Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Evaluation of platelet concentrates in regenerative endodontics: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Anna Tsiolaki, Dimitrios Theocharis, Nikolaos Tsitsipas, Anastasia Fardi, Konstantinos Kodonas
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e38. Published online November 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
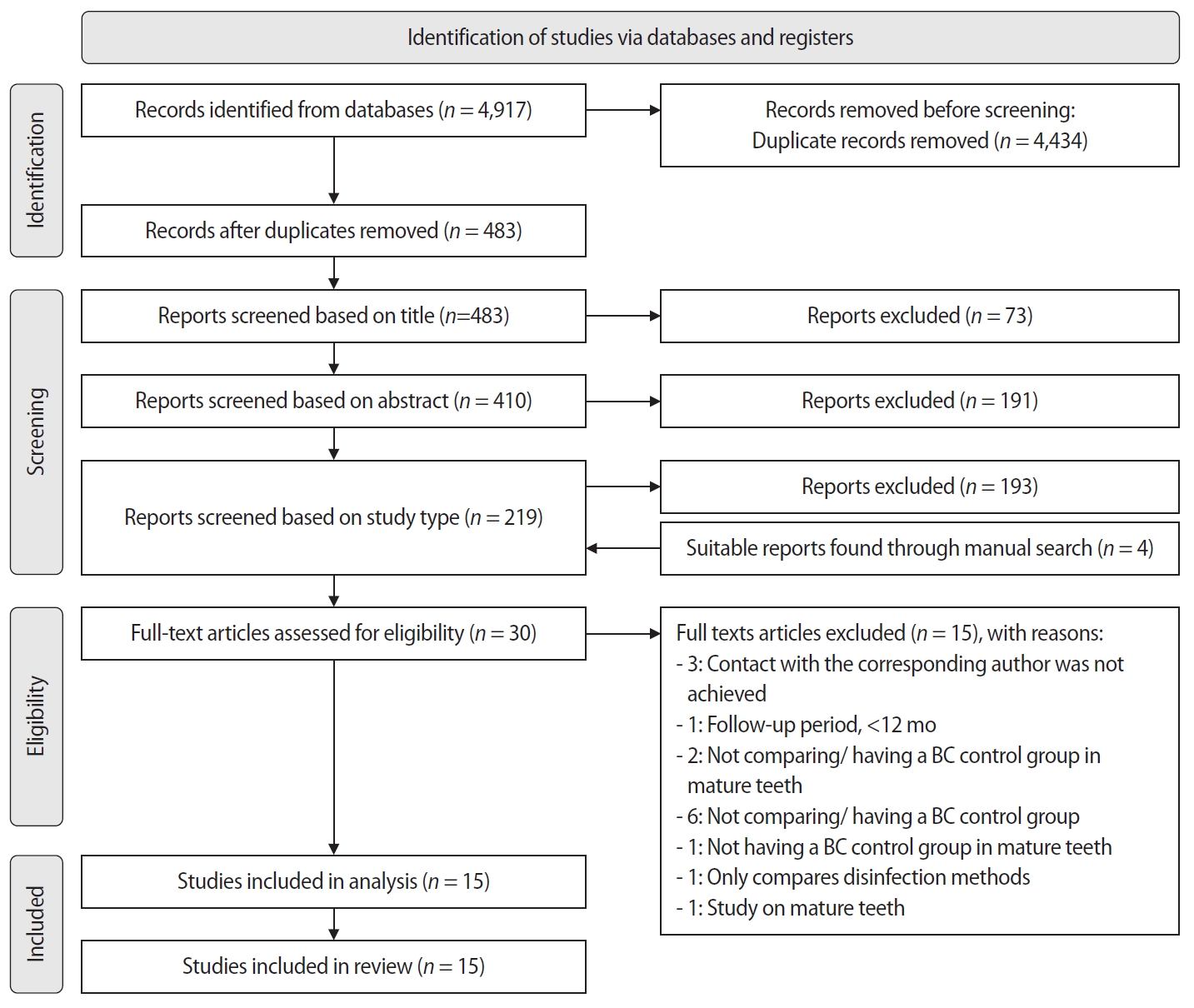
The aim of this systematic review is to compare the effectiveness of advanced platelet concentrates as regenerative endodontic therapeutic alternatives to blood clot (BC) revascularization in immature permanent necrotic teeth.
Methods
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing regenerative endodontic therapies using platelet-rich plasma (PRP), platelet-rich fibrin (PRF), or platelet pellet (PP) with the BC revascularization approach in immature permanent necrotic teeth were systematically searched in PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science until May 2025. Data was extracted and analyzed both qualitatively and quantitatively. Study quality was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool. A meta-analysis was conducted using IBM SPSS software (version 29.0), with success rates expressed as risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
The initial search yielded 4,917 studies. After removing duplicates and applying eligibility criteria, 15 RCTs were included. Meta-analysis indicated no significant difference in the risk ratio (RR), as the BC method has similar success rates with PRP (10 studies; RR = 1.01; 95% CI, 0.94–1.09; p = 0.76) and PRF (8 studies; RR = 0.98; 95% CI, 0.89–1.08; p = 0.65) at 12 months. The primary outcomes evaluated were based on clinical and radiographic success.
Conclusions
Current evidence suggests PRP, PRF, and BC are all effective in treating immature permanent necrotic teeth with similar success rates. However, further research is needed to assess long-term outcomes.
- 1,420 View
- 85 Download

- Evaluation of blood clot, platelet-rich plasma, and platelet-rich fibrin–mediated regenerative endodontic procedures in teeth with periapical pathology: a CBCT study
- Swati Markandey, Haridas Das Adhikari
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e41. Published online October 21, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
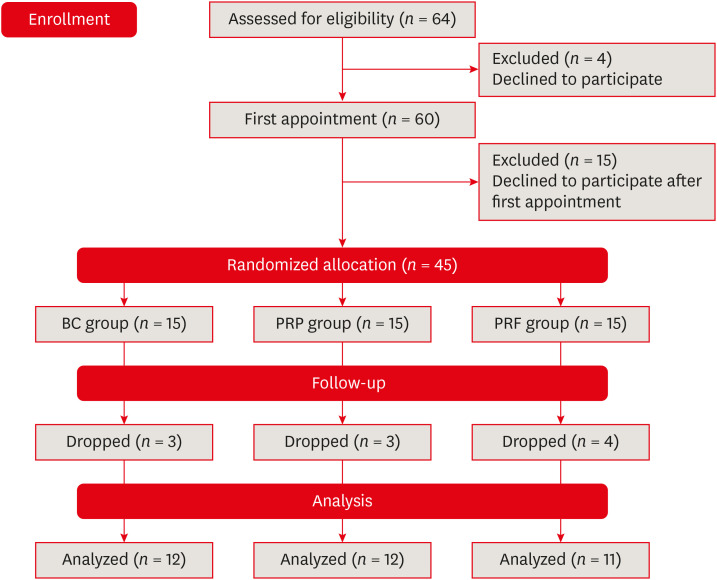
ePub Objectives This study compared the clinical and radiological outcomes of regenerative endodontic procedures (REPs) using blood clots (BCs), platelet-rich plasma (PRP), and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) through intraoral periapical radiography (IOPAR) and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Materials and Methods Forty-five single-rooted necrotic teeth with periapical pathology were randomly allocated to receive BC, PRP, or PRF as an individual scaffold. Outcomes were evaluated in 35 teeth in 23 patients with a follow-up period of 12–24 months through qualitative IOPAR scoring and quantitative CBCT measurements. Healing of periapical lesions and in immature teeth, changes in the apical foramen diameter (AFD), root wall thickness (RWT), and root length (RL) were assessed. A
p value less than 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.Results All teeth were asymptomatic except 1 in the PRP group. Periapical lesion healing was seen in all except 2 teeth in the BC group and 3 in the PRP group. Both IOPAR and CBCT revealed no significant differences in bone healing or changes in AFD, RWT, and RL among the 3 groups. A positive pulp sensibility response to the cold test was seen in 2 teeth in the BC group, but none to the electric pulp test. Intracanal calcification (ICC) was evident in more teeth in the BC group than in the PRP and PRF groups, and was also significantly higher in immature teeth.
Conclusions Our results revealed that BC, PRP, and PRF have similar potential as scaffolds in REPs, and ICC may be a concern for long-term outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Regenerative Endodontics and Stem Cell-Based Therapies – A Systematic Review
Wjoud Ahmed Alshamrani, Sarah Sulaiman Alzarea, Joud Khalid Alabbas, Ayah Khalid Alabbas, Mawiyah Ibrahim Aljaddua, Osama Khattak, Rakhi Issrani
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2026; 18(Suppl 1): S29. CrossRef - Regenerative potential of concentrated growth factor compared to platelet-rich fibrin in treatment of necrotic mature teeth: a randomized clinical trial
Taghreed Salah, Wael Hussein, Heba Abdelkafy
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic outcomes of non-surgical retreatment of mature maxillary incisors using two regenerative endodontic techniques in adolescents: a 24-month randomized clinical trial
Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Sherif Shafik EL Bahnasy, Yassmin Mohamed ElMakawi, Mohammed Turky, Eman Farouk Ahmed, Norhan Khaled Omar Wahba
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Autologous Platelet-Rich Products in Regenerative Endodontics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Raewyn Huang, Wei Chen, Matthew Fang, Ove A. Peters, Sepanta Hosseinpour
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 236. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics in the Treatment of Periapical Lesions of Endodontic Origin: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
BelHaj Salah Kawthar, Berrima Fatma, Boukhris Hanen, Gnaba Imen, Ben Youssef Souha
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(6): 623. CrossRef - Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin Plus Sealed Exclusively with Glass Ionomer Cement: Setting a New Standard for Healing, Aesthetics and Predictive Modelling in Regenerative Endodontics
Dubravka Turjanski, Dragutin Lisjak, Petra Bučević Sojčić, Jelena Valpotić, Tea Borojević Renić, Kristina Goršeta, Domagoj Glavina
Materials.2025; 18(18): 4421. CrossRef - Evaluation of different scaffolds and intracanal medications in revascularization of nonvital immature permanent teeth
Mona M. A. Sameia, Abeer M. Darrag, Neveen A. Shaheen, Dina A. Attia
Tanta Dental Journal.2025; 22(4): 693. CrossRef - Biomimetic pulp scaffolds prepared from extracellular matrix derived from stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth promote pulp–dentine complex regeneration
Ning Yang, Rou Shen, Wenxiao Yang, Shengcai Zhang, Tianxing Gong, Yao Liu
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(9): 1279. CrossRef - Arrest and Repair of Inflammatory Root Resorption After an Endodontic Regeneration Procedure – A Hypothesis and Case Report
Arieh Y. Kaufman, Bill Kahler
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(12): 1743. CrossRef - Effect of Platelet Rich Plasma in Regenerative Endodontic Treatment: A Review of Clinical Trials
Hojat Rezazadeh, Mehrnaz Okhovatfard
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2023; : 5562. CrossRef
- Regenerative Endodontics and Stem Cell-Based Therapies – A Systematic Review
- 4,713 View
- 118 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Pulp revascularization with and without platelet-rich plasma in two anterior teeth with horizontal radicular fractures: a case report
- Edison Arango-Gómez, Javier Laureano Nino-Barrera, Gustavo Nino, Freddy Jordan, Henry Sossa-Rojas
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e35. Published online August 20, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
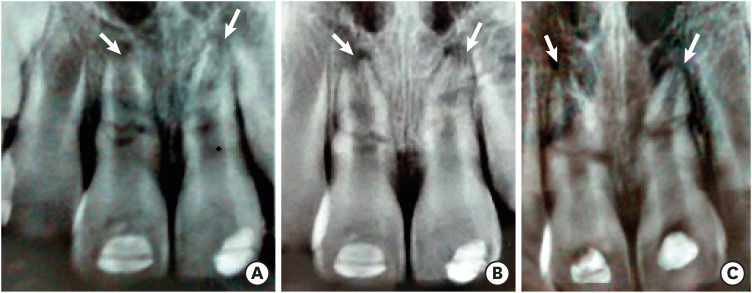
ePub Pulp revascularization is an alternative treatment in immature traumatized teeth with necrotic pulp. However, this procedure has not been reported in horizontal root fractures. This is a case report of a 9-year-old patient with multiple horizontal root fractures in 2 upper central incisors that were successfully treated with pulp revascularization. The patient presented for treatment 2 years after the initial trauma, and revascularization was attempted after the initial treatment with calcium hydroxide had failed. Prior to pulp revascularization, cone-beam computed tomography and autoradiograms demonstrated multiple horizontal fractures in the middle and apical thirds of the roots of the 2 affected teeth. Revascularization was performed in both teeth; platelet-rich plasma (PRP) was used in one tooth (#11) and the conventional method (blood clot) was used in the other tooth (#21). Clinical and radiographic follow-up over 4 years demonstrated pulp calcification in the PRP-treated tooth. Neither of the 2 teeth were lost, and the root canal calcification of tooth #11 was greater than that of tooth #21. This case suggests that PRP-based pulp revascularization may be an alternative for horizontal root fractures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Permanent Incisors: Two Case Reports with 6 Years of Follow-Up
María Biedma-Perea, Marcela Arenas-González, María José Barra-Soto, Carolina Caleza-Jiménez, David Ribas-Pérez
Children.2026; 13(2): 246. CrossRef - Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Endodontics: A Scoping Review
Simão Rebimbas Guerreiro, Carlos Miguel Marto, Anabela Paula, Joana Rita de Azevedo Pereira, Eunice Carrilho, Manuel Marques-Ferreira, Siri Vicente Paulo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(12): 5479. CrossRef - Dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells-response to fibrin hydrogel reveals ITGA2 and MMPs expression
David Tong, Stéphanie Gobert, Alicia Reuzeau, Jean-Christophe Farges, Marianne Leveque, Marie Bolon, Arthur Costantini, Marielle Pasdeloup, Jérôme Lafont, Maxime Ducret, Mourad Bekhouche
Heliyon.2024; 10(13): e32891. CrossRef - Pulp regeneration treatment using different bioactive materials in permanent teeth of pediatric subjects
Dina Abdellatif, Alfredo Iandolo, Giuseppina De Benedetto, Francesco Giordano, Davide Mancino, Edouard Euvrard, Massimo Pisano
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(5): 458. CrossRef - Retreatment of a Failed Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in an Immature Tooth with a Horizontal Root Fracture: A Case Report
Zaher Marjy, Iris Slutzky-Goldberg
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(10): 1168. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of postoperative pain and healing following regenerative endodontics using platelet‐rich plasma versus conventional endodontic treatment in necrotic mature mandibular molars with chronic periapical periodontitis. A randomized clinical trial
Yassmin Elsayed Ahmed, Geraldine Mohamed Ahmed, Angie Galal Ghoneim
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(4): 404. CrossRef - Regenerative endodontic procedures for two traumatized mature anterior teeth with transverse root fractures
Jing Lu, Bill Kahler
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Are platelet concentrate scaffolds superior to traditional blood clot scaffolds in regeneration therapy of necrotic immature permanent teeth? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Qianwei Tang, Hua Jin, Song Lin, Long Ma, Tingyu Tian, Xiurong Qin
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Platelet-Rich Fibrin Used as a Scaffold in Pulp Regeneration: Case Series
Ceren ÇİMEN, Selin ŞEN, Elif ŞENAY, Tuğba BEZGİN
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2021; 24(1): 113. CrossRef - Plasma rico en plaquetas en Odontología: Revisión de la literatura
Hugo Anthony Rosas Rozas, Hugo Leoncio Rosas Cisneros
Yachay - Revista Científico Cultural.2021; 10(1): 536. CrossRef
- Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Permanent Incisors: Two Case Reports with 6 Years of Follow-Up
- 2,741 View
- 42 Download
- 11 Crossref

- The effects of non-thermal plasma and conventional treatments on the bond strength of fiber posts to resin cement
- Maíra do Prado, Eduardo Moreira da Silva, Juliana das Neves Marques, Caroline Brum Gonzalez, Renata Antoun Simão
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):125-133. Published online April 11, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the effect of hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO) and ammonia (NH3) plasmas on the bond strength of resin cement to fiber posts with conventional treatments.
Materials and Methods Sixty-five fiber posts were divided into 5 groups: Control (no surface treatment); H2O2 (24% hydrogen peroxide for 1 min); Blasting (blasting with aluminum oxide for 30 sec); NH3 (NH3 plasma treatment for 3 min); HMDSO (HMDSO plasma treatment for 15 min). After the treatments, the Ambar adhesive (FGM Dental Products) was applied to the post surface (
n = 10). The fiber post was inserted into a silicon matrix that was filled with the conventional resin cement Allcem Core (FGM). Afterwards, the post/cement specimens were cut into discs and subjected to a push-out bond strength (POBS) test. Additionally, 3 posts in each group were evaluated using scanning electron microscopy. The POBS data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and the Tukey's honest significant differencepost hoc test (α = 0.05).Results The Blasting and NH3 groups showed the highest POBS values. The HMDSO group showed intermediate POBS values, whereas the Control and H2O2 groups showed the lowest POBS values.
Conclusion Blasting and NH3 plasma treatments were associated with stronger bonding of the conventional resin cement Allcem to fiber posts, in a procedure in which the Ambar adhesive was used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimization of Bond Strength Between Heat-Polymerized PMMA and Contemporary CAD/CAM Framework Materials: A Comparative In Vitro Study
Başak Topdağı
Polymers.2025; 17(11): 1488. CrossRef - Enhancement of Composite Resin Bonding on Dental Tissues Using Cold Atmospheric Plasma Discharge: A Systematic Literature Review and Proposal for a Redaction Grid
Thibault Canceill, Cristina Canal, Alison Prosper, Djakaou Iya‐Sou, Antoine Dubuc, Nofel Merbahi, Sarah Cousty
Plasma Processes and Polymers.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Enhanced Bonding of Silane‐Modified Adhesive Systems in Fiber Post Cementation
Thais Pantoja de França, João Victor Frazão Câmara, Leonardo Queiroz Athias, Renata Antoun Simão, Maíra Prado, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the push-out bond strength of fiber posts: Immediate vs. delayed post-space preparation with two obturation techniques
Weilin Long, Xiongjun Xu, Li Tang, Hongwei Jiang, Yihua Huang, Miriam Fatima Zaccaro Scelza
PLOS One.2025; 20(10): e0333880. CrossRef -
Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment on the Bond Strength of Glass Fiber Posts
Elif Şeyma Kaban, Gizem Dilara Özdemir, Ilgın İlgenli, Utku Kürşat Ercan
Plasma Medicine.2024; 14(1): 17. CrossRef - Effect of non-thermal argon plasma on the shear strength of adhesive systems
Isabella de Almeida Guimarães Passos, Juliana das Neves Marques, João Victor Frazão Câmara, Renata Antoun Simão, Maíra do Prado, Gisele Damiana da Silveira Pereira
Polímeros.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Oleofobization of Paper via Plasma Treatment
Matic Resnik, Eva Levičnik, Žiga Gosar, Rok Zaplotnik, Janez Kovač, Jernej Ekar, Miran Mozetič, Ita Junkar
Polymers.2021; 13(13): 2148. CrossRef - Analysis of physical properties of facial silicones with different pigmentations submitted to nonthermal plasma treatment and accelerated aging
Marcela Borghi Paulini, Daniela Micheline dos Santos, Clóvis Lamartine de Moraes Melo Neto, Sandro Basso Bitencourt, Emily Vivianne Freitas da Silva, Fernanda Pereira de Caxias, Rafael Parra Ribeiro, Elidiane Cipriano Rangel, Mariana Vilela Sônego, Marcel
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2020; 124(6): 815.e1. CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments on the shear bond strength of luting cements used with implant-supported prosthesis: Anin vitrostudy
Kubra Degirmenci, Serkan Saridag
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2020; 12(2): 75. CrossRef - Non-thermal plasma treatment to enhance the adhesion between enamel surface and orthodontic bracket
Salem Almoammar, Ibrahim AlShahrani, Moshabab A. Asiry, Simone Duarte, Malvin Janal, Edmund Khoo
Bio-Medical Materials and Engineering.2019; 30(4): 439. CrossRef
- Optimization of Bond Strength Between Heat-Polymerized PMMA and Contemporary CAD/CAM Framework Materials: A Comparative In Vitro Study
- 1,618 View
- 7 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Microsurgical re-treatment of an endodontically treated tooth with an apically located incomplete vertical root fracture: a clinical case report
- Silvio Taschieri, Massimo Del Fabbro, Ahmed El Kabbaney, Igor Tsesis, Eyal Rosen, Stefano Corbella
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):316-321. Published online June 21, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.316
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Although it is challenging, the early diagnosis of a vertical root fracture (VRF) is crucial in order to ensure tooth preservation. The purpose of this clinical case report was to describe reparative surgery performed to treat a tooth affected by an incomplete VRF. A 26 year old male patient was suspected to have a VRF in a maxillary left central incisor, and an exploratory flap was performed in order to confirm the diagnosis. After detecting the fracture, the lesion was surgically treated, the fracture and the infected root-end were removed, and a platelet-rich plasma membrane was used to cover the defect in order to prevent bacterial migration. A 24 month clinical and radiological follow-up examination showed that the tooth was asymptomatic and that the healing process was in progress. The surgical approach described here may be considered an effective treatment for a combined endodontic-periodontal lesion originating from an incomplete VRF and a recurrent periapical lesion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomechanical perspectives on dentine cracks and fractures: Implications in their clinical management
Sishi Chen, Dwayne Arola, Domenico Ricucci, Brian E. Bergeron, John A. Branton, Li-sha Gu, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 130: 104424. CrossRef - Efficacy of Autologous Platelet Concentrates in Regenerative Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review of Human Studies
Joanna Metlerska, Irini Fagogeni, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(1): 20. CrossRef - The preservation of teeth with root-originated fractures
Eyal Rosen, Ilan Beitlitum, Igor Tsesis
Evidence-Based Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Biomechanical perspectives on dentine cracks and fractures: Implications in their clinical management
- 2,436 View
- 25 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Management of apicomarginal defect in esthetic region associated with a tooth with anomalies
- Vinayak Venkoosa Meharwade, Dipali Yogesh Shah, Pradyna Prabhakar Mali, Vidya Vinayak Meharwade
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):314-321. Published online June 24, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.314
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Tooth related factors such as palatoradicular groove can be one of the causes for localized periodontal destruction. Such pathological process may result in apicomarginal defect along with inflammation of pulp. This creates challenging situation which clinician must be capable of performing advanced periodontal regenerative procedures for the successful management. This case report discusses clinical management of apicomarginal defect associated with extensive periradicular destruction in a maxillary lateral incisor, along with histopathologic aspect of the lesion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical treatment of apico-marginal defect associated with maxillary incisor teeth with a large periapical lesion using sticky bone & platelet rich fibrin membrane – A case report
Snigdho Das, Parthasarathi Mondal, Dipanjan Das, Kurchi Mandal, Kallol Kumar Saha
IP Annals of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 10(3): 250. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of sticky bone with guided tissue regeneration and platelet-rich fibrin membranes in healing of apicomarginal defects with periapical pathology: An in-vivo study
D. Das, P. Mondal, K. K. Saha, S. Das, D. Karmakar, A. Bhagawati
Endodontics Today.2024; 22(4): 335. CrossRef
- Surgical treatment of apico-marginal defect associated with maxillary incisor teeth with a large periapical lesion using sticky bone & platelet rich fibrin membrane – A case report
- 1,459 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The use of platelet rich plasma in the treatment of immature tooth with periapical lesion: a case report
- Günseli Güven Polat, Ceren Yıldırım, Özlem Martı Akgün, Ceyhan Altun, Didem Dinçer, Cansel Köse Özkan
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):230-234. Published online June 2, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.230
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study describes the treatment of an immature permanent tooth with periapical lesion which was treated with regenerative approach using platelet rich plasma (PRP). The root canal of immature human permanent tooth with periapical lesion was gently debrided of necrotic tissue and disinfected with 2.5% NaOCl, and then medicated with triple antibiotic paste comprised of ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, and tetracycline. When the tooth was asymptomatic, PRP and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) were placed into the root canal. Six months after PRP treatment, radiographical examination revealed resolution of the radiolucency and progressive thickening of the root wall and apical closure. Our findings suggest that PRP can be used for the treatment of immature permanent teeth with periapical lesion, as part of a regenerative endodontic treatment procedure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of postoperative pain and healing following regenerative endodontics using platelet‐rich plasma versus conventional endodontic treatment in necrotic mature mandibular molars with chronic periapical periodontitis. A randomized clinical trial
Yassmin Elsayed Ahmed, Geraldine Mohamed Ahmed, Angie Galal Ghoneim
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(4): 404. CrossRef - Different Approaches to the Regeneration of Dental Tissues in Regenerative Endodontics
Anna M. Krupińska, Katarzyna Skośkiewicz-Malinowska, Tomasz Staniowski
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(4): 1699. CrossRef - Coronal tooth discoloration induced by regenerative endodontic treatment using different scaffolds and intracanal coronal barriers: a 6-month ex vivo study
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Hassan Razmi, Maryam Farbod, Marzieh Alikhasi, Josette Camilleri
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Autologous Platelet Concentrates in Regenerative Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review of Human Studies
Joanna Metlerska, Irini Fagogeni, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(1): 20. CrossRef - Bone, Periodontal and Dental Pulp Regeneration in Dentistry: A Systematic Scoping Review
Luiz Alexandre Chisini, Marcus Cristian Muniz Conde, Guillermo Grazioli, Alissa Schmidt San Martin, Rodrigo Varella de Carvalho, Letícia Regina Morello Sartori, Flávio Fernando Demarco
Brazilian Dental Journal.2019; 30(2): 77. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part II: other clinical applications and complications
M. Torabinejad, M. Parirokh, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(3): 284. CrossRef - Alternative to Avoid Tooth Discoloration after Regenerative Endodontic Procedure: A Systematic Review
Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Luiz Alexandre Chisini, Camila Guerner Springmann, Beatriz Dulcineia Mendes de Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen, Flávio Fernando Demarco, Mara Cristina Santos Felippe, Wilson Tadeu Felippe
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(5): 409. CrossRef - Influence of Apical Diameter on the Outcome of Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Teeth with Pulp Necrosis: A Review
Yanjun Fang, Xinhuan Wang, Jingjing Zhu, Chaonan Su, Ying Yang, Liuyan Meng
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(3): 414. CrossRef - A scoping review of root canal revascularization: relevant aspects for clinical success and tissue formation
M. C. M. Conde, L. A. Chisini, R. Sarkis‐Onofre, H. S. Schuch, J. E. Nör, F. F. Demarco
International Endodontic Journal.2017; 50(9): 860. CrossRef - Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate, an Antibacterial Cross-linking Agent, on Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Cells Cultured in Collagen Scaffolds
Young-Sun Kwon, Hee-Jin Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Vinicius Rosa, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(2): 289. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics
Kristina Feigin, Bonnie Shope
Journal of Veterinary Dentistry.2017; 34(3): 161. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment or Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Apical Plug in Teeth with Necrotic Pulps and Open Apices: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Mahmoud Torabinejad, Ali Nosrat, Prashant Verma, Oyoyo Udochukwu
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1806. CrossRef - Platelet concentrates for revitalization of immature necrotic teeth: a systematic review of the clinical studies
Alessandra Lolato, Cristina Bucchi, Silvio Taschieri, Ahmed El Kabbaney, Massimo Del Fabbro
Platelets.2016; 27(5): 383. CrossRef - Regenerative endodontics—Creating new horizons
Harnoor Dhillon, Mamta Kaushik, Roshni Sharma
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2016; 104(4): 676. CrossRef - The impact of autologous platelet concentrates on endodontic healing: a systematic review
Nastaran Meschi, Ana B. Castro, Katleen Vandamme, Marc Quirynen, Paul Lambrechts
Platelets.2016; 27(7): 613. CrossRef - Pulp and Periodontal Regeneration of an Avulsed Permanent Mature Incisor Using Platelet-rich Plasma after Delayed Replantation: A 12-month Clinical Case Study
Harini Priya M, Pavan B. Tambakad, Jaya Naidu
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(1): 66. CrossRef - Platelet preparations in dentistry: How? Why? Where? When?
Luigi Fabrizio Rodella
World Journal of Stomatology.2015; 4(2): 39. CrossRef
- Evaluation of postoperative pain and healing following regenerative endodontics using platelet‐rich plasma versus conventional endodontic treatment in necrotic mature mandibular molars with chronic periapical periodontitis. A randomized clinical trial
- 1,705 View
- 8 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Ingredients and cytotoxicity of MTA and 3 kinds of Portland cements
- Seok-Woo Chang, Hyun-Mi Yoo, Dong Sung Park, Tae-Seok Oh, Kwang-Shik Bae
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):369-376. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.369
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to compare the compositions and cytotoxicity of white ProRoot MTA (white mineral trioxide aggregate) and 3 kinds of Portland cements. The elements, simple oxides and phase compositions of white MTA (WMTA), gray Portland cement (GPC), white Portland cement (WPC) and fast setting cement (FSC) were measured by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES), X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) and X-ray diffractometry (XRD). Agar diffusion test was carried out to evaluate the cytotoxicity of WMTA and 3 kinds of Portland cements.
The results showed that WMTA and WPC contained far less magnesium (Mg), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn) than GPC and FSC. FSC contained far more aluminum oxide (Al2O3) than WMTA, GPC, and WPC. WMTA, GPC, WPC and FSC were composed of main phases, such as tricalcicium silicate (3CaO·SiO2), dicalcium silicate (2CaO·SiO2), tricalcium aluminate (3CaO·Al2O3), and tetracalcium aluminoferrite (4CaO·Al2O3·Fe2O3). The significance of the differences in cellular response between WMTA, GPC, WPC and FSC was statistically analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis Exact test with Bonferroni's correction. The result showed no statistically significant difference (p > 0.05).
WMTA, GPC, WPC and FSC showed similar compositions. However there were notable differences in the content of minor elements, such as aluminum (Al), magnesium, iron, manganese, and zinc. These differences might influence the physical properties of cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Multi-functional Composite Cement with Strength Improvement Using Disposable Waste Masks
Jong-Won Chung, Hyun-Kyoung Yang
Journal of Power System Engineering.2022; 26(3): 31. CrossRef - The effects of mineral trioxide aggregate on osteo/odontogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive and systematic literature review
Danial Babaki, Sanam Yaghoubi, Maryam M. Matin
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2020; 7(1): 175. CrossRef - Remineralization of demineralized dentin using a dual analog system
Neha Saxena, Stefan Habelitz, Grayson W. Marshall, Laurie B. Gower
Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research.2019; 22(S1): 76. CrossRef - Chemical analysis and biological properties of two different formulations of white portland cements
Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Norhayati Luddin, Thirumulu Ponnuraj Kannan, Khairani Idah Mokhtar, Azlina Ahmad
Scanning.2016; 38(4): 303. CrossRef - In vitrocytotoxicity of four calcium silicate-based endodontic cements on human monocytes, a colorimetric MTT assay
Sedigheh Khedmat, Somayyeh Dehghan, Jamshid Hadjati, Farimah Masoumi, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 149. CrossRef - Conservative approach of a symptomatic carious immature permanent tooth using a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine): a case report
Cyril Villat, Brigitte Grosgogeat, Dominique Seux, Pierre Farge
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 258. CrossRef - Chemical characteristics of mineral trioxide aggregate and its hydration reaction
Seok-Woo Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 188. CrossRef - Physical and chemical properties of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
Yu-Na Jeong, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Yeong-Joon Park, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 344. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of bioaggregate cement on human pulp and periodontal ligament (PDL) derived cells
Choo-Ryung Chung, Euiseong Kim, Su-Jung Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 473. CrossRef - Physical properties of novel composite using Portland cement for retro-filling material
Sang-Jin Lee, Ok-In Cho, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 445. CrossRef - A bioactivity study of Portland cement mixed with β-glycerophosphosphate on human pulp cell
Young-Hwan Oh, Young-Joo Jang, Yong-Bum Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 415. CrossRef - Comparison of biocompatibility of four root perforation repair materials
Min-Kyung Kang, In-Ho Bae, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 192. CrossRef - Effects of condensation techniques and canal sizes on the microleakage of orthograde MTA apical plug in simulated canals
Deuk-Lim Nam, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 208. CrossRef
- Development of Multi-functional Composite Cement with Strength Improvement Using Disposable Waste Masks
- 1,426 View
- 3 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effect of each light curing units on the microhardness and microleakage of composite resin
- Eu-Jin Jung, Hee-Joo Lee, Bock Hur
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(1):58-65. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.1.058
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objectives of this study was to evaluate current visible light curing units regarding microhardness and microleakage. Fourty samples of composite resin(Z-250, 3M) were cured by different light curing units(Flipo, LOKKI; Credi II, 3M; XL 3000, 3M; Optilux 500,Demetron) in acrylic blocks. Microhardness was measured using a calibrated Vickers indenter on both top and bottom surfaces after 24 hours of storage in air at room temperature. Class V cavities were prepared on buccal and lingual surfaces of fourty extracted human molars. Each margin was on enamel and dentin/cementum. Composite resin(Z-250, 3M) was filled in cavities and cured by four different light curing units(Flipo, LOKKI; Credi II, 3M; XL 3000, 3M; Optilux 500, Demetron).
The results of this syudy were as follows:
Microhardness
1. Flipo showed low microhardness compared to Optilux 500, Credi II significantly in upper surface. Flipo didn't show a significant difference compared to XL 3000.
2. The microhardness resulting from curing with Flipo was lower than that of others on lower surfaces.
Microleakage
1. Dentin margin showed significantly high dye penetration rate than enamel margin in all groups(p<0.05).
2. No significant differences were found on both enamel and dentin margin regarding curing units.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Surface Microhardness of the Flowable Bulk-Fill Resin and the Packable Bulk-Fill Resin according to Light Curing Time and Distance
Hyung-Min Kim, Moon-Jin Jeong, Hee-Jung Lim, Do-Seon Lim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2023; 23(2): 123. CrossRef
- Comparison of Surface Microhardness of the Flowable Bulk-Fill Resin and the Packable Bulk-Fill Resin according to Light Curing Time and Distance
- 1,150 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Polymerization ability of several light curing sources on composite resin
- Hye-Jin Shin, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(2):156-161. Published online March 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.2.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to evaluate the polymerization ability of three different light sources by microhardness test. Stainless steel molds of 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 mm in thickness of 7 mm in diameter were prepared. The hybrid composite Z100 was packed into the hole of the mold and curing light was activated for designated time. Three different light sources, conventional halogen, light emitting diode, and plasma arc, were used for curing of composite. Two different curing times applied; one is to follow the manufacturer's recommendation and the other is to extend the curing time of LED and plasma arc for balancing the light energy with halogen. Immediately after curing, the Vickers hardness was measured at the bottom of specimen.
The results were as follows.
The composite cured with LED showed equal to higher microhardnesss than halogen.
The composite was cured with plasma arc by manufacturer's recommendation showed lowest microhardness at all thickness. However, when curing time was extended, microhardness was higher than the others.
In conclusion, this study suggested that plasma arc needs properly extended curing time.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
Hoon-Sang Chang, Young-Jun Lim, Jeong-Mi Kim, Sung-Ok Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 353. CrossRef
- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
- 1,171 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- EFFECT OF LIGHT SOURCE AND SHADE ON DEPTH OF CURE OF COMPOSITES
- Joon-Sok Na, Sun-Wa Jeong, Yun-Chan Hwang, Sun-Ho Kim, Chang Yun, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(6):561-568. Published online January 14, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.6.561
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT Purpose of this research is estimating polymerization depth of different source of light. XL 3000 for halogen light, Apollo 95E for plasma arc light and Easy cure for LED light source were used in this study. Different shade (B1 & A3) resin composites (Esthet-X, Dentsply, U.S.A.) were used to measure depth of cure. 1, 2, and 3 mm thick samples were light cured for three seconds, six seconds or 10 seconds with Apollo 95E and they were light cured with XL-3000 and Easy cure for 10 seconds, 20 seconds, or 40 seconds. Vicker's hardness test carried out after store samples for 24 hours in distilled water.
Results were as following.
Curing time increases from all source of lights, curing depth increased(p<0.05).
Depth (that except 1mm group and 2mm group which lighten to halogen source of light) deepens in all groups, Vickers hardness decreased(p<0.05).
Vicker's hardness of A3 shade composite was lower in all depths more than B1 shade composites in group that do polymerization for 10 seconds and 20 seconds using halogen source of light(p<0.05), but group that do polymerization for 40 seconds did not show difference(p>0.05).
Groups that do polymerization using Plasma arc and LED source of light did not show Vicker's hardness difference according to color at surface and 1mm depth(p>0.05), but showed difference according to color at 2mm and 3mm depth(p<0.05). The results showed that Apollo 95E need more polymerization times than manufacturer's recommendation (3 seconds), and Easy cure need polymerization time of XL-3000 at least.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
Hoon-Sang Chang, Young-Jun Lim, Jeong-Mi Kim, Sung-Ok Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 353. CrossRef
- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
- 1,154 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


