Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Calcium silicate-based sealers remnants in isthmuses of mesial roots of mandibular molars: an in vitro evaluation
- David Saldanha de Brito Alencar, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Francisco Haiter Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Marina Angélica Marciano
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e25. Published online July 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
Endodontic retreatment aims to address treatment failure through the removal of root canal filling materials. This in vitro study evaluated the presence of filling material remnants in the mesial root canals, specifically focusing on the isthmuses, of mandibular molars after retreatment.
Methods
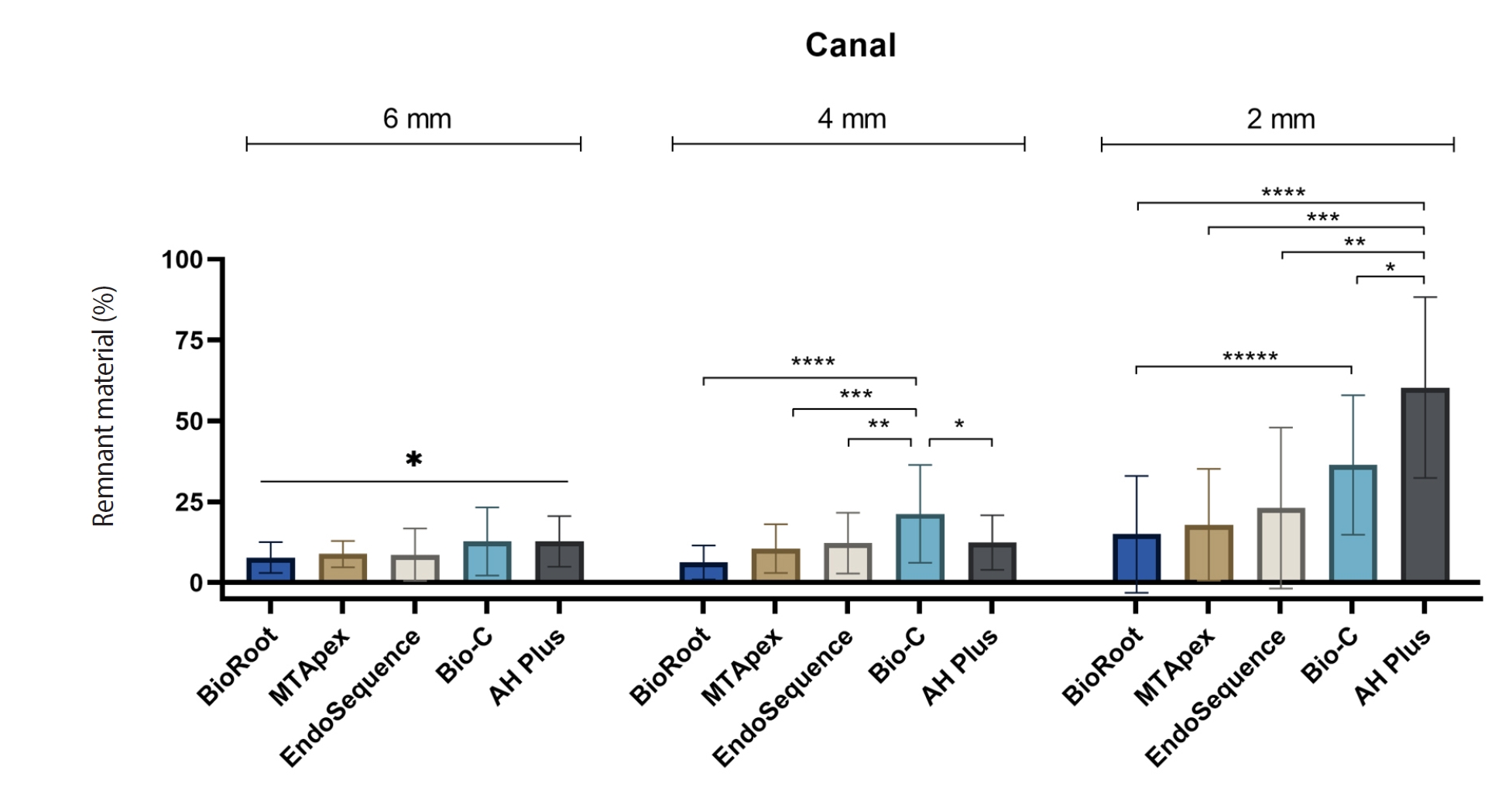
One hundred extracted mandibular molar mesial roots with isthmuses were prepared with an R25 file, obturated with one of five calcium silicate-based sealers (BioRoot RCS [Septodont], MTApex [Ultradent Products Inc.], EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow [Brasseler USA], Bio-C Sealer [Angelus]) or an epoxy resin-based sealer (AH Plus Jet [Dentsply Maillefer]), all stained with rhodamine B, and stored at 37ºC for 30 days to allow for setting. Retreatment was subsequently performed using R40 and XP-endo Finisher R instruments (FKG Dentaire) with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite irrigation. The presence of remaining filling material was then assessed using confocal microscopy, and setting times were tested per ISO 6876:2012.
Results
AH Plus Jet showed the most remnants at 2 mm and the longest retreatment time. Calcium silicate-based sealers exhibited prolonged setting times under dry conditions, with EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow showing a particularly extended setting period.
Conclusions
Despite retreatment, residues remained in all canals and isthmus regions, particularly Bio-C Sealer and AH Plus Jet in apical areas, emphasizing the difficulty of complete removal and the persistence of filling material. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bonding effects of mechanical removal of bioceramic sealer residues using glycine or glass microparticles abrasion
Jesus Aranda, Julia de Freitas Ceccato, Eduardo Fernández Godoy, João Felipe Besegato, Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb, Milton Carlos Kuga
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 148: 104289. CrossRef
- Bonding effects of mechanical removal of bioceramic sealer residues using glycine or glass microparticles abrasion
- 2,008 View
- 112 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on debris extrusion and sealer penetration
- Emel Uzunoglu-Özyürek, Hakan Karaaslan, Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Bahar Özçelik
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e2. Published online December 22, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To determine the effect of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on the amount of apical extruded debris and the amount of penetration depth of sealer using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM).
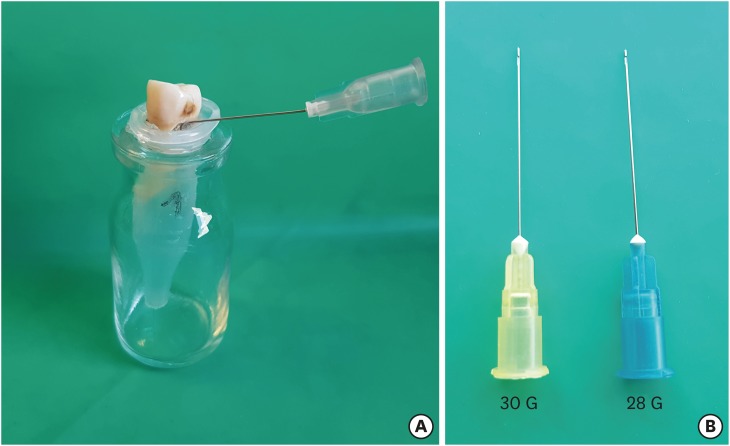
Materials and Methods Twenty maxillary premolars were assigned to 2 groups (
n = 10), according to the size of needle tip, 28 G or 30 G. Buccal roots of samples were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 1 mm short of the working length (WL), while palatal roots were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 3 mm short of the WL. Prepared teeth were removed from the pre-weighed Eppendorf tubes. Canals were filled with F3 gutta-percha cone and rhodamine B dye-labeled AH 26 sealer. Teeth were transversally sectioned at 1 and 3 mm levels from the apex and observed under a CLSM. Eppendorf tubes were incubated to evaporate the irrigant and were weighed again. The difference between pre- and post-weights was calculated, and statistical evaluation was performed.Results Inserting needles closer to the apex and using needles with wider diameters were associated with significantly more debris extrusion (
p < 0.05). The position of needles and level of sections had statistically significant effects on sealer penetration depth (p < 0.05 for both).Conclusions Following preparation, inserting narrower needles compatible with the final apical diameter of the prepared root canal at 3 mm short of WL during final irrigation might prevent debris extrusion and improve sealer penetration in the apical third.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
Geeta Asthana, Dhwani Morakhia, Ravina Parmar, Rajashree Tamuli
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 244. CrossRef - Efficacy of different irrigation needles used in endodontics: an in silico and an in vitro investigation
Maulee Sheth, Ankit Arora, Sonali Kapoor, Balraj Shukla
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2025; 12: 264. CrossRef - Preliminary insights: exploring irrigation practices during endodontic treatment among general dental practitioners in Malaysia
Kai Qi Chiew, Xin Ni Lim, Shekhar Bhatia, Naveen Chhabra
British Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of diode laser in control of post-endodontic pain: a randomized controlled trial
Hend H. Ismail, Maram Obeid, Ehab Hassanien
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2797. CrossRef - Endodontic management of an aberrant germinated composite odontome: A case report
Ankit Arora, Kavina Desai, Sonali Kapoor, Seema Gajera
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(3): 684. CrossRef - Potentials of 3D-Modeling in the Preclinical Stage of Root Needle Research
Aleksandr V. Kuligin, Larisa N. Kazakova, Oksana S. Tereshchuk, Vadim V. Bokov
I.P. Pavlov Russian Medical Biological Herald.2022; 30(1): 95. CrossRef - Effect of root canal geometry and needle type on apical extrusion of irrigant: an ex vivo study
Büşra SERÇE FİKİRLİ, Bülent ALTUNKAYNAK, Güven KAYAOĞLU
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2022; 39(3): 58. CrossRef - An in vitro radiological evaluation of irrigant penetration in the root canals using three different irrigation systems: Waterpik WP-100 device, passive irrigation, and manual dynamic irrigation systems
Suragani Hemalatha, Archana Srinivasan, A Srirekha, Lekha Santhosh, C Champa, Ashwija Shetty
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 403. CrossRef - Preparation Ability of ProTaper Next and XP-endo Shaper Instruments in Isthmus-containing Root Canal System
Mustafa Sarıkahya, Tayfun Alaçam
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2021; 5(2): 28. CrossRef - Penetration depth of irrigants into root dentine after sonic, ultrasonic and photoacoustic activation
K. M. Galler, V. Grubmüller, R. Schlichting, M. Widbiller, A. Eidt, C. Schuller, M. Wölflick, K.‐A. Hiller, W. Buchalla
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1210. CrossRef
- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
- 1,782 View
- 18 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Bonding efficacy of cured or uncured dentin adhesives in indirect resin
- Ji-Hyun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):490-497. Published online November 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.490
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study examined the effect of the uncured dentin adhesives on the bond interface between the resin inlay and dentin.
Materials and Methods Dentin surface was exposed in 24 extracted human molars and the teeth were assigned to indirect and direct resin restoration group. For indirect resin groups, exposed dentin surfaces were temporized with provisional resin. The provisional restoration was removed after 1 wk and the teeth were divided further into 4 groups which used dentin adhesives (OptiBond FL, Kerr; One-Step, Bisco) with or without light-curing, respectively (Group OB-C, OB-NC, OS-C and OS-NC). Pre-fabricated resin blocks were cemented on the entire surfaces with resin cement. For the direct resin restoration groups, the dentin surfaces were treated with dentin adhesives (Group OB-D and OS-D), followed by restoring composite resin. After 24 hr, the teeth were assigned to microtensile bond strength (µTBS) and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), respectively.
Results The indirect resin restoration groups showed a lower µTBS than the direct resin restoration groups. The µTBS values of the light cured dentin adhesive groups were higher than those of the uncured dentin adhesive groups (
p < 0.05). CLSM analysis of the light cured dentin adhesive groups revealed definite and homogenous hybrid layers. However, the uncured dentin adhesive groups showed uncertain or even no hybrid layer.Conclusions Light-curing of the dentin adhesive prior to the application of the cementing material in luting a resin inlay to dentin resulted in definite, homogenous hybrid layer formation, which may improve the bond strength.
- 1,600 View
- 10 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


