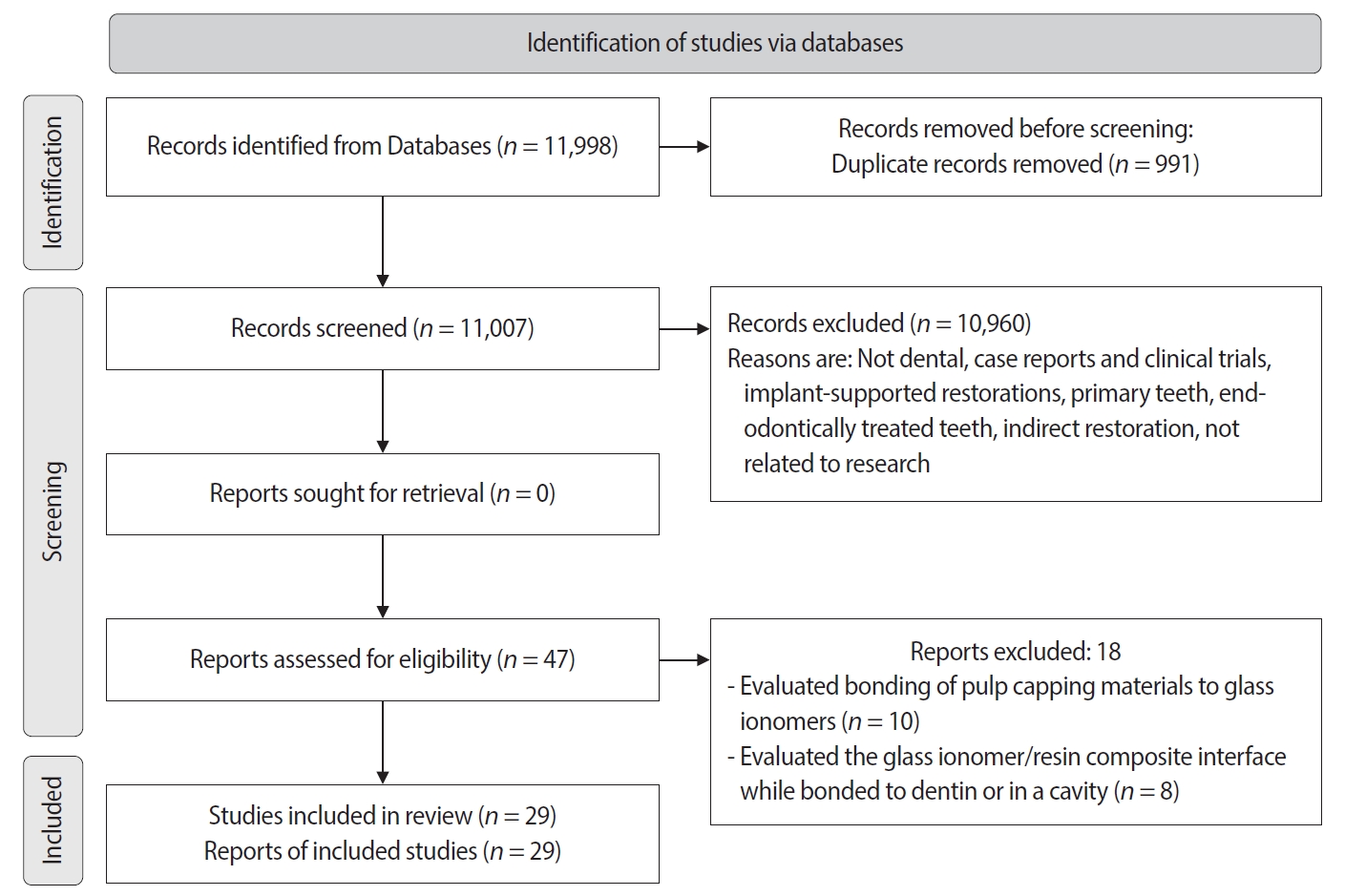
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 50(2); 2025 > Article
- Research Article Effect of surface treatment on glass ionomers in sandwich restorations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory studies
-
Hoda S. Ismail1,*
 , Ashraf Ibrahim Ali1
, Ashraf Ibrahim Ali1 , Franklin Garcia-Godoy2,3
, Franklin Garcia-Godoy2,3
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e13.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e13
Published online: March 24, 2025
1Conservative Dentistry Department, Faculty of Dentistry, Mansoura University, Egypt
2Department of Bioscience Research, College of Dentistry, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN, USA
3The Forsyth Institute, Cambridge, MA, USA
- *Correspondence to Hoda S. Ismail, BDS, MSD Conservative Dentistry Department, Faculty of Dentistry, Mansoura University, Algomhoria Street, Mansoura, Aldakhlia, Egypt Po (box) 35516, Egypt Email: hoda_saleh@mans.edu.eg
© 2025 The Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
-
Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effect of different surface treatments on the bond strength between new or aged glass ionomers (GI) and resin composites in sandwich restorations.
-
Methods A comprehensive search was conducted in three databases to identify studies focusing on the bond strength of new or aged GIs and resin composites in laboratory settings. The selected studies were assessed for potential biases based on predetermined criteria. Additionally, a meta-analysis was performed using three studies.
-
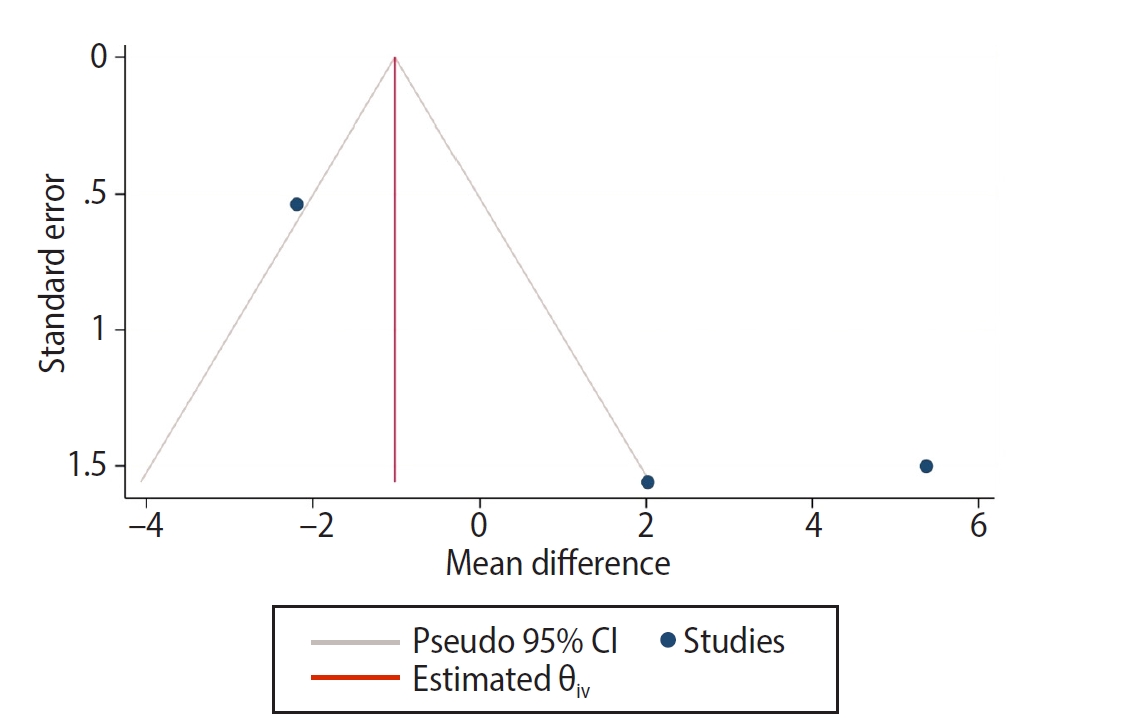
Results A total of 29 studies were included, with 24 investigating the bond strength of new GIs and five focusing on GI repair. Three studies were included in the meta-analysis (with a 95% confidence interval) which revealed no significant difference in the mean MPa values of resin-modified glass ionomer (RMGI) treated with phosphoric acid or Er,Cr:YSGG laser before the application of an etch-and-rinse adhesive. Surface treatment was found to be crucial for achieving optimal bonding between GI and resin composite, regardless of the GI’s condition.
-
Conclusions The combination of mechanical and chemical surface treatments does not significantly affect the bond strength between new RMGI and composite. However, for GI repair, it is recommended to use both treatments to enhance the bond strength.
INTRODUCTION
METHODS
RESULTS
1. Control groups
2. Finishing and polishing before bonding
3. Type of glass ionomer and overlying composite
4. Type of surface treatment
5. Aging before testing
6. Testing methods
1. Control groups
2. Finishing and polishing before bonding
3. Type of glass ionomer and overlying composite
4. Technique of aging the tested glass ionomers
5. Type of surface treatment
6. Aging before testing
7. Testing methods
1. Comparing different types of glass ionomers
2. Control vs surface treatment
3. Effect of combining mechanical and chemical surface treatments
4. Etch-and-rinse vs self-etch adhesives
5. The use of phosphoric acid solely or etch-and-rinse adhesive without phosphoric acid
6. Comparing different self-etch adhesives
7. Universal adhesive
8. Type of composite
9. Effect of aging
10. Failure mode analysis
11. Risk of bias assessment
1. Comparing different types of glass ionomers
2. Control vs surface treatment
3. Effect of combining mechanical and chemical treatment
4. The use of phosphoric acid solely or etch-and-rinse adhesive without phosphoric acid
5. Universal adhesives
6. Type of repair material
7. Failure mode analysis
8. Risk of bias assessment
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSIONS AND CLINICAL RECOMMENDATIONS
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
FUNDING/SUPPORT
None.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: Ismail HS, Garcia-Godoy F; Data curation: Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Software: Ismail HS; Investigation: Ali AI; Supervision: Ali AI, Garcia-Godoy F; Writing – original draft: Ismail HS; Writing - review & editing: Ali AI, Garcia-Godoy F. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
-
DATA SHARING STATEMENT
The datasets are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.

| Study | Sample size per group and specimens’ dimensions | Aging for GI | Surface treatment |
Test type |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1ry | 2ry | ||||
| Arora et al. (2010) [22] | 12 per group | Chemical | SBS | ||
| Dimensions for GI: 8 × 2.5 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 5 × 5.5 mm | |||||
| Boushell et al. (2011) [32] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 5 × 2 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 2.38 × 2 mm | |||||
| Zhang et al. (2011) [14] | 20 per group | Chemical | μSBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: not specified | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 1.5 × less than 2 mm | |||||
| Chandak et al. (2012) [23] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | ||
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 2.5 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 5 × 3 mm | |||||
| Kandaswamy et al. (2012) [15] | 25 per group | Chemical | SBS | FESEM/EDX analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 3 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 6 × 3 mm | |||||
| Navimipour et al. (2012) [24] | 20 per group | Chemical and mechanical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 5 × 4 mm | Surface evaluation using SEM | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 2.5 × 2 mm | |||||
| Pamir et al. (2012) [33] | 15 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 4 × 6 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 × 6 mm | |||||
| Fragkou et al. (2013) [25] | 7 per group | Chemical | TBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 22 × 5 × 1 mm | Tensile strain | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 22 × 5 × 1 mm | Young’s elastic modulus | ||||
| Kasraie et al. (2013) [26] | 4 per group | Chemical | μSBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 15 × 2 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 0.8 × 2 mm | |||||
| Otsuka et al. (2013) [13] | 10 per group | Chemical and mechanical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 4 mm | Surface free energy measurement | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 × 2 mm | |||||
| Babannavar and Shenoy (2014) [34] | 5 per group | Chemical | SBS | ||
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 3 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 6 × 3 mm | |||||
| Boruziniat and Gharaei (2014) [35] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 2 × 2 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 2 × 4 mm | |||||
| Jaberi Ansari et al. (2014) [36] | 10 per group | Chemical | |||
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 4 × 2 mm | μSBS | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 0.7 × 1 mm | |||||
| Ozer et al. (2014) [37] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 10 × 1 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 8 × 2 mm | |||||
| Panahandeh et al. (2015) [38] | 10 per group | Chemical | μSBS | Surface evaluation using SEM | |
| Dimensions for GI: 2 × 4 × 6 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 0.7 × 1 mm | |||||
| Sharafeddin and Choobineh (2016) [39] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | ||
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 3 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 6 × 3 mm | |||||
| Francois et al. (2019) [16] | 22 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 7 × 3 mm | E-SEM evaluation | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 7 × 3 mm | |||||
| Pandey et al. (2019) [27] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | ||
| Dimensions for GI: 10 × 2 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 5 × 6 mm | |||||
| Bin-Shuwaish et al. (2020) [10] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 8 × 4 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 × 4 mm | |||||
| Ghubaryi et al. (2020) [18] | 10 per group | Chemical and mechanical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 4 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 × 3 mm | |||||
| Bilgrami et al. (2022) [28] | 8 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 4 × 2 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 × 2 mm | |||||
| Farshidfar et al. (2022) [29] | 10 per group | Chemical | μTBS | ||
| Dimensions for GI: 10 × 5 × 6 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 5 × 5 × 6 mm | |||||
| Zakavi et al. (2023) [30] | 10 per group | Chemical and mechanical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 3 × 5 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 2 mm | |||||
| Dawood et al. (2024) [31] | 10 per group | Chemical and mechanical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 10 × 2 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 × 2 mm | |||||
| Maneenut et al. (2010) [12] | 15 per group | 4 days of water storage | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis |
| Dimensions for GI: 8.5 × 4 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 5.8 × 4 mm | |||||
| Welch et al. (2015) [41] | 20 per group | One-week water storage with one TC | Chemical and mechanical | SBS | Failure mode analysis |
| Dimensions for GI: 5 mm | 500 TC | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 mm | 24-hour delay in a dry environment, followed by 500 TC | ||||
| Vural and Gurgan (2019) [40] | 12 per group | Chemical | μTBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 8 × 2 × 2 mm | 5,000 TC | SEM evaluation for the bonded interface | |||
| Dimensions for composite: 8 × 2 × 2 mm | |||||
| Ozaslan et al. (2023) [17] | 10 per group | 10,000 brushing cycles and 10,000 TC | Chemical | μSBS | Failure mode analysis |
| Dimensions for GI: 10 × 2 mm | Surface evaluation using SEM | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 1.6 × 2 mm | |||||
| Silva et al. (2024) [42] | 8 per group | 14 days’ water storage and 5,000 TC | Chemical | μTBS | Failure mode analysis |
| Dimensions for GI: 8 × 8 × 4 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 8 × 8 × 4 mm | |||||
E-SEM, environmental scanning electron microscopy; FESEM/EDX, finite element scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive X-ray analysis; GI, glass ionomer; SBS, shear bond strength; μSBS, microshear bond strength; TBS, tensile bond strength test; μTBS, microtensile bond strength test; SEM, scanning electron microscope; TC, thermal cycle.
| Study | Materials used | Classification | Commercial name | Placement technique |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arora et al. (2010) [22] | GI | RMGI | Vitrebond | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Z350 | Incremental | |
| Boushell et al. (2011) [32] | GI | RMGI | Vitrebond plus | Bulk |
| Conventional GIC | GC Fuji IX GP EXTRA | |||
| Overlying composite | Silorane-based composite | Filtek LS | One increment (2 mm depth) | |
| Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | |||
| Zhang et al. (2011) [14] | GI | Two types of conventional GIC | GC Fuji IX GP EXTRA | Not specified |
| Riva Self Cure | ||||
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | Gradia Direct Anterior | One increment (2 mm depth) | |
| Chandak et al. (2012) [23] | GI | RMGI | Vitrebond | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Packable microhybrid resin composite | Filtek F‑60 | Incremental | |
| Kandaswamy et al. (2012) [15] | GI | Conventional GIC | Fuji IX | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | Solare | Incremental | |
| Navimipour et al. (2012) [24] | GI | Conventional GIC | Fuji II | Bulk |
| RMGI | Fuji II LC | |||
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | One increment (2 mm depth) | |
| Pamir et al. (2012) [33] | GI | Conventional GIC | Ketac Molar Quick Aplicap | Bulk |
| RMGI | Photac Fil Quick Aplicap | |||
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | Incremental | |
| Fragkou et al. (2013) [25] | GI | RMGI | Vitremer Tri-Cure | Not specified |
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Supreme XT | Not specified | |
| Kasraie et al. (2013) [26] | GI | RMGI | Vitrebond | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | One increment (2 mm depth) | |
| Otsuka et al. (2013) [13] | GI | Conventional GIC | Fuji IX GP | Bulk |
| Two RMGI | Fuji II LC EM, Fuji Filling LC | |||
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | Clearfil AP-X | One increment (2 mm depth) | |
| Babannavar and Shenoy (2014) [34] | GI | RMGI | Vitrebond | Incremental |
| Nanofilled RMGI | Ketac N100 | Incremental | ||
| Conventional GIC | Ketac Bond | Bulk | ||
| Overlying composite | Silorane-based composite | Filtek P90 | Incremental | |
| Boruziniat and Gharaei (2014) [35] | GI | RMGI | Fuji II LC | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Microfilled resin composite | Heliomolar | Incremental | |
| Jaberi Ansari et al. (2014) [36] | GI | Conventional GIC | Fuji II | Bulk |
| RMGI | Fuji II LC | |||
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | Filtek Z100 | Bulk | |
| Ozer et al. (2014) [37] | GI | Conventional GIC | Riva Self Cure | Bulk |
| RMGI | Fuji II LC | |||
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | Bulk | |
| Silorane-based composite | Filtek Silorane | |||
| Panahandeh et al. (2015) [38] | GI | Two RMGI | Riva Light Cure and Fuji II LC | Bulk |
| Two conventional GIC | Riva Self Cure and Fuji II | |||
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | Filtek Z100 | Bulk | |
| Sharafeddin and Choobineh (2016) [39] | GI | Conventional GIC | ChemFil Superior | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Z350 | Incremental | |
| Francois et al. (2019) [16] | GI | One glass hybrid + one conventional GIC | EQUIA Forte Fil and Fuji IX GPFast | Bulk |
| RMGI | Fuji II LC | |||
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Z350 | Incremental | |
| Pandey et al. (2019) [27] | GI | RMGI | Fuji II LC | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | Incremental | |
| Bin-Shuwaish (2020) [10] | GI | RMGI | Fuji II LC | Incremental |
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled bulk fill resin composite | Filtek One Bulk Fill | Bulk | |
| Nanohybrid bulk fill resin composite | Tetric N-Ceram Bulk Fill | Bulk | ||
| Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Z350 XT | Incremental | ||
| Ghubaryi et al. (2020) [18] | GI | RMGI | Fuji Filling LC | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | Incremental | |
| Bilgrami et al. (2022) [28] | GI | Conventional GIC | Ketac Molar | Bulk |
| Easy mix | ||||
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Z350 | Bulk (2 mm depth) | |
| Nanoceramic resin composite | Ceram X | |||
| Microhybrid resin composite | Spectrum | |||
| Farshidfar et al. (2022) [29] | GI | One glass hybrid and one conventional GIC | Equia Forte Fil | Bulk |
| Riva Self Cure | ||||
| Two RMGI | Fuji II LC | |||
| Riva Light cure | ||||
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | GC Kalore | Incremental | |
| Zakavi et al. (2023) [30] | GI | RMGI | Fuji II LC | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | Gradia direct | One increment (2 mm) | |
| Dawood et al. (2024) [31] | GI | Conventional GIC | Securafil | Bulk |
| RMGI | Glass Liner | |||
| Overlying composite | Submicron-filled resin composite | PALFIQUE LX5 | One increment (2 mm) | |
| GI repair | ||||
| Maneenut et al. (2010) [12] | GI (Both materials used also for repair) | Nanofilled RMGI | Ketac N100 | Bulk |
| RMGI | Fuji II LC | |||
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Supreme | Bulk | |
| Microfilled resin composite | Solare | |||
| Welch et al. (2015) [41] | GI | RMGI | Fuji II LC | Bulk |
| Overlying GIC | RMGI | Fuji II LC | Bulk | |
| Vural and Gurgan (2019) [40] | GI (The material was used also for repair) | Glass hybrid | EQUIA Forte Fil | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | G‑aenial posterior | Not specified | |
| Ozaslan et al. (2023) [17] | GI | Glass hybrid | EQUIA Forte HT Fil | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Nanoceramic resin composite | Neo Spectra ST HV | Bulk (2 mm depth) | |
| Silva et al. (2024) [42] | GI (The material was used also for repair) | RMGI | Riva Light Cure | Incremental |
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Z350 XT | Incremental | |
| Study | Finishing and polishing for GI | Type of surface treatment | Commercial brand and specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arora et al. (2010) [22] | No | Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Single Bond 2 |
| Two-component self-etch adhesive | Adper Prompt L Pop (pH: 0.8) | ||
| Boushell et al. (2011) [32] | Only for the Conventional GIC | Two-step silorane-based adhesive | Filtek LS adhesive (pH: 2.7) |
| Two-step self-etch adhesive | Adper Scotchbond SE (pH: 1) | ||
| Zhang et al. (2011) [14] | Yes | 37% phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | SDI acid etch gel + Adper Single Bond Plus |
| Two-step self-etch adhesives | Adper Scotchbond SE | ||
| Clearfil SE Bond (pH: 2) | |||
| One-step self-etch adhesives | Clearfil S3 Bond (pH: 2.3) | ||
| One Coat 7.0 | |||
| Chandak et al. (2012) [23] | No | Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Scotch Bond 2 |
| Two-component self-etch adhesive | Adper Prompt L Pop | ||
| Kandaswamy et al. (2012) [15] | No | Self-etch adhesives | Adper prompt self-etch (pH: 1) |
| AdheSE (pH: 1.4) | |||
| Clearfil SE | |||
| One coat SE (pH: 2.2) | |||
| Navimipour et al. (2012) [24] | No | 35% phosphoric acid gel + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Scotchbond Etchant |
| Adper Single Bond | |||
| Er,Cr:YSGG laser + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Waterlase YSGG; Biolase Europe GmbH | ||
| A pulse energy setting of 1 W was applied for 15 seconds using a G-type tip with a diameter of 600 μm, accompanied by 10% water and 11% air. | |||
| Pamir et al. (2012) [33] | Yes | %35 phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Scotchbond Etch |
| Adper Single Bond 2 | |||
| Two-component self-etch adhesive | Adper Prompt L Pop | ||
| Fragkou et al. (2013) [25] | No | Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Single Bond 2 |
| Kasraie et al. (2013) [26] | Yes | 37% phosphoric acid | Scotchbond™ Etchant |
| Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Single Bond | ||
| Self-etch adhesives | Clearfil SE Bond self-etch primer | ||
| Clearfil S3 Bond self-etch adhesive | |||
| Otsuka et al. (2013) [13] | No | 35% phosphoric acid + one-step self-etch adhesive | Gel Etchant (Kerr) |
| G-Bond Plus | |||
| Air abrasion acid + one-step self-etch adhesive | Airborne particle abrasion with 50-μm aluminum oxide at 0.3 MPa for 5 seconds | ||
| Babannavar and Shenoy (2014) [34] | No | Two-step self-etch silorane-based adhesive | Filtek P90 adhesive (pH: 2.7) |
| Boruziniat and Gharaei (2014) [35] | No | Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Tetric N-Bond |
| Two-step self-etch adhesive | AdheSE | ||
| One-step self-etch adhesive | AdheSE One F (pH: 1.5) | ||
| Jaberi Ansari et al. (2014) [36] | No | Two-component one-step self-etch adhesive | Adper Prompt L Pop |
| Two-step self-etch adhesives | Clearfil SE Bond | ||
| Clearfil Protect bond (pH: 2) | |||
| AdheSE | |||
| Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Single bond | ||
| Ozer et al. (2014) [37] | Yes | Two-step self-etch adhesive | Clearfil SE Bond |
| Two-step self-etch silorane-based adhesive | Filtek P90 adhesive | ||
| Panahandeh et al. (2015) [38] | No | 37% phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Stae, SDI |
| Two-step self-etch adhesive | Frog, SDI (pH: 2) | ||
| Sharafeddin and Choobineh (2016) [39] | No | Two-step self-etch adhesive | Clearfil SE Bond |
| One-step self-etch adhesive | Optibond (pH: 1.4) | ||
| Two-component one-step self-etch adhesive | Adper Prompt L Pop | ||
| 37% phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Single Bond 2 | ||
| Francois et al. (2019) [16] | No | One-step universal adhesive used in self-etch mode | Scotchbond Universal (pH: 2.7) |
| 32% phosphoric acid + universal adhesive used in etch-and-rinse mode | Scotchbond Universal Etchant + Scotchbond Universal | ||
| 32% phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Scotchbond Universal Etchant + Scotchbond 1XT | ||
| One-step self-etch adhesive | Optibond All-In-One (pH: 2.5) | ||
| Universal primer + one-step self-etch adhesive | Monobond Plus + Optibond All-in-One | ||
| Coating material | EQUIA Forte Coat | ||
| Pandey et al. (2019) [27] | No | Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Single Bond 2 |
| One-step self-etch adhesive | Optibond All-In-One | ||
| Bin-Shuwaish (2020) [10] | No | 35% phosphoric acid + Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Ultra-Etch + OptiBond Solo Plus |
| Two-step self-etch adhesive | Clearfil SE Bond 2 | ||
| Universal adhesive used in both etch-and-rinse (with 35% phosphoric acid) and self-etch modes | Single Bond Universal | ||
| Ghubaryi et al. (2020) [18] | No | Methylene blue photosensitizers activated with photodynamic therapy + Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Sisco Research Lab |
| A single-wavelength light source with an 810 nm wavelength and a power output of 1.5 W was used at a concentration of 100 mg/L. This light was directed perpendicularly onto the RMGI and continuously applied for 60 seconds. | |||
| Adper Single Bond 2 | |||
| Er,Cr:YSGG laser + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Biolase- Waterlase iPlus | ||
| For a duration of 5 seconds at 2.8 MPa | |||
| Nd-YAG laser + etch-and-rinse adhesive | NianSheng | ||
| A noncontact circular motion technique was used with a power setting of 1.5 W for a duration of 60 seconds. During the procedure, the 400 μm quartz micro tip was kept at a 90-degree angle to the cement surface. | |||
| Aluminum oxide sandblasting + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Aluminum trioxide, Dentsply | ||
| With a power of 1.5 W and a frequency of 30 Hz, the MZ8 tip was used in a circular motion for 60 seconds, held 2 mm away from the surface. | |||
| 37% phosphoric acid + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Aqua Etch | ||
| Bilgrami et al. (2022) [28] | No | 37% and 36% phosphoric acid gel | Scotchbond Etchant |
| Dentsply | |||
| Farshidfar et al. (2022) [29] | No | 35% phosphoric acid | Ultra-Etch |
| Two universal adhesives (used in both etch-and-rinse and self-etch modes) | CLEARFIL Universal Bond (pH: 2.3) | ||
| G-Premio Bond (pH: 1.5) | |||
| Zakavi et al. (2023) [30] | No | Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Single Bond 2 |
| 37% phosphoric acid + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Morva Etch | ||
| Aluminum oxide sandblasting + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Microblaster Dento-Prep, Dental Microblaster | ||
| 30-μm Al2O3 particles for 10 seconds | |||
| Rough diamond bur + etch-and-rinse adhesive | 012 Cylinder Flat End | ||
| The diamond bur was employed for 3 seconds at high speed with an accompanying water spray. | |||
| Er: YAG laser + etch-and-rinse adhesive | M021-3AF/4, Fotona | ||
| With a 1,064 nm wavelength, delivering 1.5 W of power, at a frequency of 5 Hz, with 8% water output and 4% air output, positioned 10 mm away from the target. The laser was operated in micro-short pulse mode, delivering energy at 300 mJ | |||
| Er, Cr: YSGG laser + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Water Lase iPlus, Biolase | ||
| An MZ8 tip with a diameter of 800 μm and a spot size of 0.502 mm² was used. This tip emitted laser light at a 2,780-nm wavelength, 1 W of power, and a frequency of 20 Hz. The water output was set at 20%, and the air output was 10%, with the tip held 1 mm from the surface for 15 seconds. This setup provided an intensity of 53.07 J/cm² | |||
| Dawood et al. (2024) [31] | No | Sandblasted | Air Prophy Unit |
| Sandblasted + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | For 30 seconds with an air abrasion unit using 50-μm aluminum oxide particles | ||
| 37% phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Scotchbond 1XT | ||
| Universal adhesive used in self-etch mode | Scotchbond Universal | ||
| Maneenut et al. (2010) [12] | Yes | Repair with nanofilled RMGI | Ketac Nano-ionomer Primer |
| Nanofilled RMGI Primer | GC Dentin Conditioner | ||
| Dentin Conditioner + Nanofilled RMGI Primer | |||
| 37% phosphoric acid gel + Nanofilled RMGI Primer | |||
| Repair with both resin composites | Scotchbond Etching Gel | ||
| 37% phosphoric acid gel + two-step etch-and-rinse/or one-step self-etch adhesive | Single Bond | ||
| Etch-and-rinse/or one-step self-etch adhesive | G-Bond (pH: 2.8) | ||
| Repair with RMGI | |||
| One-step self-etch adhesive | |||
| Dentin Conditioner + one-step self-etch adhesive | |||
| 37% phosphoric acid gel + one-step self-etch adhesive | |||
| Welch et al. (2015) [41] | No | Sanding using wet 800-grit silicon carbide paper | Leco |
| Sanding + 37.5% phosphoric acid | |||
| Sanding + 37.5% phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Kerr Gel Etchant | ||
| Optibond Solo Plus | |||
| Vural and Gurgan (2019) [40] | No | Repair using glass hybrid | DIATECH, Swiss Dental |
| Roughened using a diamond coarse fissure bur | Cavity conditioner, GC | ||
| 20% mild polyacrylic acid | G‑premio Bond | ||
| 20% mild polyacrylic acid + a universal adhesive | |||
| A universal adhesive | |||
| Repair using resin composite | GC etching gel | ||
| Roughened using a diamond coarse fissure bur | |||
| Roughening + universal adhesive | |||
| 40% phosphoric acid + universal adhesive | |||
| Universal adhesive | |||
| Ozaslan et al. (2023) [17] | Yes | Silane + universal adhesive | Clearfil Ceramic Primer Plus |
| Prime & Bond Universal (pH: 2.7) | |||
| Silva et al. (2024) [42] | Yes | Universal adhesive in self-etch mode | Scotchbond Universal |
| 37% phosphoric acid + universal adhesive |
| Study | Test type | Testing machine and speed | Aging condition | Method of failure analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arora et al. (2010) [22] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Boushell et al. (2011) [32] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | ×2.5 |
| Zhang et al. (2011) [14] | μSBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours, 1- and 6-month water storage | Light microscope at ×40 |
| Chandak et al. (2012) [23] | SBS | UTM, 3 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Kandaswamy et al. (2012) [15] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Navimipour et al. (2012) [24] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | Stereomicroscope at ×20 |
| Pamir et al. (2012) [33] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 48 hours | Light microscope at ×10 or ×20 |
| Fragkou et al. (2013) [25] | TBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | - | Stereomicroscope at ×16 |
| Kasraie et al. (2013) [26] | μSBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | Stereomicroscope at ×40 |
| Otsuka et al. (2013) [13] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours | Optical microscope at ×10 |
| Babannavar and Shenoy (2014) [34] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Boruziniat and Gharaei (2014) [35] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 48 hours | Stereomicroscope |
| Jaberi Ansari et al. (2014) [36] | μSBS | MTT, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Ozer et al. (2014) [37] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | 500 TC | Stereomicroscope at ×25 |
| Panahandeh et al. (2015) [38] | μSBS | MTT, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Sharafeddin and Choobineh (2016) [39] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Francois et al. (2019) [16] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 48 hours | Binocular microscope at ×30 |
| Pandey et al. (2019) [27] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Bin-Shuwaish (2020) [10] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | 5,000 TC | Digital stereomicroscope at ×30 |
| Ghubaryi et al. (2020) [18] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 48 hours | Optical microscope at ×10 |
| Bilgrami et al. (2022) [28] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | 500 TC | The exact technique and magnification are not specified |
| Farshidfar et al. (2022) [29] | μTBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Zakavi et al. (2023) [30] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | 5,000 TC | Light microscope |
| Dawood et al. (2024) [31] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours | Stereomicroscope at ×10 |
| GI repair | ||||
| Maneenut et al. (2010) [12] | SBS | UTM, 0.75±0.25 mm/min | After 24 hours | Light microscope at ×2 |
| Welch et al. (2015) [41] | SBS | UTM | - | SEM at ×13 |
| Vural and Gurgan (2019) [40] | μTBS | MTT, 1 mm/min | - | Stereomicroscope at ×40 |
| Ozaslan et al. (2023) [17] | μSBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | Stereomicroscope at ×30 |
| Silva et al. (2024) [42] | μTBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours | Stereomicroscope at ×40 |
| Study | Description of sample size calculation | Specimen preparation carried out by the same operator | Randomization of specimens | Use of control group (without the tested surface treatment) | Use of materials according to manufacturers’ instructions | Evaluation of failure mode | Blinding of examiner | Risk of bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arora et al. (2010) [22] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | High |
| Boushell et al. (2011) [32] | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Zhang et al. (2011) [14] | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Chandak et al. (2012) [23] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | High |
| Kandaswamy et al. (2012) [15] | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | High |
| Navimipour et al. (2012) [24] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Pamir et al. (2012) [33] | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | High |
| Fragkou et al. (2013) [25] | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Kasraie et al. (2013) [26] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Otsuka et al. (2013) [13] | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Babannavar and Shenoy (2014) [34] | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | High |
| Boruziniat and Gharaei (2014) [35] | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Jaberi Ansari et al. (2014) [36] | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | High |
| Ozer et al. (2014) [37] | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | High |
| Panahandeh et al. (2015) [38] | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | High |
| Sharafeddin and Choobineh (2016) [39] | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | High |
| Francois et al. (2019) [16] | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | High |
| Pandey et al. (2019) [27] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | High |
| Bin-Shuwaish (2020) [10] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Ghubaryi et al. (2020) [18] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Bilgrami et al. (2022) [28] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Farshidfar et al. (2022) [29] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | High |
| Zakavi et al. (2023) [30] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Dawood et al. (2024) [31] | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Maneenut et al. (2010) [12] | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Welch et al. (2015) [41] | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Vural and Gurgan (2019) [40] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Ozaslan et al. (2023) [17] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Silva et al. (2024) [42] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Study |
Er,Cr:YSGG laser-treated |
Phosphoric acid-treated |
Difference, mean (95% CI) | p-value | Weight | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean ± SD | n | Mean ± SD | ||||
| Ghubaryi et al. [18] | 10 | 14.26 ± 1.67 | 10 | 16.45 ± 0.32 | –2.19 (–3.244 to –1.136) | 36.46 | |
| Navimipour et al. [24] | 20 | 22.81 ± 4.27 | 20 | 17.44 ± 5.18 | 5.37 (2.428 to 8.312) | 31.95 | |
| Zakavi et al. [30] | 10 | 17.22 ± 3.36 | 10 | 15.20 ± 3.61 | 2.02 (–1.037 to 5.077) | 31.59 | |
| Total (random effects) | 40 | 40 | 1.555 (–2.857 to 5.968) | 0.490 | 100 | ||
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Q | 26.66 |
| Degree of freedom | 2 |
| p-value | <0.001 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 0.9083 |
- 1. Davidson CL. Advances in glass-ionomer cements. J Appl Oral Sci 2006;14 Suppl:3-9.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Ismail HS, Ali AI, Mehesen RE, Juloski J, Garcia-Godoy F, Mahmoud SH. Deep proximal margin rebuilding with direct esthetic restorations: a systematic review of marginal adaptation and bond strength. Restor Dent Endod 2022;47:e15.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 3. Ismail HS, Ali AI, Mehesen RE, Garcia-Godoy F, Mahmoud SH. In vitro marginal and internal adaptation of four different base materials used to elevate proximal dentin gingival margins. J Clin Exp Dent 2022;14:e550-e559.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Tyas MJ. Clinical evaluation of glass-ionomer cement restorations. J Appl Oral Sci 2006;14 Suppl:10-13.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Opdam NJ, VanBeek V, VanBeek W, Loomans BA, Pereira-Cenci T, Cenci MS, et al. Long term clinical performance of ‘open sandwich’ and ‘total-etch’ Class II composite resin restorations showing proximal deterioration of glass-ionomer cement. Dent Mater 2023;39:800-806.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Mount GJ, Tyas MJ, Ferracane JL, Nicholson JW, Berg JH, Simonsen RJ, et al. A revised classification for direct tooth-colored restorative materials. Quintessence Int 2009;40:691-697.PubMed
- 7. Gopikrishna V, Abarajithan M, Krithikadatta J, Kandaswamy D. Shear bond strength evaluation of resin composite bonded to GIC using three different adhesives. Oper Dent 2009;34:467-471.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Sidhu SK. Clinical evaluations of resin-modified glass-ionomer restorations. Dent Mater 2010;26:7-12.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Gupta R, Mahajan S. Shear bond strength evaluation of resin composite bonded to GIC using different adhesives. J Clin Diagn Res 2015;9:ZC27-ZC29.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Bin-Shuwaish MS. Shear bond strength of bulk-fill composites to resin-modified glass ionomer evaluated by different adhesion protocols. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent 2020;12:367-375.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Moncada G, Fernández E, Martín J, Arancibia C, Mjör IA, Gordan VV. Increasing the longevity of restorations by minimal intervention: a two-year clinical trial. Oper Dent 2008;33:258-264.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Maneenut C, Sakoolnamarka R, Tyas MJ. The repair potential of resin-modified glass-ionomer cements. Dent Mater 2010;26:659-665.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Otsuka E, Tsujimoto A, Takamizawa T, Furuichi T, Yokokawa M, Tsubota K, et al. Influence of surface treatment of glass-ionomers on surface free energy and bond strength of resin composite. Dent Mater J 2013;32:702-708.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Zhang Y, Burrow MF, Palamara JE, Thomas CD. Bonding to glass ionomer cements using resin-based adhesives. Oper Dent 2011;36:618-625.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Kandaswamy D, Rajan KJ, Venkateshbabu N, Porkodi I. Shear bond strength evaluation of resin composite bonded to glass-ionomer cement using self-etching bonding agents with different pH: In vitro study. J Conserv Dent 2012;15:27-31.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Francois P, Vennat E, Le Goff S, Ruscassier N, Attal JP, Dursun E. Shear bond strength and interface analysis between a resin composite and a recent high-viscous glass ionomer cement bonded with various adhesive systems. Clin Oral Investig 2019;23:2599-2608.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Ozaslan S, Celiksoz O, Tepe H, Tavas B, Yaman BC. A comparative study of the repair bond strength of new self-adhesive restorative materials with a resin composite material. Cureus 2023;15:e44309.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. Ghubaryi AA, Ingle N, Basser MA. Surface treatment of RMGIC to composite resin using different photosensitizers and lasers: a bond assessment of closed Sandwich restoration. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2020;32:101965.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev 2015;4:1.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021;372:n71.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Elkaffas AA, Hamama HH, Mahmoud SH. Do universal adhesives promote bonding to dentin?: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Restor Dent Endod 2018;43:e29.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 22. Arora V, Kundabala M, Parolia A, Thomas MS, Pai V. Comparison of the shear bond strength of RMGIC to a resin composite using different adhesive systems: an in vitro study. J Conserv Dent 2010;13:80-83.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Chandak MG, Pattanaik N, Das A. Comparative study to evaluate shear bond strength of RMGIC to composite resin using different adhesive systems. Contemp Clin Dent 2012;3:252-255.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Navimipour EJ, Oskoee SS, Oskoee PA, Bahari M, Rikhtegaran S, Ghojazadeh M. Effect of acid and laser etching on shear bond strength of conventional and resin-modified glass-ionomer cements to composite resin. Lasers Med Sci 2012;27:305-311.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 25. Fragkou S, Nikolaidis A, Tsiantou D, Achilias D, Kotsanos N. Tensile bond characteristics between composite resin and resin-modified glass-ionomer restoratives used in the open-sandwich technique. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 2013;14:239-245.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Kasraie S, Shokripour M, Safari M. Evaluation of micro-shear bond strength of resin modified glass-ionomer to composite resins using various bonding systems. J Conserv Dent 2013;16:550-554.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 27. Pandey SA, Lokhande MT, Gulve MN, Kolhe SJ, Aher GB. Shear bond strength of composite resin to resin-modified glass ionomer cement using 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-based and 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-free adhesive system. J Conserv Dent 2019;22:292-295.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 28. Bilgrami A, Maqsood A, Alam MK, Ahmed N, Mustafa M, Alqahtani AR, et al. Evaluation of shear bond strength between resin composites and conventional glass ionomer cement in class II restorative technique: an in vitro study. Materials (Basel) 2022;15:4293.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Farshidfar N, Agharokh M, Ferooz M, Bagheri R. Microtensile bond strength of glass ionomer cements to a resin composite using universal bonding agents with and without acid etching. Heliyon 2022;8:e08858.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Zakavi F, Gholizadeh S, Dibazar S, Esmaeili M. A comparison of laser and mechanical surface pretreatment methods on shear bond strength of resin composite to resin-modified glass ionomer. J Dent (Shiraz) 2023;24(1 Suppl):103-111.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Dawood AE, Alkhalidi EF, Saeed MA. Shear bond strength between conventional composite resin and alkasite-based restoration used in sandwich technique: an in vitro study. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent 2024;14:161-166.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Boushell LW, Getz G, Swift EJ Jr, Walter R. Bond strengths of a silorane composite to various substrates. Am J Dent 2011;24:93-96.PubMed
- 33. Pamir T, Sen BH, Evcin O. Effects of etching and adhesive applications on the bond strength between composite resin and glass-ionomer cements. J Appl Oral Sci 2012;20:636-642.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Babannavar R, Shenoy A. Evaluation of shear bond strength of silorane resin to conventional, resin-modified glass ionomers and nano-ionomer cements. J Investig Clin Dent 2014;5:295-300.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 35. Boruziniat A, Gharaei S. Bond strength between composite resin and resin modified glass ionomer using different adhesive systems and curing techniques. J Conserv Dent 2014;17:150-154.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Jaberi Ansari Z, Panahandeh N, Tabatabaei Shafiei ZS, Akbarzadeh Baghban A. Effect of self-etching adhesives on the bond strength of glass-ionomer cements. J Dent (Tehran) 2014;11:680-686.PubMedPMC
- 37. Ozer S, Sen Tunc E, Gonulol N. Bond strengths of silorane- and methacrylate-based composites to various underlying materials. Biomed Res Int 2014;2014:782090.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 38. Panahandeh N, Torabzadeh H, Ghassemi A, Mahdian M, Akbarzadeh Bagheban A, Moayyedi S. Effect of bonding application time on bond strength of composite resin to glass ionomer cement. J Dent (Tehran) 2015;12:859-867.PubMedPMC
- 39. Sharafeddin F, Choobineh MM. Assessment of the shear bond strength between nanofilled composite bonded to glass-ionomer cement using self-etch adhesive with different pHs and total-etch adhesive. J Dent (Shiraz) 2016;17:1-6.PubMedPMC
- 40. Vural UK, Gurgan S. Repair potential of a new glass hybrid restorative system. Niger J Clin Pract 2019;22:763-770.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Welch D, Seesengood B, Hopp C. Surface treatments that demonstrate a significant positive effect on the shear bond strength of repaired resin-modified glass ionomer. Oper Dent 2015;40:403-409.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 42. Silva CL, Cavalheiro CP, Silva CG, Raggio DP, Casagrande L, Lenzi TL. Restoration-repair potential of resin-modified glass ionomer cement. Braz Oral Res 2024;38:e076.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 43. Ismail HS, Ali AI, El Mehesen R, Garcia-Godoy F, Mahmoud SH. Clinical evaluation of subgingival open sandwich restorations: 3-year results of a randomized double-blind trial. J Esthet Restor Dent 2024;36:573-587.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Sirisha K, Rambabu T, Ravishankar Y, Ravikumar P. Validity of bond strength tests: a critical review: part II. J Conserv Dent 2014;17:420-426.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 45. Angerame D, De Biasi M. Do nanofilled/nanohybrid composites allow for better clinical performance of direct restorations than traditional microhybrid composites?: a systematic review. Oper Dent 2018;43:E191-E209.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 46. Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. BMJ 2011;343:d4002.ArticlePubMed
- 47. Santerre JP, Shajii L, Leung BW. Relation of dental composite formulations to their degradation and the release of hydrolyzed polymeric-resin-derived products. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 2001;12:136-151.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 48. Tanumiharja M, Burrow MF, Tyas MJ. Microtensile bond strengths of glass ionomer (polyalkenoate) cements to dentine using four conditioners. J Dent 2000;28:361-366.ArticlePubMed
- 49. Almuammar MF, Schulman A, Salama FS. Shear bond strength of six restorative materials. J Clin Pediatr Dent 2001;25:221-225.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 50. Heintze SD. Clinical relevance of tests on bond strength, microleakage and marginal adaptation. Dent Mater 2013;29:59-84.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Ismail HS, Ali AI, Abo El-Ella MA, Mahmoud SH. Effect of different polishing techniques on surface roughness and bacterial adhesion of three glass ionomer-based restorative materials: in vitro study. J Clin Exp Dent 2020;12:e620-e625.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

- The impact of alloy treatment on the dynamic cyclic fatigue resistance of triangular base cross-section NiTi endodontic instruments
Rashid El Abed, Amre R. Atmeh, Mohamed Jamal, Anas Al Jadaa, Hamza El-Faraj, Abdel Rahman Bani Amer, Taher Al Omari
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Figure
- Related articles
-
- Evaluation of platelet concentrates in regenerative endodontics: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Fracture resistance and failure modes of endodontically-treated permanent teeth restored with Ribbond posts vs other post systems: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
- Success rate of direct pulp capping on permanent teeth using bioactive materials: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
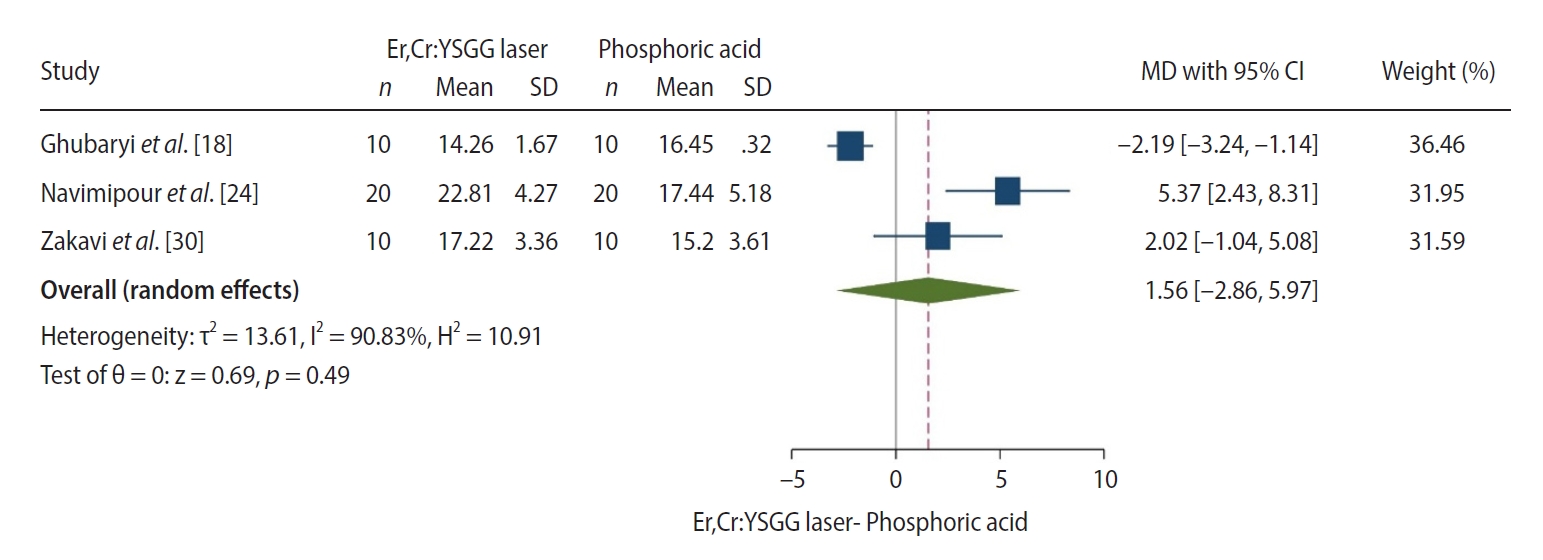

Figure 1.
Figure 2.
Figure 3.
| Study | Sample size per group and specimens’ dimensions | Aging for GI | Surface treatment | Test type |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1ry | 2ry | ||||
| Arora et al. (2010) [22] | 12 per group | Chemical | SBS | ||
| Dimensions for GI: 8 × 2.5 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 5 × 5.5 mm | |||||
| Boushell et al. (2011) [32] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 5 × 2 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 2.38 × 2 mm | |||||
| Zhang et al. (2011) [14] | 20 per group | Chemical | μSBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: not specified | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 1.5 × less than 2 mm | |||||
| Chandak et al. (2012) [23] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | ||
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 2.5 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 5 × 3 mm | |||||
| Kandaswamy et al. (2012) [15] | 25 per group | Chemical | SBS | FESEM/EDX analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 3 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 6 × 3 mm | |||||
| Navimipour et al. (2012) [24] | 20 per group | Chemical and mechanical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 5 × 4 mm | Surface evaluation using SEM | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 2.5 × 2 mm | |||||
| Pamir et al. (2012) [33] | 15 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 4 × 6 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 × 6 mm | |||||
| Fragkou et al. (2013) [25] | 7 per group | Chemical | TBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 22 × 5 × 1 mm | Tensile strain | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 22 × 5 × 1 mm | Young’s elastic modulus | ||||
| Kasraie et al. (2013) [26] | 4 per group | Chemical | μSBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 15 × 2 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 0.8 × 2 mm | |||||
| Otsuka et al. (2013) [13] | 10 per group | Chemical and mechanical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 4 mm | Surface free energy measurement | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 × 2 mm | |||||
| Babannavar and Shenoy (2014) [34] | 5 per group | Chemical | SBS | ||
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 3 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 6 × 3 mm | |||||
| Boruziniat and Gharaei (2014) [35] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 2 × 2 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 2 × 4 mm | |||||
| Jaberi Ansari et al. (2014) [36] | 10 per group | Chemical | |||
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 4 × 2 mm | μSBS | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 0.7 × 1 mm | |||||
| Ozer et al. (2014) [37] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 10 × 1 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 8 × 2 mm | |||||
| Panahandeh et al. (2015) [38] | 10 per group | Chemical | μSBS | Surface evaluation using SEM | |
| Dimensions for GI: 2 × 4 × 6 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 0.7 × 1 mm | |||||
| Sharafeddin and Choobineh (2016) [39] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | ||
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 3 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 6 × 3 mm | |||||
| Francois et al. (2019) [16] | 22 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 7 × 3 mm | E-SEM evaluation | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 7 × 3 mm | |||||
| Pandey et al. (2019) [27] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | ||
| Dimensions for GI: 10 × 2 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 5 × 6 mm | |||||
| Bin-Shuwaish et al. (2020) [10] | 10 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 8 × 4 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 × 4 mm | |||||
| Ghubaryi et al. (2020) [18] | 10 per group | Chemical and mechanical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 6 × 4 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 × 3 mm | |||||
| Bilgrami et al. (2022) [28] | 8 per group | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 4 × 2 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 × 2 mm | |||||
| Farshidfar et al. (2022) [29] | 10 per group | Chemical | μTBS | ||
| Dimensions for GI: 10 × 5 × 6 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 5 × 5 × 6 mm | |||||
| Zakavi et al. (2023) [30] | 10 per group | Chemical and mechanical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 3 × 5 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 2 mm | |||||
| Dawood et al. (2024) [31] | 10 per group | Chemical and mechanical | SBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 10 × 2 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 × 2 mm | |||||
| Maneenut et al. (2010) [12] | 15 per group | 4 days of water storage | Chemical | SBS | Failure mode analysis |
| Dimensions for GI: 8.5 × 4 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 5.8 × 4 mm | |||||
| Welch et al. (2015) [41] | 20 per group | One-week water storage with one TC | Chemical and mechanical | SBS | Failure mode analysis |
| Dimensions for GI: 5 mm | 500 TC | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 4 mm | 24-hour delay in a dry environment, followed by 500 TC | ||||
| Vural and Gurgan (2019) [40] | 12 per group | Chemical | μTBS | Failure mode analysis | |
| Dimensions for GI: 8 × 2 × 2 mm | 5,000 TC | SEM evaluation for the bonded interface | |||
| Dimensions for composite: 8 × 2 × 2 mm | |||||
| Ozaslan et al. (2023) [17] | 10 per group | 10,000 brushing cycles and 10,000 TC | Chemical | μSBS | Failure mode analysis |
| Dimensions for GI: 10 × 2 mm | Surface evaluation using SEM | ||||
| Dimensions for composite: 1.6 × 2 mm | |||||
| Silva et al. (2024) [42] | 8 per group | 14 days’ water storage and 5,000 TC | Chemical | μTBS | Failure mode analysis |
| Dimensions for GI: 8 × 8 × 4 mm | |||||
| Dimensions for composite: 8 × 8 × 4 mm | |||||
| Study | Materials used | Classification | Commercial name | Placement technique |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arora et al. (2010) [22] | GI | RMGI | Vitrebond | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Z350 | Incremental | |
| Boushell et al. (2011) [32] | GI | RMGI | Vitrebond plus | Bulk |
| Conventional GIC | GC Fuji IX GP EXTRA | |||
| Overlying composite | Silorane-based composite | Filtek LS | One increment (2 mm depth) | |
| Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | |||
| Zhang et al. (2011) [14] | GI | Two types of conventional GIC | GC Fuji IX GP EXTRA | Not specified |
| Riva Self Cure | ||||
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | Gradia Direct Anterior | One increment (2 mm depth) | |
| Chandak et al. (2012) [23] | GI | RMGI | Vitrebond | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Packable microhybrid resin composite | Filtek F‑60 | Incremental | |
| Kandaswamy et al. (2012) [15] | GI | Conventional GIC | Fuji IX | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | Solare | Incremental | |
| Navimipour et al. (2012) [24] | GI | Conventional GIC | Fuji II | Bulk |
| RMGI | Fuji II LC | |||
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | One increment (2 mm depth) | |
| Pamir et al. (2012) [33] | GI | Conventional GIC | Ketac Molar Quick Aplicap | Bulk |
| RMGI | Photac Fil Quick Aplicap | |||
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | Incremental | |
| Fragkou et al. (2013) [25] | GI | RMGI | Vitremer Tri-Cure | Not specified |
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Supreme XT | Not specified | |
| Kasraie et al. (2013) [26] | GI | RMGI | Vitrebond | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | One increment (2 mm depth) | |
| Otsuka et al. (2013) [13] | GI | Conventional GIC | Fuji IX GP | Bulk |
| Two RMGI | Fuji II LC EM, Fuji Filling LC | |||
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | Clearfil AP-X | One increment (2 mm depth) | |
| Babannavar and Shenoy (2014) [34] | GI | RMGI | Vitrebond | Incremental |
| Nanofilled RMGI | Ketac N100 | Incremental | ||
| Conventional GIC | Ketac Bond | Bulk | ||
| Overlying composite | Silorane-based composite | Filtek P90 | Incremental | |
| Boruziniat and Gharaei (2014) [35] | GI | RMGI | Fuji II LC | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Microfilled resin composite | Heliomolar | Incremental | |
| Jaberi Ansari et al. (2014) [36] | GI | Conventional GIC | Fuji II | Bulk |
| RMGI | Fuji II LC | |||
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | Filtek Z100 | Bulk | |
| Ozer et al. (2014) [37] | GI | Conventional GIC | Riva Self Cure | Bulk |
| RMGI | Fuji II LC | |||
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | Bulk | |
| Silorane-based composite | Filtek Silorane | |||
| Panahandeh et al. (2015) [38] | GI | Two RMGI | Riva Light Cure and Fuji II LC | Bulk |
| Two conventional GIC | Riva Self Cure and Fuji II | |||
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | Filtek Z100 | Bulk | |
| Sharafeddin and Choobineh (2016) [39] | GI | Conventional GIC | ChemFil Superior | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Z350 | Incremental | |
| Francois et al. (2019) [16] | GI | One glass hybrid + one conventional GIC | EQUIA Forte Fil and Fuji IX GPFast | Bulk |
| RMGI | Fuji II LC | |||
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Z350 | Incremental | |
| Pandey et al. (2019) [27] | GI | RMGI | Fuji II LC | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | Incremental | |
| Bin-Shuwaish (2020) [10] | GI | RMGI | Fuji II LC | Incremental |
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled bulk fill resin composite | Filtek One Bulk Fill | Bulk | |
| Nanohybrid bulk fill resin composite | Tetric N-Ceram Bulk Fill | Bulk | ||
| Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Z350 XT | Incremental | ||
| Ghubaryi et al. (2020) [18] | GI | RMGI | Fuji Filling LC | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | Filtek Z250 | Incremental | |
| Bilgrami et al. (2022) [28] | GI | Conventional GIC | Ketac Molar | Bulk |
| Easy mix | ||||
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Z350 | Bulk (2 mm depth) | |
| Nanoceramic resin composite | Ceram X | |||
| Microhybrid resin composite | Spectrum | |||
| Farshidfar et al. (2022) [29] | GI | One glass hybrid and one conventional GIC | Equia Forte Fil | Bulk |
| Riva Self Cure | ||||
| Two RMGI | Fuji II LC | |||
| Riva Light cure | ||||
| Overlying composite | Nanohybrid resin composite | GC Kalore | Incremental | |
| Zakavi et al. (2023) [30] | GI | RMGI | Fuji II LC | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | Gradia direct | One increment (2 mm) | |
| Dawood et al. (2024) [31] | GI | Conventional GIC | Securafil | Bulk |
| RMGI | Glass Liner | |||
| Overlying composite | Submicron-filled resin composite | PALFIQUE LX5 | One increment (2 mm) | |
| GI repair | ||||
| Maneenut et al. (2010) [12] | GI (Both materials used also for repair) | Nanofilled RMGI | Ketac N100 | Bulk |
| RMGI | Fuji II LC | |||
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Filtek Supreme | Bulk | |
| Microfilled resin composite | Solare | |||
| Welch et al. (2015) [41] | GI | RMGI | Fuji II LC | Bulk |
| Overlying GIC | RMGI | Fuji II LC | Bulk | |
| Vural and Gurgan (2019) [40] | GI (The material was used also for repair) | Glass hybrid | EQUIA Forte Fil | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Microhybrid resin composite | G‑aenial posterior | Not specified | |
| Ozaslan et al. (2023) [17] | GI | Glass hybrid | EQUIA Forte HT Fil | Bulk |
| Overlying composite | Nanoceramic resin composite | Neo Spectra ST HV | Bulk (2 mm depth) | |
| Silva et al. (2024) [42] | GI (The material was used also for repair) | RMGI | Riva Light Cure | Incremental |
| Overlying composite | Nanofilled resin composite | Z350 XT | Incremental | |
| Study | Finishing and polishing for GI | Type of surface treatment | Commercial brand and specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arora et al. (2010) [22] | No | Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Single Bond 2 |
| Two-component self-etch adhesive | Adper Prompt L Pop (pH: 0.8) | ||
| Boushell et al. (2011) [32] | Only for the Conventional GIC | Two-step silorane-based adhesive | Filtek LS adhesive (pH: 2.7) |
| Two-step self-etch adhesive | Adper Scotchbond SE (pH: 1) | ||
| Zhang et al. (2011) [14] | Yes | 37% phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | SDI acid etch gel + Adper Single Bond Plus |
| Two-step self-etch adhesives | Adper Scotchbond SE | ||
| Clearfil SE Bond (pH: 2) | |||
| One-step self-etch adhesives | Clearfil S3 Bond (pH: 2.3) | ||
| One Coat 7.0 | |||
| Chandak et al. (2012) [23] | No | Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Scotch Bond 2 |
| Two-component self-etch adhesive | Adper Prompt L Pop | ||
| Kandaswamy et al. (2012) [15] | No | Self-etch adhesives | Adper prompt self-etch (pH: 1) |
| AdheSE (pH: 1.4) | |||
| Clearfil SE | |||
| One coat SE (pH: 2.2) | |||
| Navimipour et al. (2012) [24] | No | 35% phosphoric acid gel + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Scotchbond Etchant |
| Adper Single Bond | |||
| Er,Cr:YSGG laser + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Waterlase YSGG; Biolase Europe GmbH | ||
| A pulse energy setting of 1 W was applied for 15 seconds using a G-type tip with a diameter of 600 μm, accompanied by 10% water and 11% air. | |||
| Pamir et al. (2012) [33] | Yes | %35 phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Scotchbond Etch |
| Adper Single Bond 2 | |||
| Two-component self-etch adhesive | Adper Prompt L Pop | ||
| Fragkou et al. (2013) [25] | No | Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Single Bond 2 |
| Kasraie et al. (2013) [26] | Yes | 37% phosphoric acid | Scotchbond™ Etchant |
| Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Single Bond | ||
| Self-etch adhesives | Clearfil SE Bond self-etch primer | ||
| Clearfil S3 Bond self-etch adhesive | |||
| Otsuka et al. (2013) [13] | No | 35% phosphoric acid + one-step self-etch adhesive | Gel Etchant (Kerr) |
| G-Bond Plus | |||
| Air abrasion acid + one-step self-etch adhesive | Airborne particle abrasion with 50-μm aluminum oxide at 0.3 MPa for 5 seconds | ||
| Babannavar and Shenoy (2014) [34] | No | Two-step self-etch silorane-based adhesive | Filtek P90 adhesive (pH: 2.7) |
| Boruziniat and Gharaei (2014) [35] | No | Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Tetric N-Bond |
| Two-step self-etch adhesive | AdheSE | ||
| One-step self-etch adhesive | AdheSE One F (pH: 1.5) | ||
| Jaberi Ansari et al. (2014) [36] | No | Two-component one-step self-etch adhesive | Adper Prompt L Pop |
| Two-step self-etch adhesives | Clearfil SE Bond | ||
| Clearfil Protect bond (pH: 2) | |||
| AdheSE | |||
| Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Single bond | ||
| Ozer et al. (2014) [37] | Yes | Two-step self-etch adhesive | Clearfil SE Bond |
| Two-step self-etch silorane-based adhesive | Filtek P90 adhesive | ||
| Panahandeh et al. (2015) [38] | No | 37% phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Stae, SDI |
| Two-step self-etch adhesive | Frog, SDI (pH: 2) | ||
| Sharafeddin and Choobineh (2016) [39] | No | Two-step self-etch adhesive | Clearfil SE Bond |
| One-step self-etch adhesive | Optibond (pH: 1.4) | ||
| Two-component one-step self-etch adhesive | Adper Prompt L Pop | ||
| 37% phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Single Bond 2 | ||
| Francois et al. (2019) [16] | No | One-step universal adhesive used in self-etch mode | Scotchbond Universal (pH: 2.7) |
| 32% phosphoric acid + universal adhesive used in etch-and-rinse mode | Scotchbond Universal Etchant + Scotchbond Universal | ||
| 32% phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Scotchbond Universal Etchant + Scotchbond 1XT | ||
| One-step self-etch adhesive | Optibond All-In-One (pH: 2.5) | ||
| Universal primer + one-step self-etch adhesive | Monobond Plus + Optibond All-in-One | ||
| Coating material | EQUIA Forte Coat | ||
| Pandey et al. (2019) [27] | No | Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Single Bond 2 |
| One-step self-etch adhesive | Optibond All-In-One | ||
| Bin-Shuwaish (2020) [10] | No | 35% phosphoric acid + Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Ultra-Etch + OptiBond Solo Plus |
| Two-step self-etch adhesive | Clearfil SE Bond 2 | ||
| Universal adhesive used in both etch-and-rinse (with 35% phosphoric acid) and self-etch modes | Single Bond Universal | ||
| Ghubaryi et al. (2020) [18] | No | Methylene blue photosensitizers activated with photodynamic therapy + Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Sisco Research Lab |
| A single-wavelength light source with an 810 nm wavelength and a power output of 1.5 W was used at a concentration of 100 mg/L. This light was directed perpendicularly onto the RMGI and continuously applied for 60 seconds. | |||
| Adper Single Bond 2 | |||
| Er,Cr:YSGG laser + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Biolase- Waterlase iPlus | ||
| For a duration of 5 seconds at 2.8 MPa | |||
| Nd-YAG laser + etch-and-rinse adhesive | NianSheng | ||
| A noncontact circular motion technique was used with a power setting of 1.5 W for a duration of 60 seconds. During the procedure, the 400 μm quartz micro tip was kept at a 90-degree angle to the cement surface. | |||
| Aluminum oxide sandblasting + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Aluminum trioxide, Dentsply | ||
| With a power of 1.5 W and a frequency of 30 Hz, the MZ8 tip was used in a circular motion for 60 seconds, held 2 mm away from the surface. | |||
| 37% phosphoric acid + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Aqua Etch | ||
| Bilgrami et al. (2022) [28] | No | 37% and 36% phosphoric acid gel | Scotchbond Etchant |
| Dentsply | |||
| Farshidfar et al. (2022) [29] | No | 35% phosphoric acid | Ultra-Etch |
| Two universal adhesives (used in both etch-and-rinse and self-etch modes) | CLEARFIL Universal Bond (pH: 2.3) | ||
| G-Premio Bond (pH: 1.5) | |||
| Zakavi et al. (2023) [30] | No | Two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Adper Single Bond 2 |
| 37% phosphoric acid + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Morva Etch | ||
| Aluminum oxide sandblasting + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Microblaster Dento-Prep, Dental Microblaster | ||
| 30-μm Al2O3 particles for 10 seconds | |||
| Rough diamond bur + etch-and-rinse adhesive | 012 Cylinder Flat End | ||
| The diamond bur was employed for 3 seconds at high speed with an accompanying water spray. | |||
| Er: YAG laser + etch-and-rinse adhesive | M021-3AF/4, Fotona | ||
| With a 1,064 nm wavelength, delivering 1.5 W of power, at a frequency of 5 Hz, with 8% water output and 4% air output, positioned 10 mm away from the target. The laser was operated in micro-short pulse mode, delivering energy at 300 mJ | |||
| Er, Cr: YSGG laser + etch-and-rinse adhesive | Water Lase iPlus, Biolase | ||
| An MZ8 tip with a diameter of 800 μm and a spot size of 0.502 mm² was used. This tip emitted laser light at a 2,780-nm wavelength, 1 W of power, and a frequency of 20 Hz. The water output was set at 20%, and the air output was 10%, with the tip held 1 mm from the surface for 15 seconds. This setup provided an intensity of 53.07 J/cm² | |||
| Dawood et al. (2024) [31] | No | Sandblasted | Air Prophy Unit |
| Sandblasted + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | For 30 seconds with an air abrasion unit using 50-μm aluminum oxide particles | ||
| 37% phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Scotchbond 1XT | ||
| Universal adhesive used in self-etch mode | Scotchbond Universal | ||
| Maneenut et al. (2010) [12] | Yes | Repair with nanofilled RMGI | Ketac Nano-ionomer Primer |
| Nanofilled RMGI Primer | GC Dentin Conditioner | ||
| Dentin Conditioner + Nanofilled RMGI Primer | |||
| 37% phosphoric acid gel + Nanofilled RMGI Primer | |||
| Repair with both resin composites | Scotchbond Etching Gel | ||
| 37% phosphoric acid gel + two-step etch-and-rinse/or one-step self-etch adhesive | Single Bond | ||
| Etch-and-rinse/or one-step self-etch adhesive | G-Bond (pH: 2.8) | ||
| Repair with RMGI | |||
| One-step self-etch adhesive | |||
| Dentin Conditioner + one-step self-etch adhesive | |||
| 37% phosphoric acid gel + one-step self-etch adhesive | |||
| Welch et al. (2015) [41] | No | Sanding using wet 800-grit silicon carbide paper | Leco |
| Sanding + 37.5% phosphoric acid | |||
| Sanding + 37.5% phosphoric acid + two-step etch-and-rinse adhesive | Kerr Gel Etchant | ||
| Optibond Solo Plus | |||
| Vural and Gurgan (2019) [40] | No | Repair using glass hybrid | DIATECH, Swiss Dental |
| Roughened using a diamond coarse fissure bur | Cavity conditioner, GC | ||
| 20% mild polyacrylic acid | G‑premio Bond | ||
| 20% mild polyacrylic acid + a universal adhesive | |||
| A universal adhesive | |||
| Repair using resin composite | GC etching gel | ||
| Roughened using a diamond coarse fissure bur | |||
| Roughening + universal adhesive | |||
| 40% phosphoric acid + universal adhesive | |||
| Universal adhesive | |||
| Ozaslan et al. (2023) [17] | Yes | Silane + universal adhesive | Clearfil Ceramic Primer Plus |
| Prime & Bond Universal (pH: 2.7) | |||
| Silva et al. (2024) [42] | Yes | Universal adhesive in self-etch mode | Scotchbond Universal |
| 37% phosphoric acid + universal adhesive |
| Study | Test type | Testing machine and speed | Aging condition | Method of failure analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arora et al. (2010) [22] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Boushell et al. (2011) [32] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | ×2.5 |
| Zhang et al. (2011) [14] | μSBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours, 1- and 6-month water storage | Light microscope at ×40 |
| Chandak et al. (2012) [23] | SBS | UTM, 3 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Kandaswamy et al. (2012) [15] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Navimipour et al. (2012) [24] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | Stereomicroscope at ×20 |
| Pamir et al. (2012) [33] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 48 hours | Light microscope at ×10 or ×20 |
| Fragkou et al. (2013) [25] | TBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | - | Stereomicroscope at ×16 |
| Kasraie et al. (2013) [26] | μSBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | Stereomicroscope at ×40 |
| Otsuka et al. (2013) [13] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours | Optical microscope at ×10 |
| Babannavar and Shenoy (2014) [34] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Boruziniat and Gharaei (2014) [35] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 48 hours | Stereomicroscope |
| Jaberi Ansari et al. (2014) [36] | μSBS | MTT, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Ozer et al. (2014) [37] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | 500 TC | Stereomicroscope at ×25 |
| Panahandeh et al. (2015) [38] | μSBS | MTT, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Sharafeddin and Choobineh (2016) [39] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Francois et al. (2019) [16] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 48 hours | Binocular microscope at ×30 |
| Pandey et al. (2019) [27] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Bin-Shuwaish (2020) [10] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | 5,000 TC | Digital stereomicroscope at ×30 |
| Ghubaryi et al. (2020) [18] | SBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 48 hours | Optical microscope at ×10 |
| Bilgrami et al. (2022) [28] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | 500 TC | The exact technique and magnification are not specified |
| Farshidfar et al. (2022) [29] | μTBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | - |
| Zakavi et al. (2023) [30] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | 5,000 TC | Light microscope |
| Dawood et al. (2024) [31] | SBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours | Stereomicroscope at ×10 |
| GI repair | ||||
| Maneenut et al. (2010) [12] | SBS | UTM, 0.75±0.25 mm/min | After 24 hours | Light microscope at ×2 |
| Welch et al. (2015) [41] | SBS | UTM | - | SEM at ×13 |
| Vural and Gurgan (2019) [40] | μTBS | MTT, 1 mm/min | - | Stereomicroscope at ×40 |
| Ozaslan et al. (2023) [17] | μSBS | UTM, 0.5 mm/min | After 24 hours | Stereomicroscope at ×30 |
| Silva et al. (2024) [42] | μTBS | UTM, 1 mm/min | After 24 hours | Stereomicroscope at ×40 |
| Study | Description of sample size calculation | Specimen preparation carried out by the same operator | Randomization of specimens | Use of control group (without the tested surface treatment) | Use of materials according to manufacturers’ instructions | Evaluation of failure mode | Blinding of examiner | Risk of bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arora et al. (2010) [22] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | High |
| Boushell et al. (2011) [32] | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Zhang et al. (2011) [14] | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Chandak et al. (2012) [23] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | High |
| Kandaswamy et al. (2012) [15] | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | High |
| Navimipour et al. (2012) [24] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Pamir et al. (2012) [33] | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | High |
| Fragkou et al. (2013) [25] | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Kasraie et al. (2013) [26] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Otsuka et al. (2013) [13] | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Babannavar and Shenoy (2014) [34] | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | High |
| Boruziniat and Gharaei (2014) [35] | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Jaberi Ansari et al. (2014) [36] | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | High |
| Ozer et al. (2014) [37] | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | High |
| Panahandeh et al. (2015) [38] | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | High |
| Sharafeddin and Choobineh (2016) [39] | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | High |
| Francois et al. (2019) [16] | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | High |
| Pandey et al. (2019) [27] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | High |
| Bin-Shuwaish (2020) [10] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Ghubaryi et al. (2020) [18] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Bilgrami et al. (2022) [28] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Farshidfar et al. (2022) [29] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | High |
| Zakavi et al. (2023) [30] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Dawood et al. (2024) [31] | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Maneenut et al. (2010) [12] | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Welch et al. (2015) [41] | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Vural and Gurgan (2019) [40] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate |
| Ozaslan et al. (2023) [17] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | High |
| Silva et al. (2024) [42] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Study | Er,Cr:YSGG laser-treated |
Phosphoric acid-treated |
Difference, mean (95% CI) | p-value | Weight | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean ± SD | n | Mean ± SD | ||||
| Ghubaryi et al. [18] | 10 | 14.26 ± 1.67 | 10 | 16.45 ± 0.32 | –2.19 (–3.244 to –1.136) | 36.46 | |
| Navimipour et al. [24] | 20 | 22.81 ± 4.27 | 20 | 17.44 ± 5.18 | 5.37 (2.428 to 8.312) | 31.95 | |
| Zakavi et al. [30] | 10 | 17.22 ± 3.36 | 10 | 15.20 ± 3.61 | 2.02 (–1.037 to 5.077) | 31.59 | |
| Total (random effects) | 40 | 40 | 1.555 (–2.857 to 5.968) | 0.490 | 100 | ||
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Q | 26.66 |
| Degree of freedom | 2 |
| p-value | <0.001 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 0.9083 |
E-SEM, environmental scanning electron microscopy; FESEM/EDX, finite element scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive X-ray analysis; GI, glass ionomer; SBS, shear bond strength; μSBS, microshear bond strength; TBS, tensile bond strength test; μTBS, microtensile bond strength test; SEM, scanning electron microscope; TC, thermal cycle.
GI, glass ionomer; RMGI, resin-modified glass ionomer; GIC, glass ionomer cement.
Er,Cr:YSGG, erbium, chromium:yttrium, scandium, gallium garnet; Er:YAG, erbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet; GI, glass ionomer; GIC, glass ionomer cement; ; Nd-YAG, neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet; RMGI, resin-modified glass ionomer.
GI, glass ionomer; SBS, shear bond strength; μSBS, microshear bond strength; TBS, tensile bond strength; μTBS, microtensile bond strength; MTT, microtensile tester; SEM, scanning electron microscope; TC, thermal cycle; UTM, universal testing machine.
CI, confidence interval;

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

