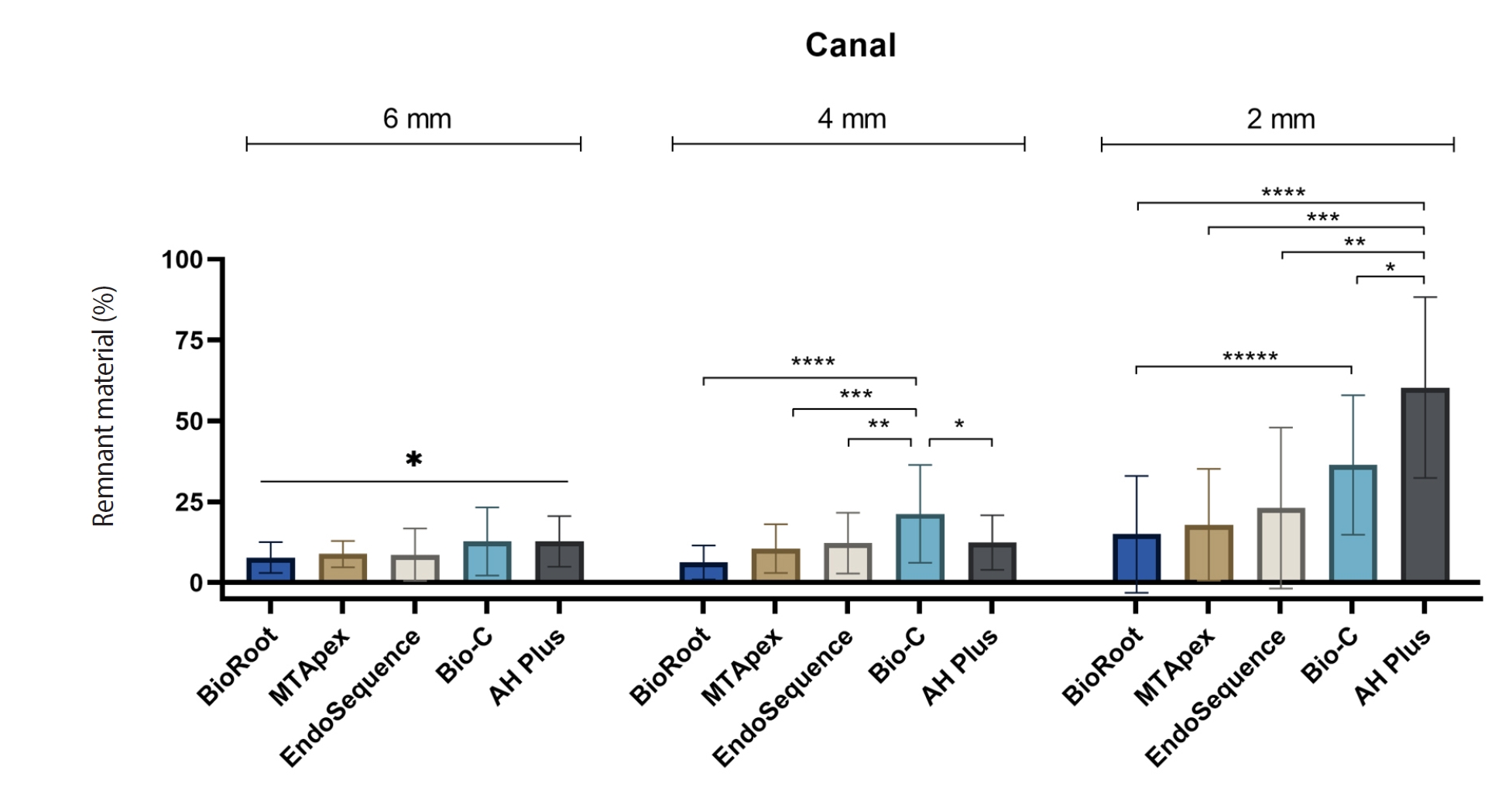
AH Plus Jet showed the most remnants at 2 mm and the longest retreatment time. Calcium silicate-based sealers exhibited prolonged setting times under dry conditions, with EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow showing a particularly extended setting period.
Conclusions
Despite retreatment, residues remained in all canals and isthmus regions, particularly Bio-C Sealer and AH Plus Jet in apical areas, emphasizing the difficulty of complete removal and the persistence of filling material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Bonding effects of mechanical removal of bioceramic sealer residues using glycine or glass microparticles abrasion
Jesus Aranda, Julia de Freitas Ceccato, Eduardo Fernández Godoy, João Felipe Besegato, Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb, Milton Carlos Kuga
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 148: 104289. CrossRef
-
2,038
View
-
113
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
Apical root canal cleaning after preparation with endodontic instruments: a randomized trial in vivo analysis
-
Volmir João Fornari, Mateus Silveira Martins Hartmann, José Roberto Vanni, Rubens Rodriguez, Marina Canali Langaro, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Alexandre Augusto Zaia
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e38. Published online June 24, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e38
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
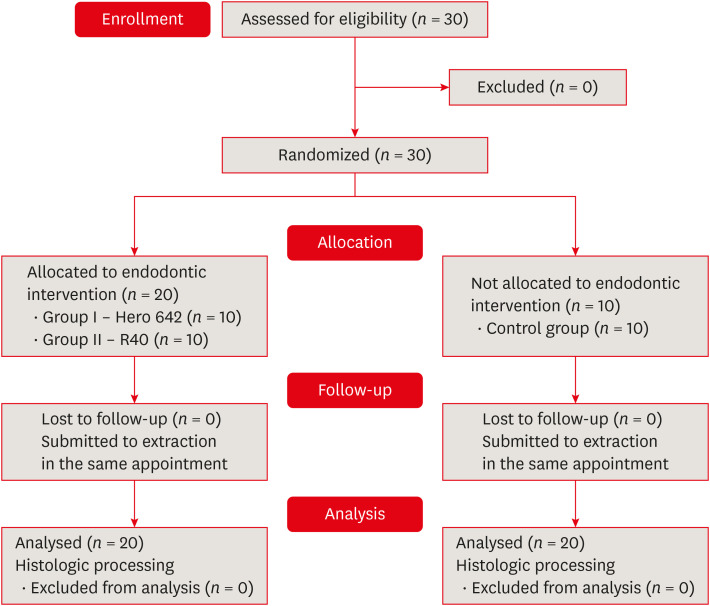
This study aimed to evaluate vital pulp tissue removal from different endodontic instrumentation systems from root canal apical third in vivo. Materials and MethodsThirty mandibular molars were selected and randomly divided into 2 test groups and one control group. Inclusion criteria were a positive response to cold sensibility test, curvature angle between 10 and 20 degrees, and curvature radius lower than 10 mm. Root canals prepared with Hero 642 system (size 45/0.02) (n = 10) and Reciproc R40 (size 40/0.06) (n = 10) and control (n = 10) without instrumentation. Canals were irrigated only with saline solution during root canal preparation. The apical third was evaluated considering the touched/untouched perimeter and area to evaluate the efficacy of root canal wall debridement. Statistical analysis used t-test for comparisons. ResultsUntouched root canal at cross-section perimeter, the Hero 642 system showed 41.44% ± 5.62% and Reciproc R40 58.67% ± 12.39% without contact with instruments. Regarding the untouched area, Hero 642 system showed 22.78% ± 6.42% and Reciproc R40 34.35% ± 8.52%. Neither instrument achieved complete cross-sectional root canal debridement. Hero 642 system rotary taper 0.02 instruments achieved significant greater wall contact perimeter and area compared to reciprocate the Reciproc R40 taper 0.06 instrument. ConclusionsHero 642 achieved higher wall contact perimeter and area but, regardless of instrument size and taper, vital pulp during in vivo instrumentation is not entirely removed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Unveiling the correlation between in vivo endodontic reciprocate instrumentation and crack formation
Mateus Silveira Martins Hartmann, José Roberto Vanni, Karla Rovaris, Lucas Jeziorski Hartmann, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Volmir João Fornari
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 150: 105367. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of stress distribution against the root canal wall at three different levels using novel NiTi rotary files – A finite element analysis
Rimjhim Singh, Sandeep Dubey, Palak Singh, Praveen Singh Samant, Suparna Ganguly Saha
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(1): 62. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Ultrasonic and Sonic Irrigant Activation Systems: Assessing Extrusion Risk, Debridement, and Biofilm Removal in Distinct Apical Preparation Sizes
Sara Paixão, Pedro Sousa Gomes, Maria Helena Fernandes, Cláudia Rodrigues, Liliana Grenho
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(9): 3904. CrossRef - A Short Report on the Effectiveness of Edge Taper Platinum and XP-3D Shaper for the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis Count in the Root Canal System: An Ex Vivo Study
Hanie Moaveni, Parastou Ghahari, Samira Behrad, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Sobhan Rashmee, Somayeh Teimoori
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2024; 16(2): 77. CrossRef - Comparative in Vitro Study on the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Endodontic Sealers Against Common Oral Pathogens
Csaba Dudás, Zsuzsanna Bardocz-Veres, Anita Iulia Gyulai, Silvia Izabella Pop, Melinda Székely, Bernadette Kerekes-Máthé, Mónika Kovács
Dentistry Journal.2024; 13(1): 17. CrossRef - Periradicular repair after single- and two-visit root canal treatments using ultrasonic irrigant activation and calcium hydroxide dressing of teeth with apical periodontitis: study protocol for randomized controlled trials
Gustavo M. Almeida, Vitor Hugo M. Carvalho, Érika B. P. Silva, Marco Antonio F. Cançado, Leonardo S. Barroso, Erica L. Queiroz, Tien Li An, Ana Paula D. Ribeiro, Jacy R. Carvalho-Junior, André F. Leite
Trials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of EndoSeal MTA, iRoot SP, and AH Plus against Planktonic Bacteria
Siew Thong Mak, Xin Fang Leong, In Meei Tew, Endang Kumolosasi, Lishen Wong
Materials.2022; 15(6): 2012. CrossRef - Influence of apical preparation size and final irrigation protocol on the debridement of oval root canals
Carolina Pessoa Stringheta, Rina Andréa Pelegrine, Victor Angelo Martins Montalli, James L Gutmann, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(6): 16. CrossRef
-
2,590
View
-
29
Download
-
8
Crossref
|