Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 36(6); 2011 > Article
- Case Report Subcutaneous emphysema during fracture line inspection: case report
- Min-Young Kim, DDS, Sung-Ho Park, DDS, MSD, PhD, Yoo-Seok Shin, DDS, MSD, Euiseong Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD
-
2011;36(6):-509.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.506
Published online: November 30, 2011
Department of Conservative Dentistry, Microscope Center, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- Correspondence to Euiseong Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD. Professor, Department of Conservative Dentistry, Microscope Center, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, 50 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea 120-752. TEL, +82-2-2228-8700; FAX, +82-2-313-7575; andyendo@yuhs.ac
• Received: June 30, 2011 • Revised: August 23, 2011 • Accepted: August 29, 2011
Copyright © 2011 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,029 Views
- 6 Download
Abstract
-
The development of subcutaneous emphysema is a well-known complication that has been reported after dental extraction, endodontic treatment, or restorative preparation. Gaseous invasion, leading to swelling, crepitus on palpation, is commonly restricted to the connective tisssues immediately adjacent to the entry site. However, the use of compressed air- and water-cooled turbines may allow large amounts of air and water to be driven through the fascial planes into the mediastinum, pleural space, or even the retroperitoneum.This case report is about the patient who presented with subcutaneous emphysema that occurred after fracture line inspection. Possible cause, treatment, and prevention of emphysema will be discussed.
- 1. Gamboa Vidal CA, Vega Pizarro CA, Almeida Arriagada A. Subcutaneous emphysema secondary to dental treatment: case report. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2007;12: E76-E78.PubMed
- 2. Smatt Y, Browaeys H, Genay A, Raoul G, Ferri J. Iatrogenic pneumomediastinum and facial emphysema after endodontic treatment. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;42: 160-162.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Zemann W, Feichtinger M, Kaärcher H. Cervicofacial and mediastinal emphysema after crown preparation: a rare complication. Int J Prosthodont. 2007;20: 143-144.PubMed
- 4. Heyman SN, Babayof I. Emphysematous complications in dentistry, 1960-1993: an illustrative case and review of the literature. Quintessence Int. 1995;26: 535-543.PubMed
- 5. McKenzie WS, Rosenberg M. Iatrogenic subcutaneous emphysema of dental and surgical origin: a literature review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67: 1265-1268.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Szubin L, La Bruna A, Levine J, Komisar A. Subcutaneous and retropharyngeal emphysema after dental procedures. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997;117: 122-123.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Arai I, Aoki T, Yamazaki H, Ota Y, Kaneko A. Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema after dental extraction detected incidentally by regular medical checkup: a case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;107: e33-e38.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Reiche-Fischel O, Helfrick JF. Intraoperative lifethreatening emphysema associated with endotracheal intubation and air insufflation devices: report of two cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1995;53: 1103-1107.PubMed
- 9. Horowitz I, Hirshberg A, Freedman A. Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema following surgical extraction of mandibular third molars: three case reports. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1987;63: 25-28.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Aragon SB, Dolwick MF, Buckley S. Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous cervical emphysema during third molar extraction under general anesthesia. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1986;44: 141-144.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Gulati A, Baldwin A, Intosh IM, Krishnan A. Pneumomediastinum, bilateral pneumothorax, pleural effusion, and surgical emphysema after routine apicectomy caused by vomiting. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46: 136-137.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure 1
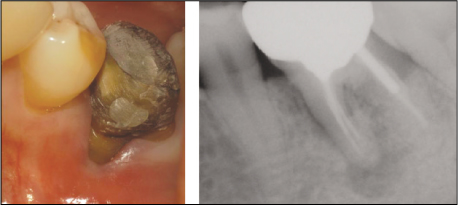
Preoperative clinical photograph and radiograph
: Buccal surface of mesial root is exposed due to severe gingival recession. Periapical radiograph revealed periapical radiolucency around mesial root of #36.

Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

Subcutaneous emphysema during fracture line inspection: case report
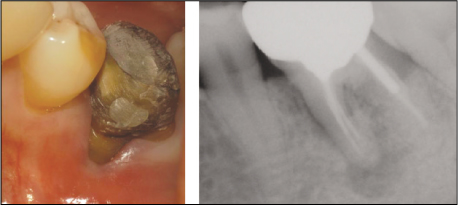
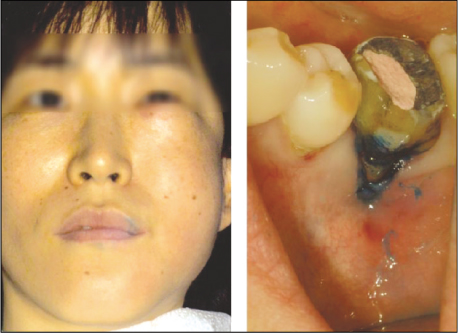
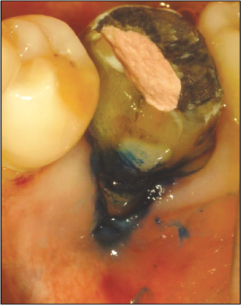
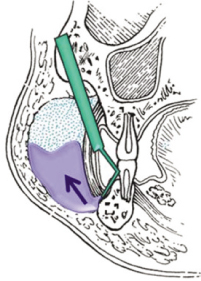
Figure 1
Preoperative clinical photograph and radiograph
: Buccal surface of mesial root is exposed due to severe gingival recession. Periapical radiograph revealed periapical radiolucency around mesial root of #36.
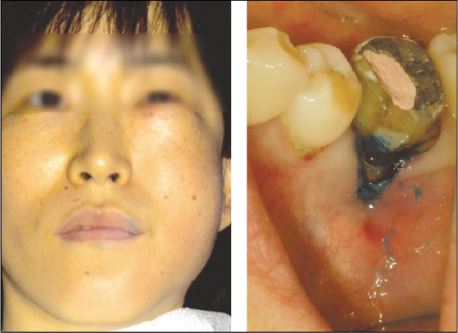
Figure 2
Extraoral and intraoral photographs after onset of subcutaneous emphysema
: Sudden onset of swelling on left infraorbital, buccal, vestibular area.
Figure 3
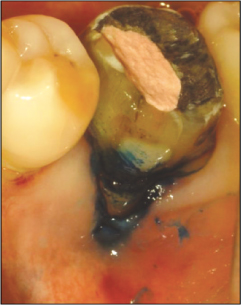
Methylene blue staining procedure.
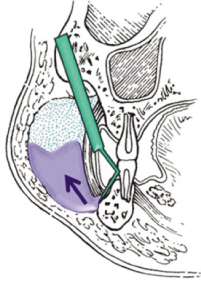
Figure 4
Schematic of the pathogenesis of subcutaneous emphysema.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
Subcutaneous emphysema during fracture line inspection: case report

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

