Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 28(5); 2003 > Article
- Original Article Evaluation of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate as a root canal irrigation solution; Cl- concentration, pH, Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial effect in vitro
- Woo-Cheol Lee, Bong-Sun Kang, Cheol-Ho Kim, Ho-Hyun Son
-
2003;28(5):-430.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.5.425
Published online: September 30, 2003
Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Korea.
- Corresponding author (hhson@snu.ac.kr)
Copyright © 2003 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,280 Views
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref
Abstract
-
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical applications of the Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate effervescent tablet as a routine root canal irrigant by performing several in vitro tests such as Cl- content, cytotoxicity, antimicrobial effect as well as its pH level compared to the equivalent concentration of sodium hypochlorite solution.
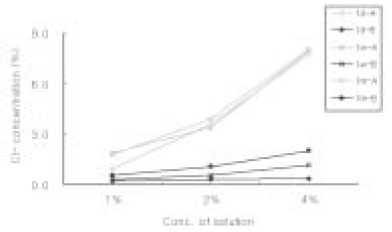
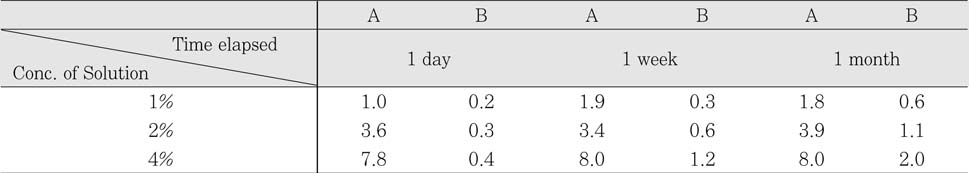
Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate demonstrated lower level of Cl- concentation than each dilution of sodium hypochlorite solution. Both solution has increased level of Cl- as the concentration of each solution increased. There was no significant change of Cl- concentration in sodium hypochlorite as time goes by. However, Cl- concentration in Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate was increased.
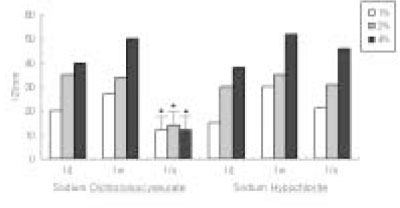
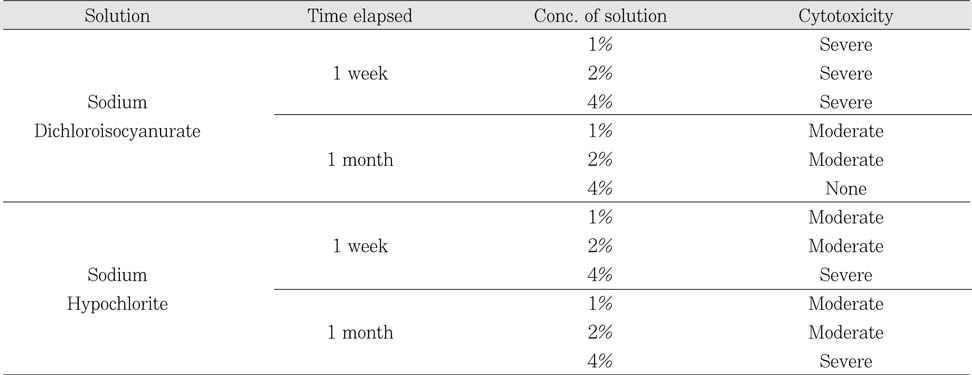
The antimicrobial effects of both solutions were increased when their concentrations were increased. One day after dilution, antimicrobial effect of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate was slightly higher than sodium hypochlorite, however, there was no difference in 1 week dilution solution. One month dilution solution of sodium hypochlorite still retain its activity, but antimicrobial effect of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate was drastically decreased 1 month after dilution.
The cytotoxicity of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate was rather higher than same concentration of sodium hypochlorite solution until 1 week after dilution. Then in 1 month, cytotoxicity of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate was decreased than that of 1 week dilution solution, especially 4% Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate solution has almost no toxicity. However, 1% and 2% sodium hypochlorite solution has unchanged moderate degree of cytotoxicity after the dilution. Furthermore, 4% sodium hypochlorite solution showed high level of toxicity.
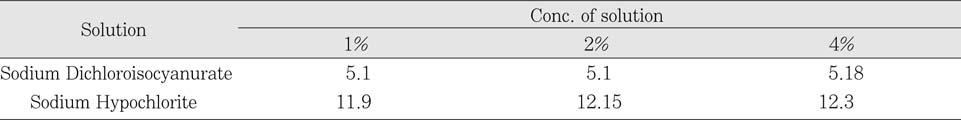
The pH level of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate showed that the solution was weak acid (pH5). On the other hand, sodium hypochlorite was revealed as a strong alkaline solution (pH12). There was no change in pH following the dilution of each solution.
As results, Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate solution fully satisfy the basic requirements as a root canal irrigation solution. However, we strongly recommend to use this solution clinically in low concentration and try to apply into the root canal within 1 week after dilution.
- 1. Walker A. Definite and dependable therapy for pulpless teeth. J Am Dent Assoc. 1936;23: 1418.
- 2. Senia ES, Marshall FJ, Rosen S. The solvent action of sodium hypochlorite on pulp tissue of extracted teeth. Oral Surg. 1971;31: 96.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Hand RE, Smith ML, Harrison JW. Analysis of the effect of dilution on the necrotic tissue dissolution property of sodium hypochlorite. J Endod. 1978;4: 60.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Siqueira JF Jr, Machado AG, Silveira RM, Lopes HP, De Uzeda M. Evaluation of the effectiveness of sodium hypochlorite used with three irrigation methods in the elimination of enterococcus faecalis from the root canal, in vitro. Int Endod J. 1997;30: 279.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Yesilsoy C, Whitaker E, Cleveland D, Phillips E, Trope M. Antimicrobial and toxic effects of established and potential root canal irrigants. J Endod. 1995;21: 513.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Spangberg L. In: Grossman LI, editor. Cellular reaction to intracanal medicaments. Trans Fifth Conf Endod. 1973;Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania; 108-123.
- 7. Block SS. Disinfection, sterilization, and preservation. 1971;4th Ed. Philadelphia, USA.
- 8. Bystrom A, Sundqvist G. Bacteriologic evaluation of the effect of 0.5% sodium hypochlorite in endodontic therapy. Oral Surg. 1983;55: 307.PubMed
- 9. Bystrom A, Sundqvist G. The antibacterial action of sodium hypochlorite and EDTA in 60 cases of endodontic therapy. Int Endod J. 1985;18: 35.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Svec TA, Harrison JW. Chemomechanical removal of pulpal and dentinal debris with sodium hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide vs normal saline solution. J Endod. 1977;3: 49.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Murray PR, Kobayashi GS, Pfaller MA, Rosenthal KS. Medical microbiology. 1994;2nd Ed. St Loius, USA: C.V. Mosby Co.
- 12. Siqueira JF Jr, Racas IN, Favieri A, Lima KC. Chemomechanical reduction of the bacterial population in the root canal after instrumentation and irrigation with 1%, 2.5%, and 5.25% sodium hypochlorite. J Endod. 2000;26: 331.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Martin H. Quantitative bactericidal effectiveness of an old and a new endodontic irrigant. J Endod. 1975;1: 164.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

- Evaluation of pH, free available chlorine and tissue dissolution property of solid dosage chlorine releasing agents for root canal irrigation based on contact time – An in vitro study
S. Aishwarya, Debolina Bishayi, Vinod Rakesh Jathanna, Manuel S. Thomas, Srikant Natarajan, Suchitra Shenoy, Aradhana Marathe
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 217. CrossRef - Evaluation of time-dependent antimicrobial effect of sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) onEnterococcus faecalisin the root canal
Hye-Jeong Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(2): 121. CrossRef
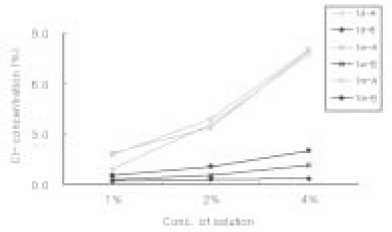
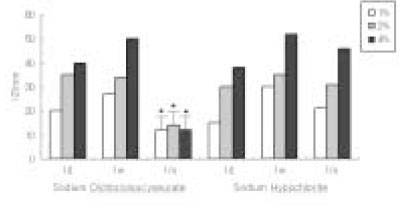
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Ingredients of NeoDental®-F
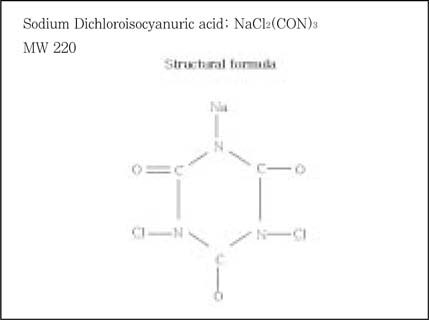
Molecule of Sodium Dichloroisocyanuric acid
Cl- concentration(%) in each solution
A : Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate
B : Sodium Hypochlorite
Result of cytotoxicity after 4 hr incubation
pH of each solution
A : Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate B : Sodium Hypochlorite

 KACD
KACD

 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

