-
Resolvin E1 incorporated carboxymethyl chitosan scaffold accelerates repair of dental pulp stem cells under inflammatory conditions: a laboratory investigation
-
Hemalatha P Balasubramanian, Nandini Suresh, Vishnupriya Koteeswaran, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e40. Published online November 28, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e40
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
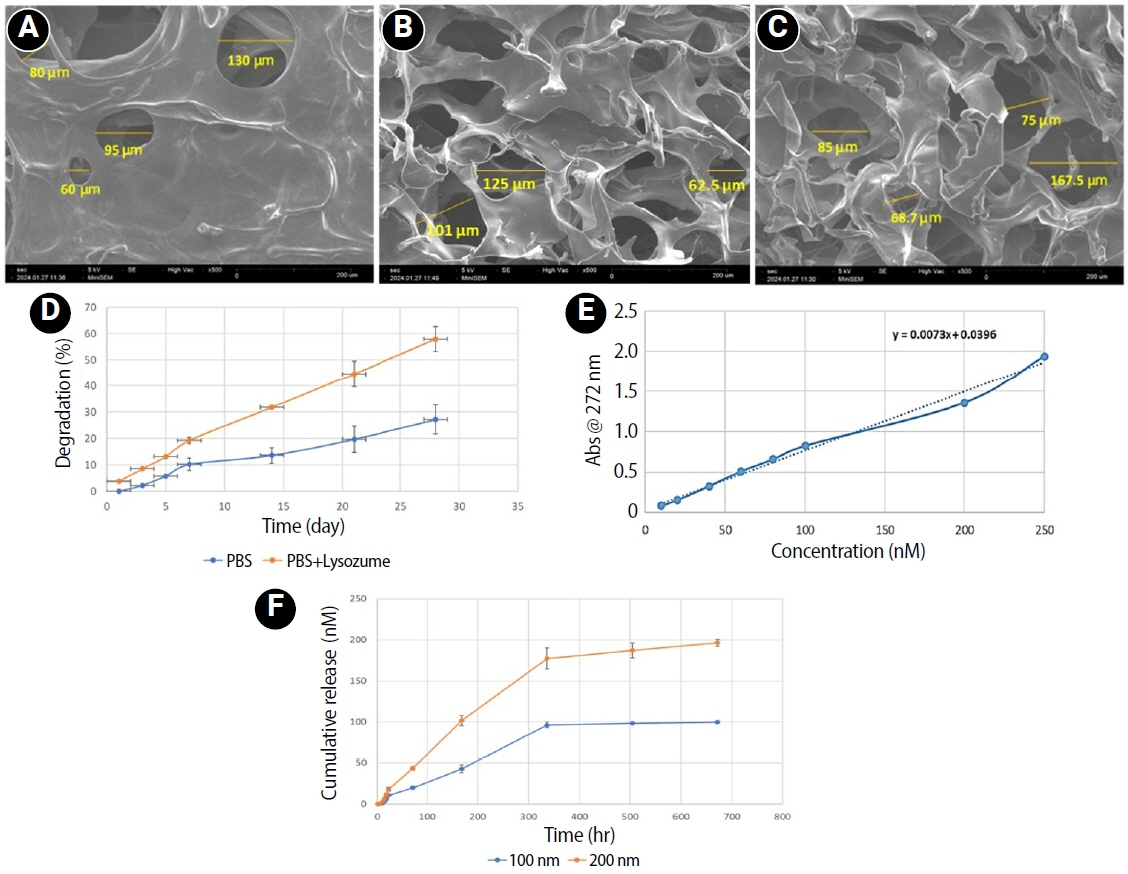
This study fabricated and characterized a resolvin E1 (RvE1)-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan (CMC) scaffold and determined its cytotoxicity and mineralization potential on inflamed human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs).
Methods
CMC scaffold incorporated with two concentrations of RvE1 (100 and 200 nM) was fabricated and characterized. The scaffolds’ porosity, drug release kinetics, and degradation were assessed. The impact of RvE1 on inflamed hDPSCs proliferation, proinflammatory gene expression (tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α]), alkaline phosphatase activity, and alizarin red S staining was evaluated.
Results
Scanning electron microscopy analysis demonstrated a highly porous interconnected microstructure. Release kinetics showed gradual RvE1 release peaking at day 14. Cumulative degradation of the CMC scaffold at 28 days was 57.35%. Inflamed hDPSCs exposed to 200 nM RvE1-CMC scaffold exhibited significantly improved viability compared to 100 nM. Both RvE1-CMC scaffolds significantly suppressed the expression of TNF-α at 7 days. Alkaline phosphatase activity was enhanced by both RvE1 concentrations on days 7 and 14. Alizarin red staining revealed superior mineralization potential of 200 nM RvE1 on days 14 and 21.
Conclusions
This study concludes 200 nM RvE1-CMC scaffold is a promising therapy for inflamed pulp conditions, enhancing cell proliferation and biomineralization potential in inflamed hDPSCs.
-
Concentrated growth factor scaffold-based pulpotomy of permanent molars with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis
-
Arthi K. Harith, Vishnupriya Koteeswaran, Dinesh Kowsky, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan, Suresh Nandini
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e1. Published online January 17, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e1
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
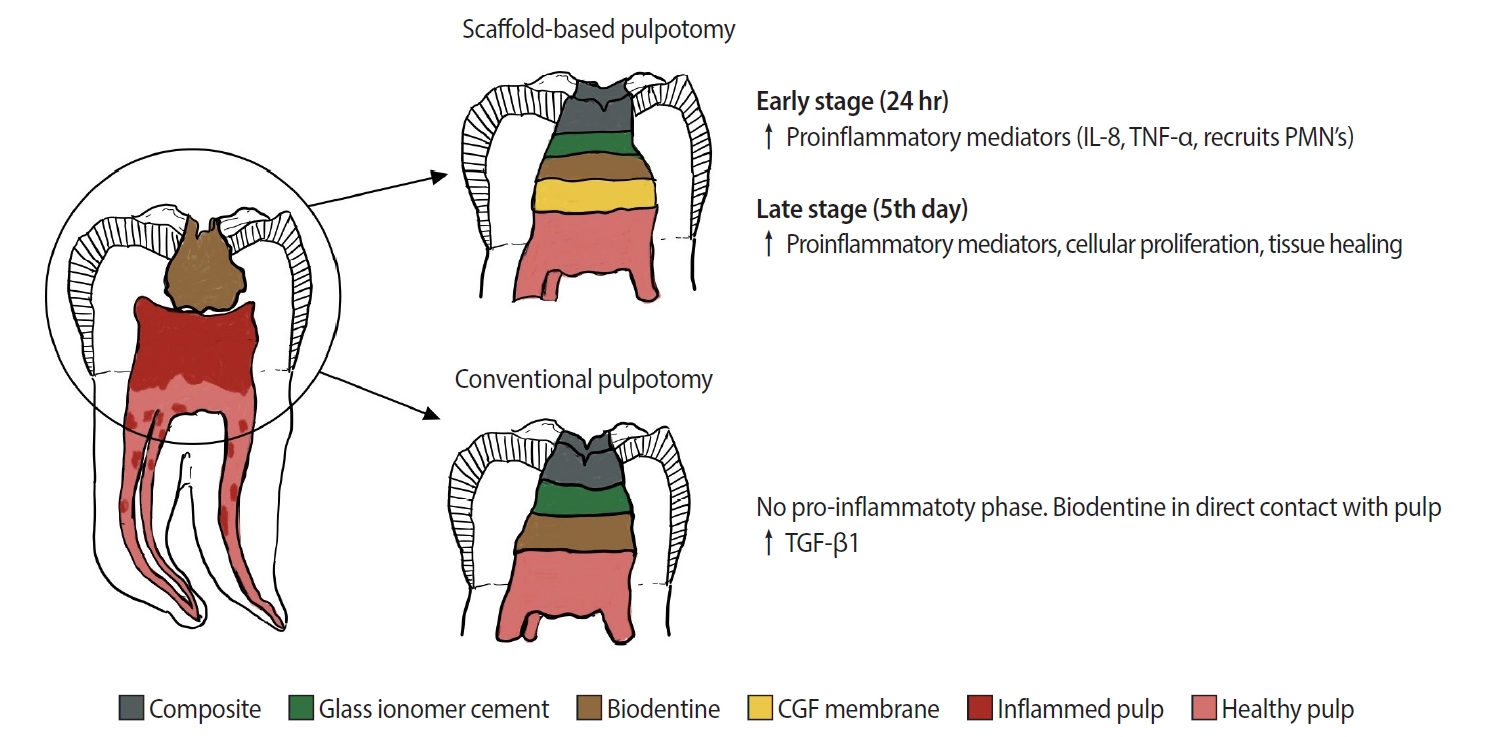
Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure that aims to retain the vitality of the radicular pulp by removing the inflamed coronal pulp tissue. This case series presents the successful management of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis by pulpotomy with concentrated growth factor (CGF) scaffolds.
Methods
Six permanent mandibular molars with a diagnosis of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis were included. Under Local anesthesia and rubber dam isolation, caries were excavated using high-speed bur under coolant. Full coronal pulpotomy was done and hemostasis was achieved. CGF membrane was prepared and placed over the radicular pulp and layered with Biodentine (Septodont). Final restoration of type IX glass ionomer cement and bulk fill composite resin was placed. Patients were assessed for various clinical and radiographic parameters at intervals of 1 week and 3, 6, and 12 months. Five patients fulfilled the success criteria at the end of 1 year.
Results
Pulpotomy is considered an alternative treatment modality for root canal treatment in symptomatic irreversible pulpitis aiming at alleviating symptoms and maintaining vitality. CGF scaffold when used as a capping material acts as a reservoir for growth factors with anti-inflammatory properties and enhances healing.
Conclusions
Scaffold-based pulpotomy can be considered a biological approach to healing inflamed pulp.
|