Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Does photobiomodulation on the root surface decrease the occurrence of root resorption in reimplanted teeth? A systematic review of animal studies
- Theodoro Weissheimer, Karolina Frick Bischoff, Carolina Horn Troian Michel, Bruna Barcelos Só, Manoela Domingues Martins, Matheus Albino Souza, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e24. Published online June 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
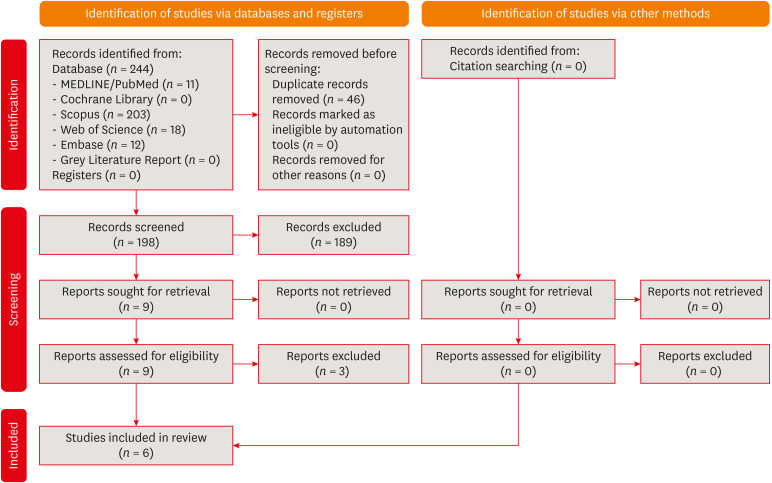
ePub This review aimed to answer the following question “Does photobiomodulation treatment of the root surface decrease the occurrence of root resorption in reimplanted teeth?” Electronic searches were performed in the MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, and Grey Literature Report databases. Risk of bias was evaluated using SYRCLE Risk of Bias tool. The Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations (GRADE) tool was used to assess the certainty of evidence. In total, 6 studies were included. Five studies reported a reduced occurrence of root resorption in teeth that received photobiomodulation treatment of the root surface prior to replantation. Only 1 study reported contradictory results. The photobiomodulation parameters varied widely among studies. GRADE assessment showed a low certainty of evidence. It can be inferred that photobiomodulation treatment of the root surface prior to replantation of teeth can reduce the occurrence of root resorption. Nonetheless, further clinical studies are needed.
Trial Registration PROSPERO Identifier: CRD42022349891
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility and Outcomes of Cell-based Regenerative Endodontic Therapy in Postautogenous Transplantation of a Mature Tooth: A Case Report
Noriaki Yoshihashi
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(1): 85. CrossRef - Evidence Mapping and Quality Assessment of Systematic Reviews in Dental Traumatology: A 54 Months Update
Nitesh Tewari, Pavithra Devi, Hemlata Nehta, Ekta Wadhwani, Rigzen Tamchos, Georgios Tsilingaridis, Vijay Prakash Mathur, Morankar Rahul
Dental Traumatology.2025; 41(6): 727. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation Literature Watch September 2023
James D. Carroll
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2024; 42(7): 498. CrossRef
- Feasibility and Outcomes of Cell-based Regenerative Endodontic Therapy in Postautogenous Transplantation of a Mature Tooth: A Case Report
- 2,874 View
- 44 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of calcium hydroxide on inflammatory root resorption and ankylosis in replanted teeth compared with other intracanal materials: a review
- Maryam Zare Jahromi, Mahmood Reza Kalantar Motamedi
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e32. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Calcium hydroxide (CH) is the gold-standard intracanal dressing for teeth subjected to traumatic avulsion. A common complication after the replantation of avulsed teeth is root resorption (RR). The current review was conducted to compare the effect of CH with that of other intracanal medications and filling materials on inflammatory RR and replacement RR (ankylosis) in replanted teeth. The PubMed and Scopus databases were searched through June 2018 using specific keywords related to the title of the present article. The materials that were compared to CH were in 2 categories: 1) mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) and endodontic sealers as permanent filling materials for single-visit treatment, and 2) Ledermix, bisphosphonates, acetazolamide, indomethacin, gallium nitrate, and enamel matrix-derived protein (Emdogain) as intracanal medicaments for multiple-visit management of avulsed teeth prior to the final obturation. MTA can be used as a single-visit root filling material; however, there are limited data on its efficacy due to a lack of clinical trials. Ledermix and acetazolamide were comparable to CH in reducing RR. Emdogain seems to be an interesting material, but the data supporting its use as an intracanal medication remain very limited. The conclusions drawn in this study were limited by the insufficiency of clinical trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
Anu Priya Guruswamy Pandian, Depti Bellani, Ritya Mary Jibu, Varsha Agnihotri
Dental Clinics of North America.2026; 70(1): 45. CrossRef - Efficacy of Simvastatin in Inhibiting Bone Resorption and Promoting Healing in Delayed Tooth Avulsion: A Case Series
Rajesh Kumar, Supraja N Atluri, Alekhya Achanta, Chittaranjan Bogishetty, Tejaswini R Chunduri, Tejaswini PSS, Ramakrishna Ravi
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Interdisziplinäre Lösung nach dentalem Trauma mit Avulsion und Wurzelresorption
Eva Maier, Julia Lubauer, Kerstin M. Galler
Oralprophylaxe & Kinderzahnmedizin.2025; 47(3): 161. CrossRef - Bioactive potential of Bio-C Temp demonstrated by systemic mineralization markers and immunoexpression of bone proteins in the rat connective tissue
Camila Soares Lopes, Mateus Machado Delfino, Mário Tanomaru-Filho, Estela Sasso-Cerri, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The use of mineral trioxide aggregate for treatment of children with complications of dental trauma
L.Yu. Kharkova, M.V. Korolenkova
Stomatology.2024; 103(4): 59. CrossRef - Instant Re-Implantation of Avulsed Teeth
Smita Paul, Sambarta Das, Nirmal Debbarma, Barun Dasgupta, Bidyut Seal, Ayesha Satapathy
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 4): S3461. CrossRef - Interpretation by literature review of the use of calcium hydroxide as an intra-ductal medication
María Belén Muñoz Padilla, Verónica Alicia Vega Martínez, Camila Alejandra Villafuerte Moya
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología.2024; 4: 924. CrossRef - Evaluation of the physicochemical properties of intracanal medications used in traumatized teeth
Patricia Almeida da Silva de Macedo, Walbert de Andrade Vieira, Paulo Henrique Gabriel, Karla de Faria Vasconcelos, Francisco Haiter Neto, Ana Carolina Correia Laurindo de Cerqueira Neto, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, Marcos Roberto dos Santo
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e242997. CrossRef - Treatment of Teeth with Root Resorptions: A Case Report and Systematic Review
Damla Erkal, Abdullah Başoğlu, Damla Kırıcı, Nezahat Arzu Kayar, Simay Koç, Kürşat Er
Galician Medical Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Successful outcome of permanent maxillary incisor reimplanted after 30 hours of extra‐oral time—a case report with 5‐year follow‐up
Ibadat Preet Kaur, Ashok Kumar, Mukul Kumar, Kanistika Jha
Clinical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Replantation of an Avulsed Tooth: A Case Report
Nishad Kadulkar, Rubi Kataki, Adrija Deka, Salouno Thonai
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Avulsion of Permanent Mandibular Incisors: A Report of Two Cases with Pertinent Literature
Ibadat Preet Kaur, Jitendra Sharan, Pallawi Sinha, Ashok Kumar, Anand Marya, Leandro Napier de Souza
Case Reports in Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - The Impact of Autologous Platelet Concentrates on the Periapical Tissues and Root Development of Replanted Teeth: A Systematic Review
Zohaib Khurshid, Faris Yahya I. Asiri, Shariq Najeeb, Jithendra Ratnayake
Materials.2022; 15(8): 2776. CrossRef
- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
- 4,010 View
- 83 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Surgical management with intentional replantation on a tooth with palato-radicular groove
- Jorge Forero-López, Luis Gamboa-Martínez, Laura Pico-Porras, Javier Laureano Niño-Barrera
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):166-171. Published online December 22, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.166
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub A palato-radicular groove (PRG) is a developmental anomaly primarily found in the maxillary lateral incisors. It is a potential communication path between the root canal and the periodontium that decreases the survival prognosis of the affected tooth, therefore compromising the stability of the dental structure in the oral cavity. The aim of this case report is to present an original technique where a PRG was treated by means of intracanal disinfection, PRG sealing with glass ionomer, replantation with intentional horizontal 180 degree rotation of the tooth, and an aesthetic veneer placed to provide adequate tooth morphology. The clinical and biological benefits of this novel technique are presented and discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Therapeutic Effect of Intentional Replantation
Jiani Zhu, Xiangfen Li, Qin Su
Journal of Endodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A classification of radicular grooves from the perspective of periodontology
Huxiao Li, Zhaowei Tai, Jiachen Dong, Zhongchen Song
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Approaches of Palatogingival Groove: A Systematic Review
Greta Venskutė
Journal of Dental Health and Oral Research.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Palatogingival Groove: A Plaque Trap Leading to Bone Loss in a Maxillary Lateral Incisor – A Rare Case Report
Gayathri Priyadharshini Elangovan, Indra Kumar Periyasamy, Saravana Kumar R, Gopinath Vivekanandhan
Dental Journal of Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences.2024; 3: 104. CrossRef - Palatogingival Groove: The Known–unknown Devourer
Sandeep Tandon, Rinku Mathur, Ambika S Rathore, Tripti S Rai, Kanchan Kumari Dhaker, Sumedha Gupta
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(S1): S95. CrossRef - Palatal groove associated with periodontal lesions: a systematic review illustrated by a decisional tree for management
Yvan Gaudex, Vianney Gandillot, Isabelle Fontanille, Philippe Bouchard, Stephane Kerner, Maria Clotilde Carra
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of palatogingival groove affecting maxillary anterior teeth in Saudi subpopulation: A cone-beam computed tomographic study with literature review
Ali Ibrahim Aljuailan, Roqayah Aljuailan, Rahul N. Gaikwad, Shaul Hameed Kolarkodi, Nasser Rufaydan Alamri
The Saudi Dental Journal.2023; 35(8): 1039. CrossRef - Interdisciplinary approach for diagnosis and management of the tooth with type III palatogingival groove
Harakh Chand Baranwal, Jyoti Yadav
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(2): 211. CrossRef - Management of Palatogingival Groove in Maxillary Lateral Incisor: A Report of a Rare Case With a Brief Review of Literature
Irfan Ansari, Sanjay Miglani, Vijay Yadav, Shamimul Hasan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Intentional replantation combined root resection therapy for the treatment of type III radicular groove with two roots: A case report
Dan Tan, Shi-Ting Li, Hao Feng, Zhong-Chao Wang, Cai Wen, Min-Hai Nie
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(20): 6991. CrossRef - The incidence of radicular groove on maxillary lateral incisors of Saudi population: CBCT evaluation
Sarah M. Alkahtany, Fatemah Alrwais, Asma Altamimi, Sundus M. Bukhary, Amani Mirdad
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrospective Study of Intentional Replantation for Type IIIb Dens Invaginatus with Periapical Lesions
Na Li, Huihui Xu, Cunhui Kan, Jing Zhang, Song Li
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(3): 329. CrossRef - Combined Periodontal and Endodontic Management of Palatal Radicular Groove with Platelet‐Rich Fibrin and Biodentine®
Arjun Hari Rijal, Bhageshwar Dhami, Pratistha Ghimire, Konstantinos Michalakis
Case Reports in Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intentional Replantation of Single-Rooted and Multi-Rooted Teeth: A Systematic Review
Massimo Pisano, Federica Di Spirito, Stefano Martina, Giuseppe Sangiovanni, Francesco D’Ambrosio, Alfredo Iandolo
Healthcare.2022; 11(1): 11. CrossRef - Management of the palato-radicular groove with a periodontal regenerative procedure and prosthodontic treatment: A case report
Dan-Hua Ling, Wei-Ping Shi, Yan-Hong Wang, Dan-Ping Lai, Yan-Zhen Zhang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(17): 5732. CrossRef - Prevalence and Periodontal Conditions of Developmental Grooves in an Italian School of Dentistry and Dental Hygiene: A Cross-Sectional Study
Giovanna Laura Di Domenico, Simone Fabrizi, Paolo Capparè, Maria Teresa Sberna, Massimo de Sanctis
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(7): 4047. CrossRef - Clinical Observation and Research Progress of Comprehensive Treatment of Palatogingival Groove
华姣 胡
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2021; 11(03): 846. CrossRef - Palato-gingival groove: A silent nidus. Recognition and an innovative management approach: A report of 3 cases
Purushothama Rangaswamy, Sri Harsha Tummala, Samrat R Magarvalli, Sujith Ramachandra, Kavitha Govindappa, Shwetha E
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2021; 6(2): 114. CrossRef - Periodontal Regenerative Treatment of Intrabony Defects Associated with Palatal Grooves: A Report of Two Cases
Stefano Corbella, Alice Alberti, Beatrice Zotti, Luca Francetti, Jiiang H. Jeng
Case Reports in Dentistry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Recognition and management of palatogingival groove for tooth survival: a literature review
Hee-Jin Kim, Yoorina Choi, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(2): 77. CrossRef - The use of Intentional Replantation to Repair an External Cervical Resorptive Lesion not am Enable to Conventional Surgical Repair
Kreena Pa Tel, Federico Foschi, Ioana Pop, Shanon Patel, Francesco Mannocci
Primary Dental Journal.2016; 5(2): 78. CrossRef - Management of apicomarginal defect in esthetic region associated with a tooth with anomalies
Vinayak Venkoosa Meharwade, Dipali Yogesh Shah, Pradyna Prabhakar Mali, Vidya Vinayak Meharwade
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(4): 314. CrossRef
- Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Therapeutic Effect of Intentional Replantation
- 2,164 View
- 11 Download
- 22 Crossref

- Enamel matrix derivative for replanted teeth in animal models: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Sahng G. Kim, Steven I. Ryu
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):194-203. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.194
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To investigate the effect of enamel matrix derivative (EMD) on periodontal healing of replanted teeth in animal models.
Materials and Methods The authors searched MEDLINE, PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, Web of Knowledge and Scopus for articles published up to Oct 2012. Animal studies in which EMD was applied in transplanted or replanted teeth with adequate controls and histological data were considered. Normal periodontal healing or root resorption determined by histology after EMD was applied in replanted teeth with adequate controls was used as outcome measures. The following search strategy was used: ('Emdogain' OR 'enamel matrix proteins' OR 'enamel matrix derivative') AND ('avulsion' OR 'transplantion' OR 'autotransplantation' OR 'replantation').
Results Six animal studies were included in the final review. There was great heterogeneity in study design among included studies. Two studies with similar study designs were identified and analyzed by a meta-analysis. The pooled estimates showed a significantly higher normal healing and surface resorption and significantly less inflammatory and replacement resorption in EMD-treated groups compared with non-EMD-treated groups.
Conclusions With the limitations of this systematic review, the use of EMD led to greater normal periodontal healing and surface root resorption and less inflammatory and replacement root resorption in the presence of periodontal ligaments. However, no definite conclusion could be drawn with regard to the effect of EMD on periodontal healing and root resorption when no periodontal ligaments exist.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intentional Replantation of Failed Root Canal Treated Tooth
Pritesh Kisanlal Agrawal, Narayan G. Jibhkate, Saurabh A. Redij
Journal of Interdisciplinary Dentistry.2024; 14(2): 128. CrossRef - Enamel matrix derivative in the treatment of tooth replantation: from a biological basis to clinical application
Yao Lin, Liangping Chen, Yuling Xu, Mingwei Xu, Qinghua Liu, Junbing He
Annals of Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Fibrillin protein, a candidate for creating a suitable scaffold in PDL regeneration while avoiding ankylosis
Kyoko Oka
genesis.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Can delayed grafting of frozen teeth achieve periodontal ligament healing?
Yue Chen, Liang Chen, Min Zhou, Shouyin Yi, Juan Ran, Yuansi Long, Jing Luo, Kun Tian
Medical Hypotheses.2022; 167: 110945. CrossRef - Permanent tooth avulsion in children and adults: Therapeutic options for longer survival
Simona Stojanović, Miloš Tijanić, Kristina Burić, Nina Burić, Milan Spasić, Kosta Todorović, Branislava Stojković, Marija Jovanović, Milica Petrović, Dušan Mitić
Acta stomatologica Naissi.2021; 37(83): 2213. CrossRef - Evidence mapping and quality assessment of systematic reviews in dental traumatology
Nitesh Tewari, Vijay Prakash Mathur, Amandeep Kaur, Divesh Sardana, Morankar Rahul, Rigzen Tamchos, Priyanshi Ritwik, Shubhi Goel, Julie Schiavo
Dental Traumatology.2021; 37(1): 17. CrossRef - Application of Enamel Matrix Derivative (Emdogain) in Endodontic Therapy: A Comprehensive Literature Review
Howard H. Wang, Nima D. Sarmast, Elham Shadmehr, Nikola Angelov, Shahrokh Shabahang, Mahmoud Torabinejad
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(7): 1066. CrossRef - Periodontal wound healing following reciprocal autologous root transplantation in class III furcation defects
Naoshi Takeuchi, Yoshinori Shirakata, Yukiya Shinohara, Kotaro Sena, Kazuyuki Noguchi
Journal of Periodontal & Implant Science.2017; 47(6): 352. CrossRef - Effects of Fibrillin Application on Periodontal Ligament Regeneration in Mouse Model of Tooth Replantation
Shougo Tamura, Kyoko Oka, Satoshi Itaya, Michiko Kira-Tatsuoka, Masako Toda, Arisa Higa, Masao Ozaki
Journal of Hard Tissue Biology.2016; 25(3): 295. CrossRef - Autotransplantation: a viable treatment option for adolescent patients with significantly compromised teeth
D Ong, Y Itskovich, G Dance
Australian Dental Journal.2016; 61(4): 396. CrossRef - Influence of enamel matrix derivative on healing of root surfaces after bonding treatment and intentional replantation of vertically fractured roots
Tsutomu Sugaya, Mahito Tomita, Youji Motoki, Hirofumi Miyaji, Masamitsu Kawamami
Dental Traumatology.2016; 32(5): 397. CrossRef - The effect of cathepsin K inhibitor on osteoclastic activity compared to alendronate and enamel matrix protein
Wonkyung Yang, Hyunjung Ko, Heesun Kim, Miri Kim
Dental Traumatology.2015; 31(3): 202. CrossRef - The effects of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and enamel matrix derivative on the bioactivity of mineral trioxide aggregate in MC3T3-E1cells
Youngdan Jeong, Wonkyung Yang, Hyunjung Ko, Miri Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 187. CrossRef - What is the Best Root Surface Treatment for Avulsed Teeth?
Elif B Tuna , Duygu Yaman , Seiko Yamamato
The Open Dentistry Journal.2014; 8(1): 175. CrossRef
- Intentional Replantation of Failed Root Canal Treated Tooth
- 1,695 View
- 4 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Clinical evaluation of a new extraction method for intentional replantation
- Yong-Hoon Choi, Ji-Hyun Bae
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):211-218. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.211
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Purpose Intentional replantation (IR) is a suitable treatment option when nonsurgical retreatment and periradicular surgery are unfeasible. For successful IR, fracture-free safe extraction is crucial step. Recently, a new extraction method of atraumatic safe extraction (ASE) for IR has been introduced.
Patients and Methods Ninety-six patients with the following conditions who underwent IR at the Department of Conservative Dentistry, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, in 2010 were enrolled in this study: failed nonsurgical retreatment and periradicular surgery not recommended because of anatomical limitations or when rejected by the patient. Preoperative orthodontic extrusive force was applied for 2-3 weeks to increase mobility and periodontal ligament volume. A Physics Forceps was used for extraction and the success rate of ASE was assessed.
Results Ninety-six premolars and molars were treated by IR. The complete success rate (no crown and root fracture) was 93% (
n = 89); the limited success rates because of partial root tip fracture and partial osteotomy were 2% (n = 2) and 5% (n = 5), respectively. The clinical and overall success rates of ASE were 95% and 100%, respectively; no failure was observed.Conclusions ASE can be regarded as a reproducible, predictable method of extraction for IR.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bone Loss and Soft Tissue Loss Following Orthodontic Extraction Using Conventional Forceps versus Physics Forceps: A Prospective Split Mouth Study
D. Alden Schnyder Jason, S. Gidean Arularasan, Murugesan Krishnan, M. P. Santhosh Kumar, Saravanan Lakshmanan
Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery.2025; 24(1): 301. CrossRef - Survival outcomes of third molar autotransplantation according to impaction severity: a retrospective cohort study
Kang-Hee Lee, Yong-Suk Choi, Pil-Young Yun, Ji-Young Yoon, Jeong-Kui Ku
Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.2025; 51(4): 198. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Extraction System Benex—Clinical Evaluation and Comparison
Lyubomir Chenchev, Vasilena Ivanova, Krikor Giragosyan, Tasho Gavrailov, Ivan Chenchev
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 234. CrossRef - Minimally invasive extractions with physics forceps – clinical evaluation and comparison
Lyubomir I. Chenchev, Vasilena V. Ivanova, Ivan L. Chenchev, Hristo I. Daskalov
Folia Medica.2024; 66(2): 235. CrossRef - Orthodontic Extrusion vs. Surgical Extrusion to Rehabilitate Severely Damaged Teeth: A Literature Review
Martina Cordaro, Edoardo Staderini, Ferruccio Torsello, Nicola Maria Grande, Matteo Turchi, Massimo Cordaro
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(18): 9530. CrossRef - Comparison of the efficiency of arm force versus arm force plus wrist movement in closed method extractions an observational study
Prashanth Sundaram, Saravanan Kandasamy, Reena Rachel John, K. C. Keerthana Sri
National Journal of Maxillofacial Surgery.2021; 12(2): 250. CrossRef - Surgical extrusion of a maxillary premolar after orthodontic extrusion: a retrospective study
Yong-Hoon Choi, Hyo-Jung Lee
Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.2019; 45(5): 254. CrossRef - A Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Study of Apical Surgery–related Morphological Characteristics of the Distolingual Root in 3-rooted Mandibular First Molars in a Chinese Population
Xiao Zhang, Ning Xu, Hanguo Wang, Qing Yu
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(12): 2020. CrossRef - Influence of Apical Root Resection on the Biomechanical Response of a Single-rooted Tooth—Part 2: Apical Root Resection Combined with Periodontal Bone Loss
Youngjune Jang, Hyoung-Taek Hong, Heoung-Jae Chun, Byoung-Duck Roh
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(3): 412. CrossRef - Comparison Between Physics and Conventional Forceps in Simple Dental Extraction
Mohamed H. El-Kenawy, Wael Mohamed Said Ahmed
Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery.2015; 14(4): 949. CrossRef - Clinical outcome of intentional replantation with preoperative orthodontic extrusion: a retrospective study
Y. H. Choi, J. H. Bae, Y. K. Kim, H. Y. Kim, S. K. Kim, B. H. Cho
International Endodontic Journal.2014; 47(12): 1168. CrossRef - Sealing Ability of Three Different Materials Used as Retrograde Filling
Ji-Hoon Park, Seung-Bok Kang, Yong-Hoon Choi, Ji-Hyun Bae
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2012; 5(2): 60. CrossRef - Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study of Incidence of Distolingual Root and Distance from Distolingual Canal to Buccal Cortical Bone of Mandibular First Molars in a Korean Population
Sin-Young Kim, Sung-Eun Yang
Journal of Endodontics.2012; 38(3): 301. CrossRef
- Bone Loss and Soft Tissue Loss Following Orthodontic Extraction Using Conventional Forceps versus Physics Forceps: A Prospective Split Mouth Study
- 1,928 View
- 11 Download
- 13 Crossref

- A retrospective study of the intentionally replanted mandibular second molars with C-shaped root canal configurations
- Won-Jun Shon, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Ho Baek, Woo-Cheol Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):19-25. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this retrospective study was to evaluate the success rate of intentionally replanted mandibular second molar with C-shaped canal configurations and to access the impact of preoperative periapical lesion on the success of intentional replantation procedure.
Materials and Methods This retrospective chart review study evaluated 52 intentionally replanted mandibular second molar teeth treated at Seoul National University Dental Hospital Department of Conservative Dentistry from January 2005 to December 2007. Seventeen teeth were lost for the follow-up, and another 6 teeth did not meet inclusion criteria of C-shaped root canal configurations. Healing outcome such as success, uncertain healing, and failure after follow-up was evaluated by clinical criteria and radiographs.
Results The overall success rate was 72.4% for the 29 intentionally replanted C-shaped mandibular second molars. The success rate of replanted teeth with preoperative periapical lesions was similar to that of replanted teeth which have no periapical lesions.
Conclusions Therefore, root canal treatment failure on C-shaped mandibular second molar can be predictably treated by intentional replantation regardless of the presence of periapical lesion.
- 1,228 View
- 6 Download

- Short-term clinical outcome of intentionally replanted posterior molars
- Yong-Hoon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):12-18. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This retrospective study evaluated the therapeutic effects of the intentional replantation (IR) procedure performed on the maxillary and mandibular molars of 35 patients.
Materials and Methods For the subjects, IR was performed due to difficulties in anatomically accessing the lesions and/or close proximity to the thick cortical bone, inferior alveolar nerve, or maxillary sinus, which rendered the ordinary periradicular surgery impossible. The patients' progress was followed for a year and up to 2 years and 4 months. The success of the procedure was evaluated in terms of clinical and radiographic success (%).
Results The results revealed the following: (a) 1 case (3%) of failed tooth extraction during IR; (b) 2 cases (6%) of extraction due to periodontal diseases and inflammatory root resorption; (c) 3 cases (9%) of normally functioning teeth in the oral cavity with minor mobility and apical root resorption, and; (d) 29 cases (82%) of normally functioning teeth without obvious problems.
Conclusions IR was confirmed to be a reliably repeatable, predictable treatment option for those who cannot receive conventional periradicular surgery because of anatomic limitations or patient factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Retrospective study of intentional tooth replantation
Joo-Hyuck Park, Sel Ae Hwang, Suk-Ja Yoon, Byung-Cheol Kang, Kyung-Min Lee, Jae-Seo Lee
Oral Biology Research.2017; 41(4): 201. CrossRef - Intentional Replantation of a Root-Fractured Tooth with Pulp Canal Obliteration
Mihee Kim, Sangho Lee, Nanyoung Lee
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2016; 43(2): 200. CrossRef
- Retrospective study of intentional tooth replantation
- 1,069 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Histology of dental pulp healing after tooth replantation in rats
- Eun-Jin Go, Han-Seong Jung, Eui-Seong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung-Jong Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):273-284. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.273
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objective of this study was to observe the histology of dental pulp healing after tooth replantation in rats. The maxillary right first molars of 4-week-old rat were extracted, and then the teeth were repositioned in the original socket. At 3 days after replantation, there was localized inflammatory reaction. But, pulp revasculization and healing had already begun in the root area. At 5 days after replantation, odontoblast-like cells were observed. Tertiary dentin deposition was observed beneath the pulp-dentin border from 1 week after replantation. And tertiary dentin was increased at 2 weeks after replantation. The presence of odontoblast-like cells and the formation of tertiary dentin were continued to 4 weeks after replantation. At 4 weeks after replantation, the deposition of bone-like tissues and cementum-like tissues was observed. This results show that there is a possibility of pulp healing after tooth replantation in rats and the mineralization of tooth can progress. The mineralization of tooth after replantation was initially occurred by the deposition of tertiary dentin, but as time passed, the deposition of bone-like tissues and cementum-like tissues was begun and increased.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Doxycycline-Loaded Nitric Oxide-Releasing Nanomatrix Gel in Replanted Rat Molar on Pulp Regeneration
Kwan-Hee Yun, Mi-Ja Ko, Yong-Kown Chae, Koeun Lee, Ok-Hyung Nam, Hyo-Seol Lee, Kyounga Cheon, Sung-Chul Choi
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(13): 6041. CrossRef - Bio-Photonic Detection and Quantitative Evaluation Method for the Progression of Dental Caries Using Optical Frequency-Domain Imaging Method
Ruchire Wijesinghe, Nam Cho, Kibeom Park, Mansik Jeon, Jeehyun Kim
Sensors.2016; 16(12): 2076. CrossRef
- Doxycycline-Loaded Nitric Oxide-Releasing Nanomatrix Gel in Replanted Rat Molar on Pulp Regeneration
- 2,197 View
- 27 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


