Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 36(6); 2011 > Article
- Case Report Failure of orthograde MTA filling: MTA wash-out?
- Yuran Kim, DDS, Chan-Young Lee, DDS, PhD, Euiseoung Kim, DDS, PhD, Il-Young Jung, DDS, PhD
-
2011;36(6):-514.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.510
Published online: November 30, 2011
Department of Conservative Dentistry, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- Correspondence to Il-Young Jung, DDS, PhD. Professor, Department of Conservative Dentistry, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. TEL, +82-2-2228-8700; FAX, +82-2-313-7575; juen@yuhs.ac
• Received: August 2, 2011 • Revised: September 23, 2011 • Accepted: September 26, 2011
Copyright © 2011 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,167 Views
- 14 Download
- 5 Crossref
Abstract
-
Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), which was originally developed for repair of root perforations, is a biocompatible material with numerous clinical applications in endodontics. MTA must be allowed to set in the presence of moisture to optimize the material's physical and chemical properties. In the clinic, occasionally unset MTA has been detected after application of MTA on the tooth, and the reason has been unclear.This case report presents MTA washed-out for several years after placement at the root apex as an apical plug, and discusses the reason and things to consider in clinics.
- 1. Torabinejad M, Hong CU, McDonald F, Pitt Ford TR. Physical and chemical properties of a new root-end filling material. J Endod. 1995;21: 349-353.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Torabinejad M, Chivian N. Clinical applications of mineral trioxide aggregate. J Endod. 1999;25: 197-205.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Lee SJ, Monsef M, Torabinejad M. Sealing ability of a mineral trioxide aggregate for repair of lateral root perforations. J Endod. 1993;19: 541-544.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Bakland LK. Management of traumatically injured pulps in immature teeth using MTA. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2000;28: 855-858.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Camilleri J. Characterization of hydration products of mineral trioxide aggregate. Int Endod J. 2008;41: 408-417.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Lee YL, Lee BS, Lin FH, Yun Lin A, Lan WH, Lin CP. Effects of physiological environments on the hydration behavior of mineral trioxide aggregate. Biomaterials. 2004;25: 787-793.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Bye GC. Portland cement: composition, production and properties. 1983;1st ed. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
- 8. Nekoofar MH, Oloomi K, Sheykhrezae MS, Tabor R, Stone DF, Dummer PM. An evaluation of the effect of blood and human serum on the surface microhardness and surface microstructure of mineral trioxide aggregate. Int Endod J. 2010;43: 849-858.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Tingey MC, Bush P, Levine MS. Analysis of mineral trioxide aggregate surface when set in the presence of fetal bovine serum. J Endod. 2008;34: 45-49.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure 4
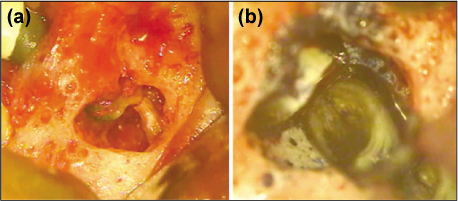
Apical surgery on mandibular second premolar.
(a) Fractured root tip was seen, (b) MTA was removed with ultrasonic instrument easily. Vertical root fracture was seen on lingual side.
MTA, mineral trioxide aggregate.

Figure 5
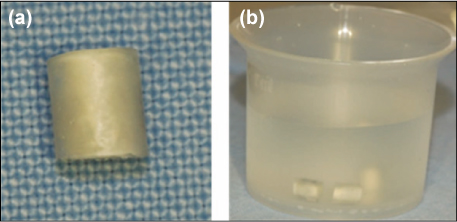
Experiment 1.
(a) MTA was filled into polyethylene mould, (b) Specimens were placed into butyric acid solution (pH5.5) and saline for 30 days.
MTA, mineral trioxide aggregate.

Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate—A Versatile Dental Material: An Insight on Applications and Newer Advancements
C. Pushpalatha, Vismaya Dhareshwar, S. V. Sowmya, Dominic Augustine, Thilla Sekar Vinothkumar, Apathsakayan Renugalakshmi, Amal Shaiban, Ateet Kakti, Shilpa H. Bhandi, Alok Dubey, Amulya V. Rai, Shankargouda Patil
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of volumetric changes of three different retrograde calcium silicate materials placed under different pH condititions
So Yeon Kwon, Min-Seock Seo
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of RetroMTA on osteoblastic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells
Hyo-Il Lee, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Ji-Hyun Jang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Bin-Na Lee, Won-Mann Oh
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2018; 45(2): 97. CrossRef - The effect of human blood on the setting and surface micro-hardness of calcium silicate cements
Minju Song, Wonyoung Yue, Soyeon Kim, Wooksung Kim, Yaelim Kim, Jeong-Woong Kim, Euiseong Kim
Clinical Oral Investigations.2016; 20(8): 1997. CrossRef - Biological Effects and Washout Resistance of a Newly Developed Fast-setting Pozzolan Cement
Yoorina Choi, Su-Jung Park, Seoung-Hoon Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(4): 467. CrossRef
Failure of orthograde MTA filling: MTA wash-out?
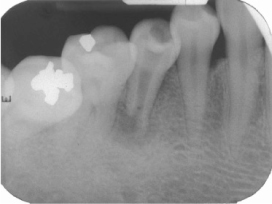
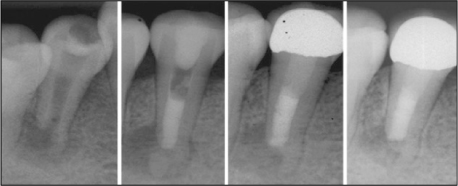
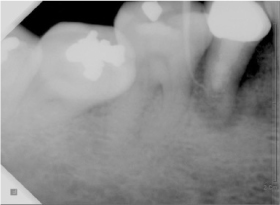
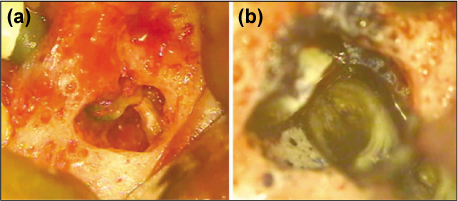
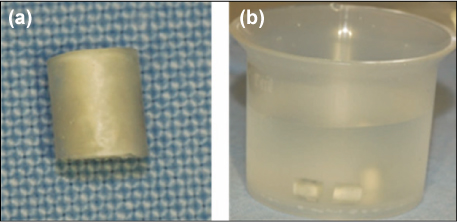
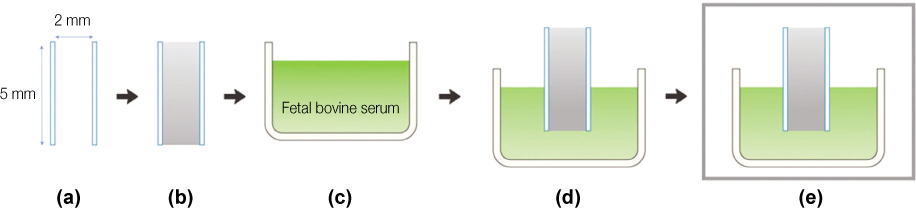
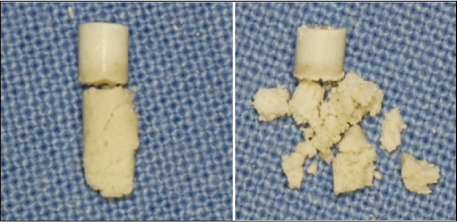
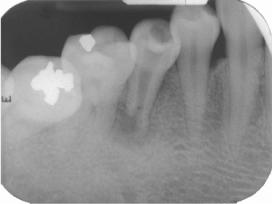
Figure 1
Periapical view: pre-operative radiograph.
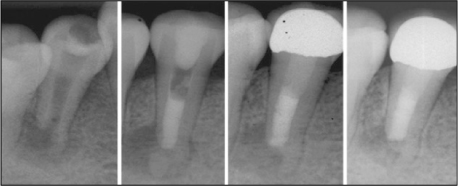
Figure 2
Root canal treatment and follow up.
MTA, mineral trioxide aggregate.
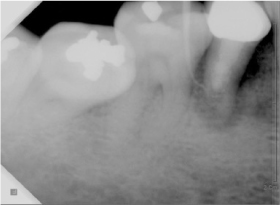
Figure 3
Periapical view: 6 years later.
Figure 4
Apical surgery on mandibular second premolar.
(a) Fractured root tip was seen, (b) MTA was removed with ultrasonic instrument easily. Vertical root fracture was seen on lingual side.
MTA, mineral trioxide aggregate.
Figure 5
Experiment 1.
(a) MTA was filled into polyethylene mould, (b) Specimens were placed into butyric acid solution (pH5.5) and saline for 30 days.
MTA, mineral trioxide aggregate.
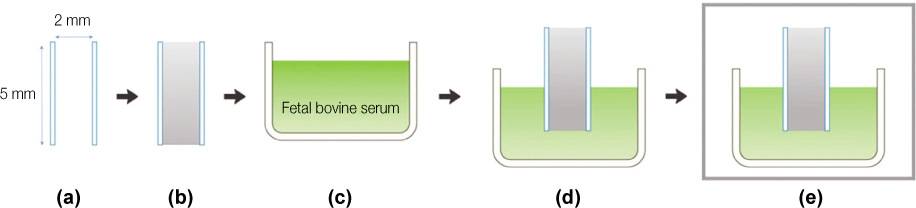
Figure 6
Experiment 2.
(a, b) MTA was filled into polyethylene mould, (c, d) Specimen was placed onto fetal bovine serum, (e) Specimen was incubated under 37℃, 100% humidity for 4 days.
MTA, mineral trioxide aggregate.
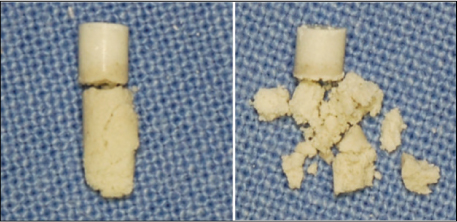
Figure 7
MTA contacted with fetal bovine serum was not set.
MTA, mineral trioxide aggregate.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
Figure 5
Figure 6
Figure 7
Failure of orthograde MTA filling: MTA wash-out?

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

